Chapter 4 Rocks
advertisement

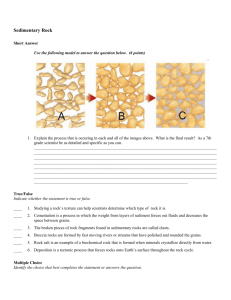
Chapter 4 Rocks Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 1. The continuous changing and reforming of rocks is called deposition. _______________ ____ 2. Metamorphic rocks form from existing rock. _______________ ____ 3. A volcanic eruption may create an intrusive igneous rock. _______________ ____ 4. Studying a rock’s texture can help scientists determine which type of rock it is. _______________ ____ 5. Volcanic glass forms when lava cools fast. _______________ ____ 6. Grains are fragments that make up rocks. _______________ ____ 7. Cementation is a process in which the weight from layers of sediment forces out fluids and decreases the space between grains. _______________ ____ 8. The broken pieces of rock fragments found in sedimentary rocks are called clasts. _______________ ____ 9. Breccia rocks are formed by fast moving rivers or streams that have polished and rounded the grains. _______________ ____ 10. Calcite is an example of a biochemical rock that is formed when minerals crystallize directly from water. _______________ ____ 11. The term plastic deformation is used to explain how rocks can bend or fold without melting. _______________ ____ 12. Nonfoliated metamorphic rocks form distinct, parallel layers. _______________ ____ 13. Contact metamorphism occurs when rocks come in contact with magma without melting. _______________ ____ 14. The rock cycle changes a rock so slowly, we cannot see it with the naked eye. _______________ ____ 15. Deposition is a tectonic process that forces rocks onto Earth’s surface throughout the rock cycle. _______________ Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the letter of your choice on the blank line. ____ ____ ____ 1. Igneous rocks that form ____ the surface are intrusive. a. above c. on b. below d. all of the above 2. The processes involved in the rock cycle include all of the following EXCEPT ____. a. condensation c. weathering b. erosion d. compaction 3. The rock cycle indicates that each type of rock can ____. a. provide materials to make other rocks b. form other rocks c. be changed by forces at Earth's surface d. all of the above ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 4. Sedimentary rocks are changed to sediments by ____. a. compaction c. cementation b. weathering and erosion d. heat and pressure 5. Igneous rocks form from ____ when it cools. a. magma c. neither a nor b b. lava d. both a and b 6. Foliated rocks are distinguished by ____. a. layers c. large mineral grains b. lack of layers d. air holes 7. Lava that cools quickly forms ____ rocks. a. extrusive metamorphic c. intrusive metamorphic b. extrusive igneous d. intrusive igneous 8. All of the following conditions in Earth can cause metamorphic rocks to form EXCEPT ____. a. exposure to air c. heat b. the presence of hot, watery fluids d. pressure 9. A classification of metamorphic rocks would include whether they are ____. a. chemical or organic c. foliated or nonfoliated b. intrusive or extrusive d. basaltic or granite 10. Sedimentary rocks are ____. a. formed from magma b. a type of foliated igneous rock c. formed because of changes in temperature and pressure, or the presence of hot watery fluids d. formed when loose materials become pressed or cemented together or when minerals form from solutions 11. A rock is always ____. a. made of molten material b. a mixture of minerals, organic matter, volcanic glass, or other materials c. formed by heat and pressure d. either igneous or sedimentary 12. The crystals that form in slowly cooled magma produce ____ mineral grains. a. tiny c. fine-grained b. invisible d. large 13. Metamorphic rocks that show layers of dark minerals alternating with layers of light minerals are classified as ____. a. nonfoliated c. foliated b. extrusive d. intrusive 14. Sedimentary rocks form because of all of the following EXCEPT ____. a. sediments becoming pressed or cemented together b. crystals solidifying from magma c. sediments forming from solution d. water evaporating, leaving crystals behind 15. Sedimentary rocks formed from the remains of once-living things are ____. a. metamorphic c. biochemical b. detrital d. none of the above 16. What type of sedimentary rock is coarse-grained with angular fragments? a. foliates c. conglomerates b. nonfoliates d. breccias ____ 17. A student finds a rock with seashells in it. What kind of rock is it? a. an igneous rock c. a metamorphic rock b. a sedimentary rock d. an extrusive rock ____ 18. Which type of scientist analyzes the composition of rocks? a. an environmentalist c. a geologist b. a naturalist d. a biologist ____ 19. Which of the following best describes what contact metamorphism is? a. using magma to turn existing rock into metamorphic rock b. a plate boundary which is exposed to high heat and pressure c. squeezing loose sediment between layers which are more dense and solid d. rock that forms quickly from magma erupting from a volcano ____ 20. Which factors allow rocks to bend or fold without melting? a. gravity and pressure c. pressure and temperature b. composition and gravity d. temperature and gravity ____ 21. The rock cycle can change the sedimentary rock limestone into _____ through metamorphoses. a. conglomerate c. granite b. gneiss d. marble ____ 22. Which is a tectonic process that forces rocks up from beneath Earth’s surface? a. melting c. deposition b. uplift d. crystallization ____ 23. Which best explains how a rock can become classified as a conglomerate? a. a rock with crystallized minerals as part of the composition b. a rock with angular clasts found at the edges of mountains c. a rock with large, rounded clasts that have been polished d. a rock made of only organic material and has been in the ground for many years ____ 24. All of the following are biochemical rocks except _____. a. chert c. limestone b. coal d. rock salt ____ 25. Chemical sedimentary rocks form when _____ crystallize directly from water. a. igneous rocks c. minerals b. metamorphic rocks d. sediment deposits ____ 26. Rocks can change throughout many different processes through the rock cycle. All of the following change rocks on Earth’s surface except _____. a. melting c. deposition b. weathering d. compaction Completion Complete each statement. 1. Granite is a(n) ____________________ rock. 2. Rock salt is a(n) ____________________ rock. 3. Obsidian is a(n) ____________________ rock. 4. Gneiss is a(n) ____________________ rock. 5. Limestone is a(n) ____________________ rock. 6. The rock that changes during metamorphism is called the _____ rock. 7. A natural, solid mixture of minerals or grains is called a _____. 8. Sedimentary rocks are formed when _____ is deposited in environments like rivers and streams. Matching Match each statement with the correct item below. a. compaction d. coal b. marble e. gneiss c. limestone ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. a kind of organic sedimentary rock 2. a kind of chemical sedimentary rock 3. The process in which pressure from the upper layers of sediment pushes down on the lower layers, causing the sediments to stick together and form solid rock. 4. a kind of foliated metamorphic rock 5. a kind of nonfoliated metamorphic rock Match each item with the correct statement below. a. clastic c. regional metamorphism b. sediment d. rock cycle ____ ____ ____ ____ 6. 7. 8. 9. continuous changing and remaking of rocks pieces of solid material deposited on Earth’s surface produced when high temperature and pressure affect large areas of Earth’s crust type of sediment made up of rock and mineral fragments produced by weathering Match the tectonic force that best explains how each type of rock is formed. a. extreme temperature and pressure b. melting c. uplift d. deposition ____ ____ ____ ____ 10. 11. 12. 13. igneous rock to sedimentary rock metamorphic rock to igneous rock sedimentary rock to metamorphic rock metamorphic rock to sedimentary rock Chapter 4 Rocks Answer Section MODIFIED TRUE/FALSE 1. ANS: F, the rock cycle PTS: REF: STA: 2. ANS: REF: STA: 3. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 5.4.6.C.2 T PTS: 1 To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 5.4.6.C.2 F, extrusive PTS: REF: STA: 4. ANS: REF: 5. ANS: REF: 6. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 2 5.4.6.C.2 T PTS: 1 To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 2 T PTS: 1 To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 2 T, Grains PTS: REF: STA: 7. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 5.4.6.C.2 F, Compaction PTS: REF: STA: 8. ANS: REF: STA: 9. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 5.4.6.C.2 T PTS: 1 To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 5.4.6.C.2 F, Conglomerate PTS: REF: STA: 10. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 5.4.6.C.2 F, chemical PTS: REF: STA: 11. ANS: REF: STA: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 5.4.8.C.1 T PTS: 1 To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 5.4.6.C.2 OBJ: 4-2 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW OBJ: 4-1 OBJ: 4-3 DIF: OBJ: DIF: OBJ: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW 4-3 Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW 4-4 OBJ: 4-1 OBJ: 4-5 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW OBJ: 4-5 OBJ: 4-5 OBJ: 4-5 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW OBJ: 4-7 12. ANS: F, Foliated PTS: REF: STA: 13. ANS: REF: STA: 14. ANS: REF: STA: 15. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 5.4.6.C.2 T PTS: 1 To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 5.4.6.C.2 T PTS: 1 To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 5.4.6.C.2 F, Uplift PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.6.C.3 OBJ: 4-8 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW OBJ: 4-8 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW OBJ: 4-2 OBJ: 4-2 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: B Igneous rocks that form as magma cools underground are called intrusive rocks. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 2 OBJ: 4-3 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 2. ANS: A The series of processes that change one type of rock into another type of rock is called the rock cycle. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-2 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 3. ANS: D The series of processes that change one type of rock into another type of rock is called the rock cycle. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-2 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 4. ANS: B Forces such as wind, running water, ice, and even gravity cause rocks on Earth’s surface to break down. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-2 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 5. ANS: D When lava cools and crystallizes, it becomes igneous rock. | Igneous rocks that form as magma cools underground are called intrusive rocks. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 2 OBJ: 4-3 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 6. ANS: A Foliated rocks contain parallel layers of flat and elongated minerals. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-8 STA: 5.4.8.D.1 7. ANS: B Materials, such as lava and ash, solidify and form extrusive igneous rocks. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 2 OBJ: 4-3 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 8. ANS: A Changes in temperature, pressure, or the addition of chemical fluids can result in the rearrangement of minerals or the formation of new minerals in a metamorphic rock. