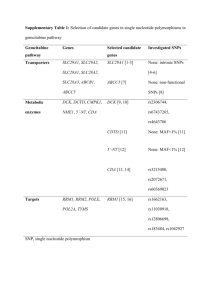
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Material and Methods Western
advertisement

SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Material and Methods Western blotting Cell lysates were prepared using protease and phosphatase inhibitors including DTT (1mM), phenylmethylsufonyl fluoride (1mM), phenylarsine oxide (5M), NaF (25mM), Na3VO4 (2mM), leupeptin (100M), pepstatin (2M), N-tosyl-Lys-chloromethyl ketone (2.8M), Ntosyl-L-phenylalanine chloromethyl ketone (2.7M), 4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride (4.17M), chymostatin (2M), aprotinin (2M), antipain (2M), N-ethylmaleimide (5mM), and MG132 (40M). Protein content in the cell extract was measured with micro-BCA assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories; Hercules, CA). The uniformity of transfer in the blot was confirmed by Ponceau staining. The binding of the primary antibody to the membrane was detected by secondary antibodies conjugated with horseradish peroxidase and a chemiluminescence system (Amersham Bioscience/GE Healthcare; Piscataway, NJ). Real time PCR The reaction synthesis for cDNA consisted of 500 ng of RNA, 2.5 µl of 10X RT buffer, 1 µl of 100 mM dNTP mix, 2.5 µl of 10X random primer and 1.25 µl of RT enzyme) and used for real-time PCR (the reaction cocktail consisted of 100 ng of template cDNA, 1 µl of 5 µM forward and reverse primers – selected using primer express software v2.0 – and 25 µl of SYBR green PCR mix). The survivin primers used were SURVIVINFOR 1 (5’CACCACTTCCAGGGTTTATTC C 3’) and SURVIVINREV (5’ TCT CCTTTCCTAAGACATTGCTAA GG 3’). Actin transcript was used as an internal control for all the samples tested using the primers hACTINFOR (5’ CTCACTGAGCGAGGCTAC AGCT 3’) and hACTINREV (5’ TTGATGTCGCGCACGATTT 3’). The survivin primers used amplify an amplicon of 75 bp whereas the actin primers amplify a 62 bp amplicon. At the end of the PCR reaction, the CT (threshold cycle) and Rn (normalized intensity of reporter dye) values were obtained. The values obtained for survivin were normalized with actin reference values and the ΔCT values were thus obtained. Each ΔCT value obtained for the ritonavir-treated samples was compared to that of the DMSO treated samples values – which was considered as the calibration value – and the relative mRNA levels of survivin calculated with the following formula: Relative mRNA level = (2-(corrected Ct)). Results Ritonavir inhibits the growth of the KRAS wild type lung adenocarcinoma line H838 but does not synergize with gemcitabine or cisplatin Ritonavir, alone or in combination with gemcitabine or cisplatin, was tested in the KRAS wild type lung adenocarcinoma line H838. Similarly to what was observed in the KRAS mutant lines A549 and H522, ritonavir was able to inhibit the growth of the H838 line exhibiting an IC50 of 35 M (Fig. S1). On the other hand, the H838 line was resistant to gemcitabine, which reduced the cell growth to a maximum of 40%. The ritonavir/gemcitabine combination failed to show a consistent synergism. In fact, such a combination was synergistic only at high concentrations of 2 ritonavir (35-70 M) and gemcitabine (0.2-.04 M), exhibiting an average CI of 1.2 0.5 (Fig. S1). Cisplatin was more efficient than ritonavir in inhibiting the growth of the H838 line and their combined action was of antagonistic nature (CI > 1) (Fig. S1). Overall, these results suggest that while ritonavir alone is efficient in inhibiting the growth of KRAS wild type lung adenocarcinoma, its use in combination with gemcitabine or ciplatin is not as beneficial as for the KRAS mutant cell lines. Figure Legends Figure S1. Ritonavir inhibits the growth of the KRAS wild type lung adenocarcinoma line H838, but its activity is not enhanced by gemcitabine or cisplatin. Ritonavir inhibited the growth of the H838 line exhibiting IC50 of 35 mM. Ritonavir did not consistently synergize with gemcitabine, while it exhibited antagonism with cisplatin. 