Methods in Molecular Biology – Theory and Practice - Ping-Pong
advertisement

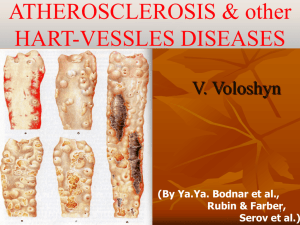
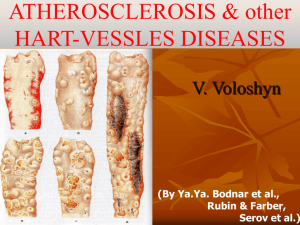
Methods in Molecular Biology – Theory and Practice Background Atherosclerosis is a progressive inflammatory disease. Macrophages play a dominating role in progression of atherosclerosis, as they remove, internalize and metabolize retained lipoproteins, giving rise to cells known as lipid-laden "foam cells". These foam cells promote atherogenesis by a number of mechanisms, including secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and although they have a long half-life, lesional macrophages undergo a steady rate of apoptosis. These foam cells and other dying inflammatory cells are cleared by neighboring macrophages. Therefore, the ability to maintain effective clearance of foam cells is necessary to limit atherosclerosis progression. One novel molecule that may influence macrophage function is CD93. This molecule is expressed on macrophages and upon stimulation is shed from the surface. Interestingly there are genetic variants of this molecule, which may play a role in atherosclerosis development. Some of the basic methods to study candidate genes that contribute to atherosclerosis include genotyping, real time RT-PCR, flow cytometry and ELISA to detect SNP, RNA and protein expression respectively. Contents of the lab The themes of the lab are: - Practical and theoretical review of basic methods in molecular biology such as: leukocyte isolation, RNA and DNA extraction, gene expression and genotype determination, flow cytometry and ELISA - Introduction to basic statistical methods for hypothesis testing - Collection, presentation and discussion of scientific results Learning outcomes By the end of the course the students are expected to have: - Increased practical and theoretical knowledge of basic methods in molecular biology - Increased understanding of how to collect and present scientific results - Increased understanding of why statistics are needed in science and which basic hypothesis testing methods are commonly used. - Gained experience in writing a scientific report Examination Examination of the learning outcomes is achieved by: 1) Writing of a short individual report of the laboratory experiment (max 1 A4 page, 12 point, Times New Roman). The report should be written in abstract form with the headings: Title, Background, Aims, Methods, Results, Conclusions. 2) Peer review and discussion of other student’s laboratory reports. Compulsory parts 100% attendance of the laboratory parts and the group discussion. Possibilities to compensate for absence can be discussed with the lab organisers. Grading Pass / Fail. To pass the lab, 100% attendance of the compulsory parts and fulfilment of the examination assignments are required (see above). Literature Compendium of molecular biology methods (will be handed out at the beginning of the course) and recommended articles. Lab organisers Josefin Skogsberg josefin.skogsberg@ki.se Dick Wågsäter dick.wagsater@ki.se 070-714 23 01 076-839 73 99