Health Education
advertisement

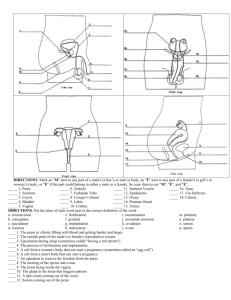
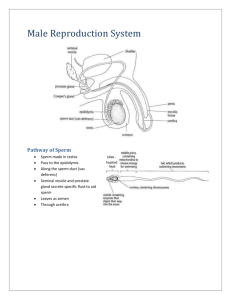
Health Education Utah State Standard 6: Students will demonstrate knowledge of human development, social skills, and strategies that encourage healthy relationships and healthy growth throughout life. Objective 1: Describe the physical, mental, social, and emotional changes that occur Materials: Utah State Office of Education consent from Background for Teachers: Become familiar with the following subjects that are described in the lesson plans. Instructional Procedures: Handout the consent forms two weeks prior to this section. Assessment Plan: At the end of each lesson plan there will be a quiz. When all of the objectives are cover students will be put into groups and assigned a topic, which they will present to the class in any form they choose, game, power point, etc. Day One Objective 1 Objective: Review the anatomy of the male and female reproductive systems. Intended Learning Outcome: Students will know the correct terms, functions, and location of the various parts of the male and female anatomy Background for Teacher: knowledge of male and female anatomy. Materials: Transparent copies of the enlarged illustration of male female genitals and reproductive organs. If you do not wish to use the illustrations provided you may draw your own while you discuss each part. Instructional Procedures: Discuss what the lesson plan is and why it is important to know, so they can be comfortable with their bodies and to know the correct function and name of the individual parts of their body. Write on the board the various parts of the female anatomy and ask the class what they are and see if they can define them. Display the female genitals and reproductive system on the overhead (or draw your own), ask students to get out a piece and paper and answer to the best of their knowledge. After a few minutes, go over the individual parts, filling in the blanks, explain their functions. Example: Ovaries- Female gonads, produces eggs/ova and the main source of female hormones which controls female develop and regulate menstruation cycle and pregnancy. Cervix- Is the lower part of the uterus/ upper part of the vagina. The cervix opens slightly during menstruation to allow flow and dilates during pregnancy allowing the fetus to enter the vaginal canal. Follow the same process with the male anatomy. Examples: Testes- Male gonads, located in the scrotum. They produce and store sperm and are the main source of male hormones which control male development Vas Deferens- Connects the testes to the urethra, transporting the sperm from the epididymis, through the ejaculatory duct and out the urethra. Take Home Activity: None Day Two Objective 1 Objective: Review physiology of the male and female reproductive systems and the changes that occur during puberty Intended Learning Outcome: Students will know the process of menstrual cycle, sperm production/ejaculatory system and understand the changes that occur during puberty. Background for Teachers: knowledge of the processes stated above. Materials: Changes of puberty illustration, transparencies of the females and male reproductive organs. You may want a little magnet or object to represent the ovum or sperm as they travel through each process. Instructional Procedures: Write on the board Male. Female. Both. Ask the class what changes occur during puberty under each heading. Once they got the basics down ask “What is the purpose of Puberty?” Display or pass out the changes in puberty handout and begin by going over the changes. Ask the class what they know about the menstrual cycle Discuss the process of menstruation 1. The lining of the uterus sheds (menstrual flow) 2. The lining of the uterus thickens with blood 3. Ovulation, egg is released from ovaries 4. Egg travels through fallopian tube 5. Egg enters uterus 6. Egg dissolves unless fertilizes 7. Lining of uterus sheds (menstrual flow) Once you finished going over the menstrual cycle, asking students what they know about sperm production/ the ejaculatory system Go over definitions. Discuss the process of sperm production 1. Sperm produced in testes 2. Travels up Vas Deferens 3. Sperm Mixes with seminal fluid=semen 4. Semen leaves penis through urethra Take Home Activity: Physiology Worksheet. Day Three Objective 1 Objective: Review conception and review fetal development. Intended Learning Outcome: Students will be familiar with the process of conception and development of a fetus Background for Teacher: Understand what is stated above. Materials: Time in the computer lab, poster boards, markers, glue, scissors, and whatever else the kids may need for their presentation. Instructional Procedures: Ask the class what they know about the process of conception Discuss conception. 1. Sperm enters vagina, traveling up the vaginal canal 2. Sperm fertilizes ovum in fallopian tube, travels down into the uterus 3. Zygote attaches to the uterus (implantation) using the lining for nourishment Now that the class knows about conception, it is time to divide them into three groups assigning them: first trimester, second trimester and third trimester. Give them the rest of the class and a day to gather information and to put together a presentation of the assigned trimester. Take Home Activity: None Changes of Puberty Physiology NAME ___________________________________________ DATE ______________ DIRECTIONS: Below are two stories. The events are all out of order. Put the sentences in chronological order. Make sure the last sentence is a good concluding statement. A) The Menstrual Cycle ___It travels through the fallopian tube. ___The ovary releases the ovum. ___About two weeks later, since the lining of the uterus is not needed for a pregnancy, it comes out through the vagina. ___It is incredible how the female body knows how to prepare for pregnancy! ___If the egg doesn't meet a sperm, it dissolves. ___While the ovum is developing, the lining of the uterus is getting thick and soft. ___Another ovum starts to develop in one of the ovaries and the process begins again. ___An ovum starts to develop. B) The Life of a Sperm Cell. ___I go from the vas deferens to the urethra. ___ I am produced in the testicles ___I go through the cervix and the uterus and into the fallopian tubes, in search of an egg cell. ___I develop for two or three months in the epididymis. ___When the penis becomes erect, I leave the epididymis and travel up into the body through the vas deferens. ___As I pass the prostate gland, the seminal vesicles, and the Cowper's glands, fluids are added so that I can live longer and swim more easily. ___Without me, an egg cell couldn't begin the amazing process of reproduction. ___The urethra carries me (along with about 200 million other sperm) out of the penis in a process called ejaculation. ___If I can find the ovum before the other sperm do, I will be the winner: part of a fertilized egg! Reproductive System NAME ______________________________________________ DATE __________________ DIRECTIONS: Put the letter of each word next to the correct definition of the word. a. circumcision b. conception c. ejaculation d. erection e. fertilization f. genitals g. implantation h. intercourse i. menstruation j. nocturnal emission k. ovulation l. ovum m. pituitary n. puberty o. semen p. sperm ____ 1. The penis or clitoris filling with blood and getting harder and larger ____ 2. The outside parts of the male's or female's reproductive system ____ 3. Ejaculation during sleep (sometimes called “having a wet dream") ____ 4. The process of fertilization and implantation ____ 5. A cell from a woman's body that can start a pregnancy (sometimes called an “egg cell”) ____ 6. A cell from a man's body that can start a pregnancy ____ 7. An operation to remove the foreskin from the penis ____ 8. The meeting of the sperm and ovum ____ 9. The penis being inside the vagina ____ 10. The gland in the brain that triggers puberty ____ 11. A ripe ovum coming out of the ovary ____ 12. Semen coming out of the penis ____ 13. The nesting of a fertilized egg in the wall of the uterus ____ 14. The body beginning to change from a child's into an adult's ____ 15. The liquid that carries sperm ____ 16. The lining of the uterus coming out through the vagina (sometimes called "having a period")