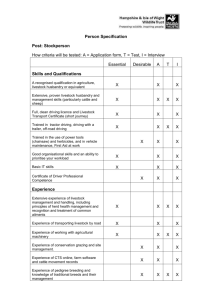
Course Contents-VEE - Veterinary Council of India
advertisement

EXISTING REVISED DEPARTMENT OF VETERINARY AND ANIMAL HUSBANDARY EXTENSION EDUCATION SEMESTER V PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES OF VETERINARY AND ANIMAL HUSBANDRY EXTENSION VAE-311 Credit Hours: 2+1=3 THEORY Concept of Sociology. Man-animal relationship (Society, Community, Association, Institutions). Difference in livestock production practices of rural, urban and tribal communities including rearing patterns. Social change and factors of change. Social groups, its types and functions. Social transformation in relation to animal rearing. Evolution of veterinary and animal husbandry extension in India. Extension education: definition, philosophy and principles. Concept of Community development. Teaching learning process, steps of teaching. Extension teaching methods; their classification and use. Information delivery system in Veterinary and Animal Husbandry extension. Information communication technology. Role of animals in economy, health and socio-psychology of rural, semi urban and urban society. Client and stakeholder dealings: techniques and procedures including tools for data collection, analysis, history taking, follow-up and appraisal on prognosis. Adoption and diffusion of livestock innovations. Leadership and role of leaders in animal husbandry extension. Farming in rural India - large and small scale farming, mixed farming, co-operative and collective farming, contractual farming, Co-operative Farming for Live Stock Production, Advantages and limitations of co-operatives. Economic principles underlying co-operative societies, co-operative milk unions in India. Social survey and its types. Social sampling. Identification of key communicators and operating through them. Identifying organizational difficulties in the way of organizing animal husbandry extension programmes. Identification of constraints in the adoption of improved animal husbandry practices. Animal Husbandry programme planning and evaluation. Feedback evaluation of extension programmes and their impact analysis. Panchayat Raj Institutions, Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK), Animal Husbandry Development Programmes in Cattle, buffalo, sheep , goat, poultry, rabbit and piggery.Key village scheme, Gosadan/Goshala, Integrated Cattle Development Programme (ICDP), Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP), ATMA. Gender considerations in Veterinary practice. Changing expectations from new recruits to the profession and employers of veterinarians. Growing changes in corporate, client influence and changes in work ethics. Information communication technologies. Virtual class room and self learning. E-learning. Information kiosks. Agriculture portals. E-commerce- scope and local application. Computer aided teaching/learning, web-sites dedicated to veterinary and animal sciences education, web directories and virtual learning institutions (e-institutions). DEPARTMENT OF VETERINARY EXTENSION EDUCATION VETERINARY EXTENSION EDUCATION Credit Hours: 3+1 THEORY UNIT-1 (LIVESTOCK BASED LIVELIHOODS & ITS EVOLUTION) History of domestication and their social dimensions. Evolution and relationship between agriculture and animal husbandry. Farming and characteristics of farming in India. Classification of farming, types and systems. Peasant farming, cooperative farming, collective farming, contract farming, estate farming, organic farming, capitalistic farming, small-scale farming, large-scale farming, intensive, extensive farming, specialized, diversified, mixed, integrated and dry land farming. Role of animals in the contemporary society. UNIT-2 (EXTENSION EDUCATION AND DEVELOPMENT) Early extension efforts in India. Types of education: Formal, non-formal and informal education. Extension education: Concept, levels, objectives and dimensions. Principles, philosophy and functions of extension education. Teaching-learning process and steps in extension teaching. Concept of need & its types. Rural development - Concept, significance and importance of rural development programmes for poverty alleviation. Problems & Issues in development. Panchayati Raj System. UNIT-3 (RURAL SOCIOLOGY IN VETERINARY EXTENSION) Concept of sociology and rural sociology in animal husbandry extension. Culture: definition, elements, change, impact on production systems. Basic sociological concepts - society, community and association. Rural society: characteristics and differences among society, community and culture. Characteristics and differences among tribal, rural and urban communities. Social control: concept & means of social control (techniques, folkways, taboos, mores and laws). Social stratification: definition, forms and characteristics (caste system and class system). Social institutions in rural society: Social, economic, political, religious and educational (definition, composition and function). Social change: concept, importance and factors. Social groups: different groups, classification of social groups and their characteristics. Leadership: definition, functions of leader, types of rural leaders, Key communicators and their role in the animal husbandry extension. UNIT-4 (TRANSFER OF TECHNOLOGY FOR LIVESTOCK DEVELOPMENT) Technology- Concept, generation process, application, merits and de-merits. Adoption and diffusion of innovations, stages of adoption, adopter categories, innovation decision process, attributes of innovations, diffusion process, factors affecting adoption and diffusion processes. Programme planning- principles, objectives and steps. Evaluation of extension programme, constraints in the adoption of scientific animal husbandry practices. Role of extension agents in diffusion of livestock innovations. Cattle and buffalo improvement programmes: Key Village Scheme, Intensive Cattle Development Project, Gosadan and Gaushala. Dairy development programmes: concept of cooperation, Rochdale principles of cooperation, objectives of cooperative, Amul pattern of dairy cooperative system and Operation Flood. Transfer of technology projects of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR): Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK), Agricultural Technology Information PRACTICAL Audio-visual equipments. Principles and use of overhead, slide and multimedia projectors, digital video/still camera. Preparation and use of visual aids like posters, charts, flash cards, flipcharts, etc. Use of literature and media in Extension. Identification of key elements in social sampling of data. Collection and analysis of data. Identification of key communicators and operation programme. Enumeration of organizational difficulties in animal husbandry extension programmes. Identification of constraints in the adoption of improved animal husbandry practices. Constraint analysis. Group discussions, techniques and procedures for awareness campaigns on different veterinary and animal husbandry practices - signs of diseases, preservation of eggs, clean milk production, controlling of ectoparasites, pail feeding of calves, sexing and culling of birds, first aid for minor wounds, disinfection of byres, branding, use of horn cauterization, timely A. I., choice of good progeny, care in pregnancy, infertility, environmental hygiene, preparation of feeds and feeding schedules, deworming, preventive hygiene, vaccination etc. Organization of animal welfare camps, exhibition, livestock shows etc. Hands on training in the use of computers for teaching and information dissemination. Rapid Rural Appraisal/Participatory Rural Appraisal in identifying livestock production/health care practices. SEMESTER VI LIVESTOCK ECONOMICS, MARKETING AND BUSINESS MANAGEMENT VAE-321 Credit Hours: 2+1=3 THEORY Economics: Introduction, definition and scope (production, consumption, exchange and distribution) of economic principles as applied to livestock. Common terms wants, goods, wealth, utility, price, value, real and money income. Important features of land, labour, capital and organization. Livestock produce and products. Livestock contributions to national economy. Demand projections of livestock produce. Theory of consumer behaviour: law of diminishing marginal utility and indifference curve analysis. Theory of demand; meaning, types of demand, demand curve and law of demand, individual and market demand, elasticities of demand and factors affecting demand. Laws and types of supply. Elasticity of supply. Cost concepts and principle of fixed and variable costs. Theory of production, law of diminishing returns, laws of returns to scale and concept of short and long run periods. Economics of animal disease and disease losses. Marketing: Livestock business- concepts, nature and scope. Components, characteristic of small business. Marketable livestock commodities. Concept of market; meaning and classification of markets. Market price and normal price, price determination under perfect competition in short and long run. Marketing of livestock, and perishable and non-perishable livestock products. Merchandising - product planning and development. Marketing functions; exchange functions- buying, selling and demand creation. Physical functions- grading, transportation, storage and warehousing. Facilitative functions - standardization, risk bearing, market information and market intelligence. Market opportunities-marketing channels of livestock and livestock products, organized/unorganized markets and cattle