Southern & Eastern Asia
advertisement
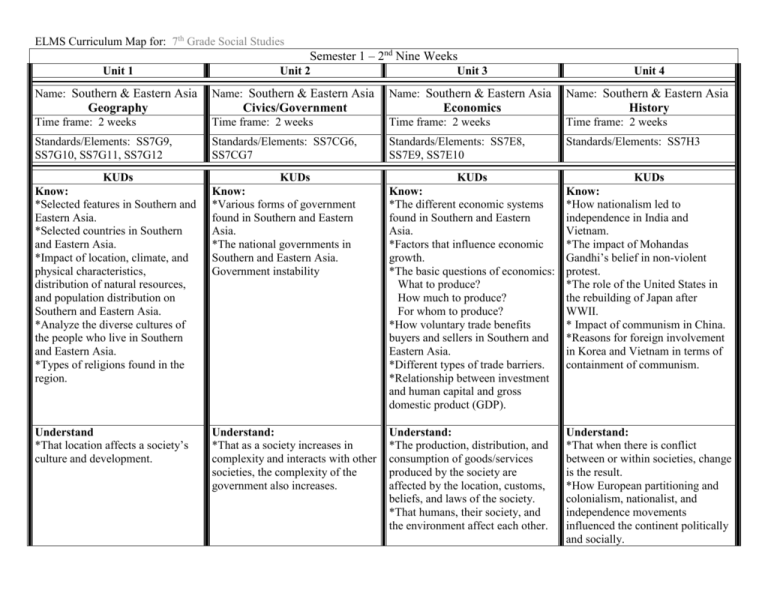
ELMS Curriculum Map for: 7th Grade Social Studies Semester 1 – 2nd Nine Weeks Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Name: Southern & Eastern Asia Name: Southern & Eastern Asia Name: Southern & Eastern Asia Name: Southern & Eastern Asia Geography Civics/Government Economics History Time frame: 2 weeks Time frame: 2 weeks Time frame: 2 weeks Time frame: 2 weeks Standards/Elements: SS7G9, SS7G10, SS7G11, SS7G12 Standards/Elements: SS7CG6, SS7CG7 Standards/Elements: SS7E8, SS7E9, SS7E10 Standards/Elements: SS7H3 KUDs KUDs KUDs KUDs Know: *Selected features in Southern and Eastern Asia. *Selected countries in Southern and Eastern Asia. *Impact of location, climate, and physical characteristics, distribution of natural resources, and population distribution on Southern and Eastern Asia. *Analyze the diverse cultures of the people who live in Southern and Eastern Asia. *Types of religions found in the region. Know: *Various forms of government found in Southern and Eastern Asia. *The national governments in Southern and Eastern Asia. Government instability Know: *The different economic systems found in Southern and Eastern Asia. *Factors that influence economic growth. *The basic questions of economics: What to produce? How much to produce? For whom to produce? *How voluntary trade benefits buyers and sellers in Southern and Eastern Asia. *Different types of trade barriers. *Relationship between investment and human capital and gross domestic product (GDP). Know: *How nationalism led to independence in India and Vietnam. *The impact of Mohandas Gandhi’s belief in non-violent protest. *The role of the United States in the rebuilding of Japan after WWII. * Impact of communism in China. *Reasons for foreign involvement in Korea and Vietnam in terms of containment of communism. Understand *That location affects a society’s culture and development. Understand: *That as a society increases in complexity and interacts with other societies, the complexity of the government also increases. Understand: *The production, distribution, and consumption of goods/services produced by the society are affected by the location, customs, beliefs, and laws of the society. *That humans, their society, and the environment affect each other. Understand: *That when there is conflict between or within societies, change is the result. *How European partitioning and colonialism, nationalist, and independence movements influenced the continent politically and socially. ELMS Curriculum Map for: 7th Grade Social Studies Do: Do: *Describe how the mountain, Compare and contrast the federal desert, and water features of republic of The Republic of India, Southern and Eastern Asia have the communist state of The affected the population in terms of People’s Republic of China, and where people live, the types of the constitutional monarchy of work they do, and how they travel. Japan. *Describe the causes and effects of pollution on the Yangtze and Ganges Rivers. *Describe the causes and effects of air pollution and flooding in India and China. *Explain the difference between an ethnic group and a religious group. *Compare and contrast the prominent religions in Southern and Eastern Asia. Vocabulary: China, Indonesia, North Korea, South Korea, Japan, India, Vietnam, Ganges River, Indus River, Yangtze River, Indian Ocean, South China Sea, Gobi Desert, Himalayan Mountains, Huang He (Yellow River), Mekong River, Bay of Bengal, Sea of Japan, Yellow Sea, Taklimakan Desert, Korean Peninsula, monsoon, typhoons, season, brown clouds, air pollution, ethnic group, religious group, Hinduism, Vedas, polytheistic, monotheistic, caste system, Buddhism, Islam, Five Vocabulary: Communism, monarchy, People’s Republic of China, unitary government system, confederation government system, federal government system, prime minister, Indian National Congress, autocratic government, oligarchy, democratic government system, parliamentary form of democratic government, presidential form of democratic government, congressional form of government, cabinet, secular, premier, emperor Do: *Compare and contrast the economic systems in China, India, Japan, and North Korea. *Explain the relationship between investment in human capital and gross domestic product. *Describe the role of natural resources in a country’s economy. Do: *Describe how nationalism led to independence in India and Vietnam. *Describe the impact of Mohandas Gandhi’s belief in non-violent protest. *Explain the role of the United States in the rebuilding of Japan after WWII. *Describe the impact of Communism in China in terms of Mao Zedong, the Great Leap Forward, the Cultural Revolution, and Tiananmen Square. *Explain the reasons for foreign involvement in Korea and Vietnam in terms of containment of Communism. Vocabulary: Gross domestic product, human capital, voluntary trade, trade barriers, tariff, quota, protective tariff, embargo, traditional economy, command economy, market economy, physical capital, entrepreneurship, currency, bartering, capitalism, free enterprise, collective farms, specialization, international trade, Vocabulary: Independence, nationalism, Mohandas Gandhi, non-violent protest, Mao Zedong, The Great Leap Forward, Tiananmen Square, Cultural Revolution, Green Revolution, apartheid, Red Army, Domino Theory, communist ELMS Curriculum Map for: 7th Grade Social Studies Pillars of Islam, Quran, Shintoism, Muslims Performance Task: Label a blank map of Southern and Eastern Asia Performance Task: Construction of graphic organizer or foldable to explain the different types of government systems Performance Task: Webquest and Essay on economic systems, entrepreneurship, the investment of human capital, and the availability of natural resources in China, India, Japan, or North Korea (student will choose country). Performance Task: RAFT – Role of a reporter covering the protest of Tiananmen Square Notes: Use of graphic organizers Notes: Use of graphic organizers Notes: Notes:








