Acids Properties

10 Science Chapter 8 Notes
Another classification of chemicals is Acids, Bases & Salts
Properties of Acids taste sour react with metals to produce hydrogen gas react with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates to produce carbon dioxide conduct electricity often recognized by H in formula
H+ ions in solution
Properties of Bases slippery taste bitter react with proteins conduct electricity sometimes recognized by OH in formula
OH- ions
Acids bases and salts are called electrolytes because when dissolved in water the produce ions (charged particles). These ions in solutions allow the solution to conduct electricity in the same way that a copper wire does.
Acid Formation nonmetals which are dull brittle & poor conductors react with oxygen to form nonmetal oxides nonmetal oxides are often liquids or gases nonmetal oxides react with water to form acids (p. 306 Nelson)
Examples
SO
3
+ H
2
O
CO
2
+ H
2
O
NO
2
+ H
2
O
H
2
SO
4
H
2
CO
3
HNO
3
Bases Formation metals which are shiny, malleable, ductile good conductors react with oxygen to form metal oxides (always solid) metal oxides react with water to form bases (p. 305 Nelson)
Examples
MgO + H
2
O
CaO + H
2
O
Mg(OH)
Ca(OH)
2
2
Na
2
O + H
2
O NaOH
Acids, Bases & Their Uses
Sulfuric Acid H
2
SO
4
Hydrochloric
Acid
Acetic Acid
HCl
CH
3
COOH battery acid fertilizer nitroglycerine stomach acid pickling metal toilet bowl cleaners vinegar
Phosphoric Acid
Nitric Acid
Citric Acid
H
3
PO
4
HNO3
C
3
H
5
O(COOH)
3 flavoring soft drinks plastics, explosives fertilizers
citrus fruits
Lactic Acid C
2
H
5
OCOOH
Sodium Hydroxide NaOH in milk drain cleaners soap oven cleaners
Ammonium
Hydroxide
NH
4
OH household cleansers smelling salts
Calcium
Hydroxide
Magnesium
Hydroxide
Potassium
Hydroxide
Sodium
Hypochlorite
Ca(OH)2
Mg(OH)2
KOH
NaClO limewater mortar in cement antacids milk of magnesia soap bleach pH & Indicators
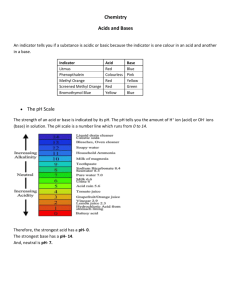
The pH of a substance is a measure of how acidic or basic a substance is
(an indication of how many hydrogen ions there are compared to hydroxide ions). pH is indicated by a number from 0 - 14. A pH of 7 indicates that the substance is neutral. A pH less than 7 indicates that the substance is acidic. A pH greater than 7 indicates that the substance is basic. A base with a pH of 9, is 10 times stronger than a base with a pH of 8. Similarly, an acid with a pH of 2 is 100 times stronger than an acid with a pH of 4. Etc. pH can be a Pain
Pain results from nerve endings in the body being exposed to changes in pH levels. A bee sting is painful because the bee injects a small amount of acid into the tissue. This acid comes in contact with nerve endings and a signal is sent to the brain. The brain's interpretation is what we consider PAIN!
The cells of our own bodies contain weak acids. When you are cut or burned, the acid leaks into the surrounding area and comes in contact with nerve endings again causing "pain".
If the acid causing the pain can be neutralized (with a weak base), the pain is reduced. For this reason, many salves and medicinal creams contain ammonia - a weak base.
Painkillers can Kill
Most painkillers are acids or bases - medically called analgesics. Many strong painkillers are derived from a plant called opium. The seed pod of this plant contains several alkaloid (basic) compounds. One of the alkaloids is called morphine. Two derivatives of morphine are codeine and heroin (highly addictive).
A common and mild pain reliever - acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is derived from the bark of a willow tree (not very tasty). Unfortunately, ASA can cause stomach irritation. An alternative to ASA is acetaminophen
(tylenol) but it is not as good at relieving inflammation.