fairs. Import and export of animal and animal products. International Agreements/Regulations (WTO and Centre (ATIC), Agricultural Technology Management Agency (ATMA), National Agricultural Innovation Project (NAIP), Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) etc. Different ongoing central and state government animal husbandry development programmes being run related to sheep, goat, poultry, piggery, fodder production etc. UNIT-5 (COMMUNICATION AND EXTENSION TEACHING METHODS) Communication and its functions. Basic concepts: communication fidelity, communication gap, time lag in communication, empathy, homophily & heterophily, propaganda, publicity, persuasion and development communication. Types of communication: Intrapersonal, interpersonal, verbal, nonverbal, vertical, horizontal, organizational communication etc. Elements of communication: Communicator, message, channel, treatment of message, audience, and audience response (feedback). Barriers of communication. Individual contact methods: Farm & home visit, farmer’s call, personal letter, adaptive or minikit trial, farm clinic etc. Group contact methods: Result demonstration, method demonstration, group meeting, training, field day or farmers’ day, study tour etc. Mass contact methods: Farm publications (leaflet, folder, pamphlet, booklet, bulletin, farm magazine, newsletter etc.), mass meeting, campaign, exhibition, newspaper, radio, television, mobile short message service. Selection and use of extension teaching methods. UNIT-6 (LIVESTOCK ECONOMICS & MARKETING) Introduction to Economics and Livestock Economics: definition and scope (production, consumption, exchange and distribution). Basic concepts- wants, goods, wealth, utility, price, value, assets, capital, money, income etc. Important features of land, labour, capital and organization. Theories of demand, supply and cost. Theories of production (law of diminishing return, increasing return, constant return and return to scale). Concept of market: market, market structure and classification of markets. Market price and normal price, price determination under perfect competition in short and long run. Marketing functions: meaning and their classification (packaging, transportation, grading, standardization, storage & warehousing, processing & value addition, buying & selling, market information, financing, risk bearing, minimization of risks (speculation and hedging). Marketing agencies, institutions and channels for livestock and livestock products. Government interventions and role in marketing of livestock and livestock products. External trade in livestock products, recent policies on trade and international trade agreements and their implications in livestock sector. UNIT-7 (LIVESTOCK ENTREPRENEURSHIP) Definition of entrepreneur, entrepreneurship, enterprise and manager. Difference between entrepreneur and entrepreneurship, entrepreneur and enterprise, entrepreneur and manager. Theories of entrepreneurship: Sociological theory, economic theory, cultural theory, psychological theory. Types, characteristics and functions of an entrepreneur. Forms of entrepreneurship: (Sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, cooperative, joint stock company, Private and Public Limited Company). Introduction to financial management: concept, function, analysis of financial statement, sources of capital (banks, venture capitals, etc.). Project appraisal- Introduction, importance, technoeconomic feasibility, criteria of project evaluation (discounted and non-discounted), capital budgeting, etc. Business plan for enterprise. Institutions promoting entrepreneurship in India. Entrepreneurship development programmes. Accounting: objectives, common terms. Personnel management-identification of work, job analysis, division of labour etc. Resource managementorganization aspect of livestock farms, resources and procurement of inputs and financial resources, break-even- analysis etc. UNIT-8 (INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY) GATT) for marketing/trade of live animals and products. Management: Resource Management- Organizational aspects of livestock farms, sources and procurement of inputs and financial resources. Break- even – analysis. Personnel (Labour) Management- Identification of work and work (job) analysis/division of labour. Accounting: Definition, objectives, common terms. Different systems of book keeping- single and double entry system. Various types of account books including books of original entry. Classification of accounts and rules of debit and credit. Recording of business transactions. Analysis of financial accounts- income and expenditure accounts, trading account, profit and loss accounts. PRACTICAL Book keeping; general entry, writing of