y9-reprod-darts
advertisement

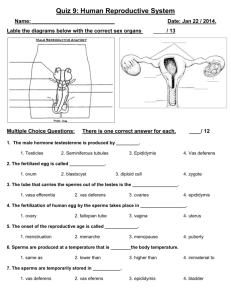
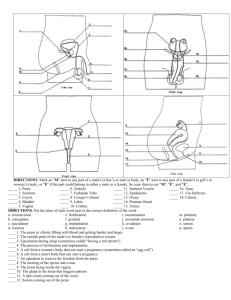
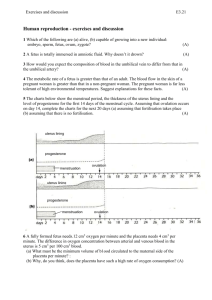
Name_______________________ AJD C:\...\106737128 106737128 21/09/97 Human Reproduction – “darts” answer sheet In both males and females, the bladder stores urine, which is a waste product removed from the bloodstream by the kidneys. The tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder are called ureters, and the tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body is called the urethra. Female Reproductive System Eggs, (also called ova) are stored in the ovaries. Eggs are present when a girl is born, her ovaries will contain about 2 million of them. But they only develop into mature eggs capable of becoming a baby after the girl has reached puberty. Each ovum contains genes that carry the female’s genetic information. Two oviducts, (also called fallopian tubes) transport the ovum from the ovary to the womb, (also called the uterus). The oviducts have delicate fronds that waft the ovum along. If the ovum is fertilised, it happens in the oviducts. The uterus is a muscular sack, about the size of a small orange. This is where a fertilised ovum will develop into a baby. The neck of the uterus, (also called the cervix) is a muscular opening at the base. The cervix leads to the vagina. This is the birth canal and the place where sperm is deposited during intercourse. Male Reproductive System Sperm are produced in the testes, up to 1,000 per second. The sperm are stored in the epididymis. Sperms carry the male’s genetic information. During intercourse, sperms travel along two sperm tubes to another tube called the urethra. On the way, the prostate gland and the seminal vesicle provide fluids to nourish them and to swim in. The mixture of sperms and fluids, called semen, then passes out through the urethra. 200 to 600 million sperms may be deposited in the woman’s vagina during intercourse, but most of them will never reach the ovum, and only one of them will actually fertilise it. Words you will need :prostate ureter ova urethra birth urethra cervix urine intercourse epididymis kidneys ovaries ovary vagina uterus fertilise fertilised sperm sperms semen Name_______________________ AJD C:\...\106737128 106737128 21/09/97 genes genetic vesicle woman fallopian puberty nourish testes Human Reproduction – “Darts” exercise In both males and females, the bladder stores ______, which is a waste product removed from the bloodstream by the _______. The tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder are called ______s, and the tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body is called the _______. Female Reproductive System Eggs, (also called ___ ) are stored in the _______. Eggs are present when a girl is born, her ovaries will contain about 2 million of them. But they only develop into mature eggs capable of becoming a baby after the girl has reached _______. Each ovum contains _____ that carry the female’s genetic information. Two oviducts, (also called _________ tubes) transport the ovum from the _____ to the womb, (also called the ______ ). The oviducts have delicate fronds that waft the ovum along. If the ovum is fertilised, it happens in the oviducts. The uterus is a muscular sack, about the size of a small orange. This is where a __________ ovum will develop into a baby. The neck of the uterus, (also called the ______ ) is a muscular opening at the base. The cervix leads to the ______. This is the _____ canal and the place where _____ is deposited during ___________. Male Reproductive System Sperm are produced in the ______, up to 1,000 per second. The sperm are stored in the __________. Sperms carry the male’s _______ information. During intercourse, ______ travel along two sperm tubes to another tube called the urethra. On the way, the ________ gland and the seminal _______ provide fluids to _______them and to swim in. The mixture of sperms and fluids, called ______, then passes out through the _______. 200 to 600 million sperms may be deposited in the _____’s vagina during intercourse, but most of them will never reach the ovum, and only one of them will actually _________ it. Words you will need :prostate ureter ova urethra birth urethra cervix urine kidneys ovaries ovary vagina fertilise fertilised sperm sperms Name_______________________ AJD C:\...\106737128 106737128 21/09/97 intercourse genes genetic epididymis vesicle woman uterus fallopian puberty semen nourish testes