Fall_2002_Exam_1 - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
advertisement

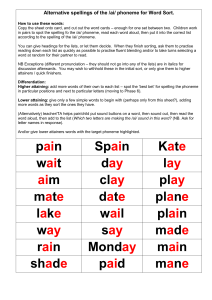
Psychology 338K Fall 2002 Exam 1 1. Voltaire wrote that writing is the painting of the voice. This is correct, in that a. writing records the spoken language. b. painting is the only way to visual express ideas. c. everyone’s voice differs from everyone else’s. a. writing represents relatively specific ideas. 2. The spoken language has priority over the written language in (at least) three ways. Which of these is NOT among them? a. ontogeny b. phylogeny c. universality d. simplicity. 3. The oldest writing we’ve found dates to about a. 320,000 B.C. b. 32,000 B.C. c. 3200 B.C. d. 320 B.C. 4. Scholars believe that writing was independently invented e. once f. twice. g. thrice. h. four or more times. 5. The alphabet was invented around a. 3200 B.C. b. 2200 B.C. c. 1200 B.C. d. 200 B.C. 6. Scholars believe that the alphabet was independently invented a. once. b. twice. c. thrice d. four or more times. 7. That writing is not quite the painting of the voice is illustrated by the example of a. alpha vs. beta. b. deep vs shallow. c. keep cool d. of 8. An orthography like Finnish is called shallow because a. each letter always represents the same phoneme. b. each phoneme is always represented by the same letter. c. both of the above. d. neither of the above 9. English orthography is called deep because a. each letter always represents the same phoneme. b. each phoneme is always represented by the same letter. c. both of the above. d. neither of the above 10. A splendid example of this is the phoneme a. /a/. 1 b. c. d. e. /e/. /i/. /o/. /u/. 11. What else constitutes part of English orthography? a. capitalization b. orientattion c. punctuation d spacing e. all of the above 12. Can punctuation change the meaning of a text? a. Yes. b. No. 13. Are words in a spoken sentence spaced? a. Yes. b. No. 14. In a comparison of literacy in 32 countries, which finished first? a. Finland b. Germany c. New Zealand d. U.S.A. 15. Almost every sentence one reads or hears is a. grammatical. b. ungrammatical. c. common. d. novel. 16. Rank these orthographies from shallow to deep. a. Finnish, Spanish, English. b. Spanish, Finnish, English c. Finnish, English, Spanish. d. Spanish, English, Finnish. 17. Korean is bi-orthographic. Which orthography is alphabetic? a. hangul. b. hanja 2 18. How many vowels are there in English? a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 24 19. How many consonants are there in English? a. 12 b. 15 c. 21 d. 24 20. Every letter in English can be mapped onto more than one phoneme. a. True. b. False. 21. That the letter-phoneme correspondences in English are context-dependent is dramatically illustrated by the word a. chord. b. chore. c. chorus. d. choreography. 22. How many phonemes does the word cheese contain? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 e. 6 23. Can a phoneme be defined by its acoustic signal? (Think about “keep cool.”) a. Yes. b. No. 24. Can a phoneme be defined by its articulation? a. Yes. b. No. 25. So where IS a phoneme? a. In the mouth. b. In the air. c. In the brain. d. In the foot. 26. The external (behavioral) part of reading consists of a series of fixations connected by saccades. The reason this is so is because of limitations in our a. alphabet. b. lexicon. c. language d. visual acuity. 3 27. The average (mean) fixation duration is _____ milliseconds. a. 20 b. 140 c. 250 d. 500 28. Fixation durations are a. constant. b. variable. 29. The average (mean) saccade length is a. 5 b. 8 c. 12 d. 15 30. Saccade lengths are a. constant. b. variable. 31. The control of fixations and saccades is a. global. b. local. 32. We fixate ____ percent of content words. a. 20 b. 40 c. 60 d. 80 33. We fixate ____ percent of function words. a. 20 b. 40 c. 60 d. 80 34. In a text, about ____ are content words. a. 10 b. 30 c. 50 d. 70 35. Linguists also call function words the _________ class. a. closed b. morphemic c. open d. syntactic 36. The reason we believe the control of fixations is global/local is that fixation durations are strongly influenced by a. the nature of the fixated word. b. The difficulty of the text. 37. Using the eye-movement contingent display change paradigm, McConkie and Rayner have shown that during a fixation we are accomplishing three things. We are a. semantically processing the word under fixation. b. (at least) limning the shape of the next word. c. determining the location and length of the word beyond that. d. doing all of the above. 4 38. In addition, we are a. disambiguating the fixated word. b. connecting that word with the preceding context. c. programming the next saccade. d. doing all of the above. 39. Westheimer has shown that sacccadic eye movements are a. ballistic. b. constant. c. fast. d. variable. 40. He did this by showing that when a student is fixating a dot, and the dot moves away for 100 milliseconds (less than the reaction time of the eye), and then returns, the student a. remains fixated on the original target. b. moves to the position where the dot was and stays there. c. moves to the position where the dot was, then returns. 41. Tale and tail are a. homographic homophones. b. homographic heterophones. c. heterographic homophones. d. heterographic heterophones. 42. Bow (/bo/ and bow (/bau/) are a. homographic homophones. b. homographic heterophones. c. heterographic homophones. d. heterographic heterophones 43. On a 100 word passages, first graders make _____ fixations while college students make a. 100, 100 b. 100, 75 c. 200, 100 d. 200, 75 44. In 100 saccades, first graders make _____ regressions, while college students make a. 15, 15 b. 25, 15 c. 35, 25 d. 45, 25 5 45. Which of these is a direct measure of word recognition? a. fixation duration b. naming latency c. lexical decision latency d. categorization latency e. none of the above 46. The reason why many researchers favor lexical decision and categorization over naming latency is that naming a. requires a vocal response. b. May not involve lexical access. c. Too many words are polyphonic. 47. The reason why many researchers favor categorization over lexical decision is that lexical decision may not involve a. a word’s meaning. b. A choice. c. A manual response. d. memory. 48. PET scans have shown that in the prestriate area both words and ________ show the same effects. a. Greek letters b. pseudowords. c. visual images. 49. A printed word falls on the retina a. right side up and forward. b. right side up and backwards. c. upsidedown and forward. d. upside down and backwords. 50. From there, it travels to the _________ lobe. a. frontal b. occipital c. parietal d. temporal 51. Gough rhymes with a. bough b. cough c. dough d. rough 6