3 Tables Table S1. siRNA sequences used for targeting survivin, c-Src and STAT3. Name Molecular Weight Sequence siControl (non-targeting) IIIIIIIV- AUGAACGUGAAUUGCUCAA UAAGGCUAUGAAGAGAUAC AUGUAUUGGCCUGUAUUAG UAGCGACUAAACACAUCAA 13358 13358 13358 13358 siSurvivin (targeting Human BIRC5) IIIIIIIV- CAAAGGAAACCAACAAUAA GCAAAGGAAACCAACAAUA CACCGCAUCUCUACAUUCA CCACUGAGAACGAGCCAGA 13343 13358 13388 13418 SiSrc (targeting Human Src) IIIIIIIVIIIIIIIV- GAGAACCUGGUGUGCAAAG CGUCCAAGCCGCAGACUCA CCUCAGGCAUGGCGUACGU CCAAGGGCCUCAACGUGAA CCAACGACCUGCAGCAAUA GGAGAAGCAUCGUGAGUGA CCACUUUGGUGUUUCAUAA UCAGGUUGCUGGUCAAAUU 13403 13433 13433 13418 13403 13403 13358 13373 SiSTAT3 (targeting Human STAT3) 4 Table S2. Quantitation of ritonavir-induced G0/G1 arrest in NSCLC lines. Cells were treated for 48 h with ritonavir, and G0/G1 arrest was evaluated by PI staining. Profiling of PI incorporation was performed by FACScan analysis using ModFit software. The table shows the results of one of three consistent experiments – results are expressed as percentage of cells in each phase. DMSO (%) Ritonavir (20 M) (%) Ritonavir (40 M) (%) G0-G1 S G2/M G0-G1 S G2/M G0-G1 S G2/M A549 38 51 11 61 31 8 79 16 5 H522 38 44 18 64 31 5 76 18 6 5 Table S3. Quantitation of ritonavir-induced alteration of cyclins, CDKs, Rb, phospho Rb, p53, and p27 expression. Cells were treated for 48 h with IC50 of ritonavir, and Western blots were performed with their protein extracts. Triplicate measurements were done by densitometry analysis of Western blotting. Measurements exhibiting P values < 0.05, <0.01, or <0.001 are marked with one, two or three asterisks, respectively. In all cell lines, GAPDH levels were unaffected by ritonavir. A549 H522 Fold-change at ritonavir Fold-change at ritonavir IC50 p IC50 p CDK2 0.73 * 0.30 * CDK4 0.25 * 0.53 ** CDK6 0.23 ** 0.56 ** Cyclin D1 0.58 *** 0.84 ** Cyclin A 0.18 ** 0.38 ** p-Rb 0.16 ** 0.08 * Rb 0.50 ** 0.55 ** P53 1.22 n.s. 0.28 * P27 1.98 ** 1.78 ** 6 Table S4a. Quantitation of ritonavir-induced inhibition of c-Src, STAT3 and their phosphorilated forms, and survivin in NSCLC lines. Cells were treated for 48 h with IC50 of ritonavir, and Western blots were performed with their protein extracts. Triplicate measurements were done by densitometry analysis of Western blotting. Measurements exhibiting P values < 0.05 or <0.01 are marked with one or two asterisks, respectively. In all lines, GAPDH levels were unaffected by ritonavir. A549 H522 Fold- Fold- change at ritonavir change at ritonavir IC50 Phospho-c-Src 0.40 Total-c-Src 1.0 Phospho-STAT3 0.63 Total-STAT3 1.04 p * IC50 p 0.10 ** 0.60 * * 0.62 ** n.s. 1.00 n.s. 0.71 * n.s. Survivin 0.55 ** Cleaved PARP 1.5 * 7 3.02 * Table S4b. Quantitation of siRNA-mediated reduction of c-Src, STAT3 and survivin. Triplicate measurements were done by densitometry analysis of Western blotting. Measurements exhibiting P values < 0.05 or <0.01 are marked with one or two asterisks, respectively. A549 Fold-change s-Src siRNA H522 p Fold-change p c-Src 0.24 ** 0.47 ** STAT3 0.49 * 0.59 * Survivin 0.64 ** 0.41 * STAT3 0.31 ** 0.17 ** Survivin 0.78 n.s. 0.75 ** Survivin 0.44 ** 0.45 ** STAT3 siRNA Survivin siRNA 8 Table S5. Quantitation of ritonavir-, gemcitabine-, and ritonavir/gemcitabine-induced reduction of survivin. Cells were treated for 48 h with IC50 of ritonavir, gemcitabine, or a combination of the two drugs and Western blots were performed with their protein extracts. Triplicate measurements were done by densitometry analysis of Western blotting. Measurements exhibiting P values < 0.05 or <0.01 are marked with one or two asterisks, respectively. R stands for ritonavir, G for gemcitabine, and R+G for the combination ritonavir/gemcitabine. Survivin Fold-change p R G R+G R G R+G A549 0.47 0.53 0.37 ** ** ** H522 0.51 0.91 0.47 ** n.s. * 9