55KB - NZQA
advertisement

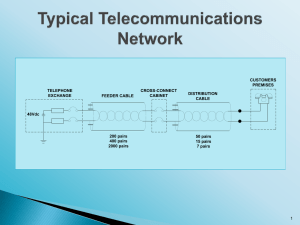
20177 version 2 Page 1 of 6 Demonstrate knowledge for telecommunications premises network cablers Level 2 Credits 2 Purpose This unit standard is for people installing and maintaining telecommunications cables on domestic, commercial, and industrial premises. People credited with this unit standard are able to: – outline the basic concepts of telecommunications premises cabling; – outline grounding, bonding, electrical protection, and circuit protection devices for telecommunications premises cabling systems; – outline campus and building backbone systems and installation practices; – outline horizontal cabling systems and termination practices; – identify cables and associated hardware; – outline fibre optic cables and installation practices; – outline testing of copper, coaxial, and fibre cables; and – outline the basic principles of fire stopping. Subfield Telecommunications Domain Telecommunications - Service Delivery Status Registered Status date 20 June 2003 Date version published 21 November 2008 Planned review date 31 December 2012 Entry information Open. Accreditation Evaluation of documentation by NZQA and industry. Standard setting body (SSB) ElectroTechnology Industry Training Organisation Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP) reference 0003 This AMAP can be accessed at http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/framework/search/index.do. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 20177 version 2 Page 2 of 6 Special notes 1 The verb outline as used in this unit standard refers to a demonstration of elementary knowledge about the subject, in which the candidate states the important features or conveys the general idea of the topic referred to, without the need to provide technical reasons or the use of mathematics. 2 References AS/NZS 3084:2003 Telecommunications installations - Telecommunications pathways and spaces for commercial buildings; AS/NZS 3080:2003 Telecommunications installations - Generic cabling for commercial premises; AS/NZS 3085.1:2004 Telecommunications installations - Basic requirements; AS/NZS ISO/IEC 15018:2005 Information technology - Generic cabling for homes; AS/NZS ISO/IEC 61935.2:2006 Testing of balanced communication cabling in accordance with ISO/IEC 11801 - Patch cords and work area cords; Electricity Regulations 1997; Safety Manual - Electricity Industry (SM-EI) (Parts 1 & 2) (2004). Available from the Electricity Engineers’ Association New Zealand. http://www.eea.co.nz, PO Box 5324, Wellington; NZECP 34:2001 New Zealand Electrical Code of Practice for Electrical Safe Distances; Telecommunications Act 2001. 3 Definitions baseband – the primary signal characteristic in a network where only one carrier frequency is used (Ethernet is an example of a baseband network). broadband – a transmission system that combines multiple independent signals onto one cable. cable – any or all of copper cable, fibre optic cable, and coaxial cable. industry practice – those practices that competent practitioners within the industry recognise as current industry best practice. Elements and performance criteria Element 1 Outline the basic concepts of telecommunications premises cabling. Performance criteria 1.1 The operation of and the services provided by the public switched telephone network (PSTN) are outlined. Range 1.2 local calls, regional calls, international calls, private automatic branch exchanges (PABXs), bandwidth limitations. The operation of and services provided by data networks are outlined. Range baseband, broadband. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 20177 version 2 Page 3 of 6 1.3 Premises cabling systems and their purpose, components, and subsystems are outlined. Range 1.4 Media types and their physical construction are outlined. Range 1.5 topologies – bus, ring, star. multi-pair, unshielded twisted pair (UTP), shielded twisted pair (STP), screened twisted pair (ScTP), coaxial, optical fibre cables. The components and interconnections of a typical commercial premises cabling system are outlined. Range multiple building campus, modern building with more than one floor distributor; building entrance facility, grounding and bonding system, campus and building backbone system, campus and building distributor, floor distributor, equipment room, telecommunications closet, consolidation points, individual and multi-user telecommunications outlets. 1.6 Telecommunications pathways and spaces are identified in accordance with industry standards. 1.7 Procedures for labelling cables, terminations, and connections and marking up as-built plans are outlined in accordance with industry practice. 1.8 The roles of regulations, codes of practice, and industry standards are stated. Element 2 Outline bonding, grounding, electrical protection, and circuit protection devices for telecommunications premises cabling systems. Performance criteria 2.1 Reasons for bonding, grounding, and the provision of telecommunications circuit protectors are stated in terms of personnel safety, equipment damage, and circuit performance. 2.2 Bonding and grounding practices associated with telecommunication premises cables are outlined. Range cables, equipment, frames, cable support systems, coaxial cable. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 20177 version 2 Page 4 of 6 Element 3 Outline campus and building backbone systems and installation practices. Performance criteria 3.1 The function and construction of a backbone system are outlined. 3.2 Cable installation practices are outlined. Range cable types – multi-pair, UTP, STP, ScTP, coaxial, fibre; suitability of cable types, handling, separation distances, permissible lengths, bending radii, tension, compression termination. Element 4 Outline horizontal cabling systems and termination practices. Performance criteria 4.1 The function and construction of a horizontal cabling system are outlined. 4.2 Cable installation practices are outlined. Range cable types – multi-pair, UTP, STP, ScTP, coaxial, fibre; industry practices - pre-installation guidelines, installation practices, separation distances, cable management, cable lengths, guidelines for slack, handling, bending radii, tension, compression. Element 5 Identify cables and associated hardware. Performance criteria 5.1 Commonly used cable types are identified by inspection, and matched with associated terminating hardware, and cross-connect systems including patch cords and jumpers, in accordance with industry practice. Element 6 Outline fibre optic cables and installation practices. Performance criteria 6.1 Basic principles of light transmission, cable types, and applications are outlined. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 20177 version 2 Page 5 of 6 6.2 Safe working practices are outlined. Range 6.3 typical hazards – eye damage from lasers, dangerous chemicals, glass fibre off-cuts. Basic installation and terminating practices are outlined. Range cable protection during installation, components, termination methods, splicing and interconnection devices. Element 7 Outline testing of copper, coaxial, and fibre cables. Performance criteria 7.1 Commonly used tests are identified, together with the quantities measured. 7.2 Commonly used test instruments are identified, and their principles of operation outlined. Element 8 Outline the basic principles of fire stopping. Performance criteria 8.1 The purpose of fire stopping is outlined. 8.2 Practical methods of fire stopping in typical situations are outlined. Please note Providers must be accredited by NZQA, or an inter-institutional body with delegated authority for quality assurance, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be accredited by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Accredited providers and Industry Training Organisations assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. Accreditation requirements and an outline of the moderation system that applies to this standard are outlined in the Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP). The AMAP also includes useful information about special requirements for organisations wishing to develop education and training programmes, such as minimum qualifications for tutors and assessors, and special resource requirements. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 20177 version 2 Page 6 of 6 Comments on this unit standard Please contact ElectroTechnology Industry Training Organisation (ETITO) reviewcomments@etito.co.nzif you wish to suggest changes to the content of this unit standard. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016