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-7 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 9. ANS: C Foliated rocks contain parallel layers of flat and elongated minerals. Metamorphic rocks that have mineral grains with a random, interlocking texture are nonfoliated rocks. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-8 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 10. ANS: D After sediments are deposited, the process of compaction and cementation begins. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 11. ANS: B A rock is a natural, solid mixture of minerals or grains. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 12. ANS: D When magma cools slowly, large well-defined crystals form. OBJ: 4-5 OBJ: 4-1 PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 2 OBJ: 4-4 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 13. ANS: C Foliated rocks contain parallel layers of flat and elongated minerals. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-8 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 14. ANS: B Sedimentary rocks can form in different environments through a series of natural steps. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-5 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 15. ANS: C Sedimentary rocks form when sediments, rock fragments, minerals, or organic materials are deposited, compacted, and then cemented together. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-5 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 16. ANS: D The angular fragments in the breccia probably weren’t transported far, because their sharp edges were not worn away. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-6 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 17. ANS: B Sedimentary rocks form when sediments, rock fragments, minerals, or organic materials are deposited, compacted, and then cemented together. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 18. ANS: C Geologists use texture and composition to classify rocks. OBJ: 4-5 PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-1 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 19. ANS: A During contact metamorphism, magma comes in contact with existing rock. Its thermal energy and gases interact with the surrounding rock and forms new metamorphic rock. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 3 | DOK 2-MOD REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-8 20. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-7 21. ANS: D The sedimentary rock limestone metamorphoses into a marble. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-2 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 22. ANS: B Uplift is a tectonic process that forces these rocks onto Earth’s surface. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.8.D.1 23. ANS: C Conglomerate rocks have rounded clasts. OBJ: 4-2 PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-5 24. ANS: D Rock salt, rock gypsum, and limestone are examples of common chemical sedimentary rocks. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-6 25. ANS: C Chemical rocks form when minerals crystallize directly from water. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-6 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 26. ANS: A Some rock cycle processes occur only beneath Earth’s surface, such as those that involve extreme temperature, pressure, and melting. PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 | 5.4.6.C.3 OBJ: 4-2 COMPLETION 1. ANS: igneous PTS: REF: STA: 2. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 2 5.4.6.C.2 sedimentary PTS: REF: STA: 3. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 5.4.6.C.2 igneous PTS: REF: STA: 4. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 2 5.4.6.C.2 metamorphic PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-4 OBJ: 4-6 OBJ: 4-4 OBJ: 4-8 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 5. ANS: sedimentary PTS: REF: STA: 6. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 5.4.6.C.2 parent PTS: REF: STA: 7. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 5.4.6.C.2 rock PTS: REF: STA: 8. ANS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 1 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 5.4.6.C.2 sediment PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 OBJ: 4-6 OBJ: 4-7 OBJ: 4-1 OBJ: 4-1 MATCHING 1. ANS: REF: STA: 2. ANS: REF: STA: 3. ANS: REF: STA: 4. ANS: REF: STA: 5. ANS: REF: STA: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-6 5.4.6.C.2 C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-6 5.4.6.C.2 A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-5 5.4.6.C.2 E PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-8 5.4.6.C.2 B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 1-LOW To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-8 5.4.6.C.2 6. ANS: REF: STA: 7. ANS: REF: STA: 8. ANS: REF: STA: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-2 5.4.6.C.2 B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-1 5.4.6.C.2 C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 4 OBJ: 4-7 5.4.6.C.2 9. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 2 | DOK 2-MOD REF: To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 3 OBJ: 4-6 STA: 5.4.6.C.2 10. ANS: REF: STA: 11. ANS: REF: STA: 12. ANS: REF: STA: 13. ANS: REF: STA: D PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 3 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-2 5.4.6.C.2 B PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 3 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-2 5.4.6.C.2 A PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 3 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-2 5.4.6.C.2 C PTS: 1 DIF: Bloom's Level 3 | DOK 2-MOD To review this topic refer to Rocks: Lesson 1 OBJ: 4-2 5.4.6.C.2