CELF-5 Language Assessment Report
advertisement

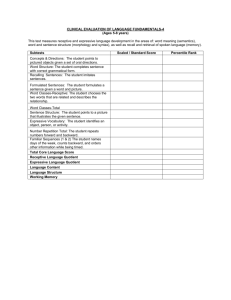
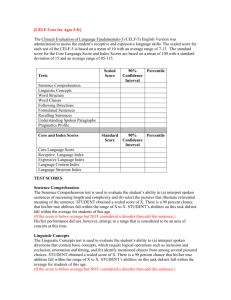
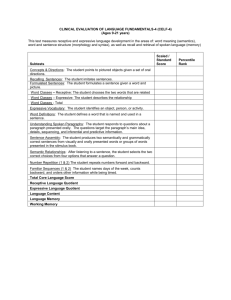
[CELF Core for Ages 9-21:] The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-5 (CELF-5) English Version was administered to assess the student’s receptive and expressive language skills. The scaled score for each test of the CELF-5 is based on a mean of 10 with an average range of 7-13. The standard score for the Core Language Score and Index Scores are based on a mean of 100 with a standard deviation of 15 and an average range of 85-115. Tests Scaled Score 90% Confidence Interval Percentile Standard Score 90% Confidence Interval Percentile Word Classes Following Directions Formulated Sentences Recalling Sentences Understanding Spoken Paragraphs Word Definitions Sentence Assembly Semantic Relationships Pragmatics Profile Core and Index Scores Core Language Score Receptive. Language Index Expressive Language Index Language Content Index Language Memory Index TEST SCORES Word Classes The Word Classes test is used to evaluate the student’s ability to understand relationships between words based on semantic class features, function, or place or time of occurrence. STUDENT obtained a scaled score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities on this task did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT considered a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. Following Directions The Following Directions test is used to evaluate the student’s ability to (a) interpret spoken directions of increasing length and complexity; (b) follow the stated order of mention of familiar shapes with varying characteristics such as color, size or location; and (c) identify from among several choices the pictured objects that were mentioned. These abilities reflect short-term and procedural memory capacities. STUDENT obtained a scaled score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities on this task did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT considered a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. Formulated Sentences The Formulated Sentences test evaluates a student’s ability to formulate complete, semantically and grammatically correct, spoken sentences of increasing length and complexity using given words and contextual constraints imposed by illustrations. These abilities reflect the capacity to integrate semantic, syntactic, and pragmatic rules and constraints while using working memory. STUDENT obtained a scaled score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities on this task did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT considered a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. Recalling Sentences The Recalling Sentences test evaluates the student’s ability to listen to spoken sentences of increasing length and complexity, and repeat the sentence without changing word meaning and content, word structure (morphology), or sentence structure (syntax). Semantic, morphological, and syntactic competence facilitates immediate recall (short-term memory). STUDENT obtained a scaled score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities on this task did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT considered a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. Understanding Spoken Paragraphs The Understanding Spoken Paragraphs test evaluates the student’s ability to (a) sustain attention and focus while listening to spoken paragraphs, (b) create meaning from oral narratives and text, (c) answer questions about the content of the information given, and (d) use critical thinking strategies for interpreting beyond the given information. The questions probe for understanding of the main idea, memory for facts and details, recall of event sequences, and making inferences and predictions. STUDENT obtained a scaled score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities on this task did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT considered a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. Word Definitions The Word Definitions test is used to evaluate the student’s ability to (a) analyze words for their meaning features, (b) define words by referring to class relationships and shared meanings, and (c) describe meanings that are unique to the reference or instance. STUDENT obtained a scaled score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities on this task did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT considered a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. Sentence Assembly The Sentence Assembly test is used to evaluate the student’s ability to formulate grammaticallyacceptable and semantically-meaningful sentences by manipulating and transforming given words and word groups. STUDENT obtained a scaled score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities on this task did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT considered a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. Semantic Relationships The Semantic Relationships test is used to evaluate the student’s ability to interpret sentences that (a) make comparisons, (b) identify location or direction, (c) specify time relationships, (d) include serial order, or (e) are expressed in passive voice. STUDENT obtained a scaled score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities on this task did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT considered a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. Pragmatics Profile The Pragmatics Profile is a checklist of speech intentions that are typically expected skills for social and school interactions in classrooms. It is used to identify verbal and nonverbal pragmatic deficits that may negatively influence social and academic communication. STUDENT obtained a scaled score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities on this task did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT considered a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. CORE LANGUAGE SCORE The Core Language score is a measure of general language ability. It quantifies a student’s overall language performance and in conjunction with the Receptive Language Index and the Expressive Language Index scores can aid in determining the presence or absence of a language disorder. The Core Language score has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. STUDENT obtained a standard score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s language skills, as measured by the CELF-5 did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. RECEPTIVE LANGUAGE INDEX The Receptive Language index is a measure of a student’s listening and auditory comprehension skills. The tests used to derive this score include: Sentence Comprehension, Word Classes and Following directions. The Receptive Language index has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. STUDENT obtained a standard score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities in the area of receptive language did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE INDEX The Expressive Language index is an overall measure of a student’s expressive language skills. The tests used to derive this score include: Word Structure, Formulated Sentences and Recalling Sentences. The Expressive Language index has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. STUDENT obtained a standard score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities in the area of expressive language did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. LANGUAGE CONTENT INDEX The Language Content index is a measure of various aspects of semantic development, including vocabulary, concept and category development, comprehension of associations and relationships among words, interpretation of factual and inferential information presented orally, and the ability to create meaningful semantically- and syntactically-correct sentences. The tests used to derive this score include Linguistic Concepts, Word Classes and Following Directions. The Language Content index has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. STUDENT obtained a standard score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities in the area of language content did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time. LANGUAGE MEMORY INDEX The Language Memory index is an overall measure of the student’s ability to recall and follow spoken directions; generate a sentence given one or two target words; and interpret sentences that make comparisons or describe location, time or ordinal relationships. The tests used to derive this score include Following Directions, Formulated Sentences and Recalling Sentences. The Language Memory index has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. STUDENT obtained a standard score of X. There is a 90 percent chance that his/her true abilities fall within the range of X to X. STUDENT’s abilities in the area of language memory did/not fall within the average for students of this age. (If the score is below average but NOT a disorder then add this sentence.) His/her performance did not, however, emerge in a range that is considered to be an area of concern at this time.