journal and ledger, cash book (two and three column), purchase-sale and purchase-sale return registers, trading account, profit and loss accounts, income and expenditure accounts, balance sheet, bills of exchange (bill of receivable and bill of payable), bank reconciliation statement. Economics of a dairy unit, poultry, piggery, sheep and goat units. Visit to farms, markets and cattle fairs, backyard units and preparation of report. SEMESTER IX LIVESTOCK ENTERPRENEURSHIP VAE-511 Credit Hours: 1+0=1 THEORY Livestock Enterpreneurship. Avenues of enterpreneurship/employment in private and public sectors. Key concepts and theories of self-employment and enterpreneurship. Essential criteria for development of enterpreneurship in livestock sector - basic requirements for enterpreneurship initiatives in livestock and allied sectors (i.e. techno economic feasibility of the enterprises under different conditions, training and management skills, business acumen, business communication, inter-personnel skills for establishing an enterprise, etc.). Enterpreneurial training/development programmes at the State and National level. Animal Insurance. Bank support for entrepreneurship. Financial credit and financial management- general Principles and practices, analyzing project appraisals and reports, capital expenditure decisions, re- investment and payback. Preparing projects for bank appraisal, banking requirements. Assessing project profits. Procurement management, quality issues, standardization, grading and packaging. Marketing channels. Retail marketing, sales operations and management, advertising, marketing of services. Expectations from a Veterinary professional. Ecojobs and sustainable development through livestock. Approach to preparation of Enterpreneurial Project on livestock. Strengths and limitations of ICTs application in livestock sector and farmers capacity building. Information kiosk, E-learning, CAD, virtual class room, virtual reality, multi-media etc. Cyber extension- problems and prospects in livestock extension. Computer networking: (LAN, MAN, WAN, Internet, tele-conferencing, tele-text, radio-text, video-text, interactive cable distribution system, satellite communication, internet, www, etc.). UNIT-9 (CONTEMPORARY ISSUES IN LIVESTOCK ENTERPRISES) Gender and animal husbandry- definition, difference between gender and sex, role of women in animal husbandry, gender sensitization, importance of gender sensitization in animal husbandry, need for gender analysis, gender budgeting & mainstreaming. Salient features of recent livestock census, livestock insurance scheme, national livestock mission. Sustainability- concept of sustainability of livestock production system (social, environmental and economic challenges faced). Introduction to environmental consequences of livestock rearing. Animal welfare: Introduction to animal welfare, ethics and rights. Importance of animal welfare in the contemporary society. Expectations from veterinary professionals. PRACTICAL UNIT-1 Tools of data collection: Preparation of instrument for conducting social survey; Visit to nearby village: Conducting social survey for assessment of farming system and constraints; Data analysis and reporting; Organizing demonstration for farmers; identification of key communicators by Socio-metric method; Familiarization with audio-visual aids; Principle and use of projectors; Preparation of Radio Script Preparation of Television script; Preparation and use of poster; Preparation and use of chart; Preparation and use of flash cards; Preparation and use of farm publications for extension work; Planning and organizing an awareness campaign (Health & Production); Planning & organization of animal health camps; Exercise on rapid rural appraisal (RRA).; Exercise on participatory rural appraisal (PRA) technique; Planning & organization of group discussion. UNIT-2 Rules of debit and credit in livestock business transactions. Journal Entry & Ledger Posting. Writing of Cash Book. Balancing & preparation of final accounts. Exercise on calculation of depreciation. Visit to commercial enterprises of livestock production. Preparation of dairy entrepreneurial project report. Preparation of sheep & goat entrepreneurial project report. Preparation of poultry entrepreneurial project report. Preparation of piggery/rabbit entrepreneurial project report. Techno-economic feasibility report. Exercise on Break-even analysis. Exercise on BCR, IRR & NPW. Case study of successful entrepreneurial project. Visit to livestock market. Visit to livestock fair. Exercise on economics of diseases ANNUAL EXAMINATION PAPERS UNITS MAXIMUM MARKS WEIGHTAGE THEORY Paper-I 1, 2, 3,4 and 5 50 25 Paper-II 6,7,8 and 9 50 25 PRACTICAL Paper-I Paper-II 1 2 30 30 15 15