Supplementary Data
advertisement

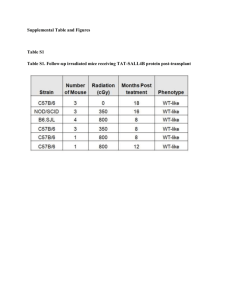
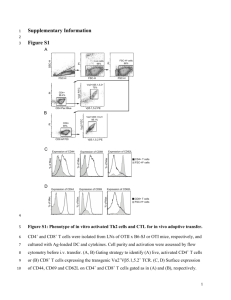
Supplementary Figures Figure S1 DCs and microglia cells express CD11b and F4/80 at different levels. CNS-MNCs were prepared at peak EAE and analyzed by flow cytometry. The left plot is gated on 7AAD-negative total CNS-MNCs. The right plot shows the expression of CD11b and F4/80 on either CD45+CD11c+ DCs (black) or CD45intCD11clo-neg microglia cells (grey). Figure S2 Expression levels of several macrophage and DC markers on lyDCs, myDCs and inflDCs. Upon enrichment of CNS-MNCs of EAE-diseased mice at peak EAE, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Dead cells were excluded by gating on 7AAD-negative cells. lyDCs, myDCs and inflDCs were defined as indicated in Fig. 1 and analyzed for their expression of the respective markers (open histograms) or the isotype controls (grey histograms). The data is representative for two experiments with three pools of mice in each experiment. Figure S3 Macrophages show lower MHCII-levels than DCs. At peak EAE, mice were sacrificed and CNS-MNCs as well as splenocytes were prepared for flow cytometric analsis. Dead cells were excluded by gating on 7AAD-negative cells. For the analysis of MHCII expression (uncoloured) or the isotype control (grey-coloured) histograms were gated on CD45hiCD11bhi and CD11c+ (dendritic cells) or CD11c– (macrophages). Numbers represent the MFI of MHCII+ cells. Figure S4 The accumulation of DCs in the CNS upon GM-CSF treatment is timedependent. GM-CSF-producing cells were injected intracerebrally into naïve mice. MNCs were isolated from the CNS at the indicated time points and analyzed by flow cytometry. DCs were quantified by gating on CD45+CD11c+ cells. The data is representative of 3 independent experiments. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.001) Figure S5 Intracerebral FL recruits predominantly lyDCs and myDCs into the CNS. 5x105 irradiated control or FL-producing B16-F10 cells were injected intracerebrally into naïve C57BL/6 mice. CNS-MNCs (left) and splenocytes (right) of FL-treated, untreated and control mice were isolated at day 7 and analyzed by flow cytometry. The indicated DCs were quantified by gating on CD45+CD11c+ cells. The data is representative of 2 independent experiments. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.005) Figure S6 FL-elicited inflDCs are not inhibitory. Irradiated FL-secreting B16-F10 cells were injected intracerebrally into naive mice and CNS-MNCs were isolated after 10 days. DC subsets were sorted by flow cytometry and tested in the inhibition assay as detailed in Fig. 1. (*p < 0.005 comparing lyDCs to myDCs and inflDCs, respectively) Figure S7 CNS-derived and periphery-derived inflDCs show no differences in MHCII, CD80, CD86 and CD40 expression. Congenic BM chimera were immunized and sacrificed at peak disease. Upon CNS-MNC preparation cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The histograms display the expression levels of MHCII, CD40, CD80 and CD86 (open histograms) of CNS-derived inflDCs and periphery-derived inflDCs as shown in figure 4A and B. The isotype controls are shown in grey-coloured histograms. Figure S8 CNS-DC subpopulations show a characteristic location. EAE was induced in congenic BM chimeric animals (CD45.1CD45.2). Cryo-histology was prepared at peak clinical stage. Consecutive sections were stained with combinations of antibodies to F4/80 (green), CD11c (red) and either CD11b, CD45.1 or CD45.2 (blue), respectively. (A and B) The merged photographs correspond to the immunohistology shown in figure 5. In each row the respective colour channel split is shown (green/ red/ blue) corresponding to the markers F4/80, CD11c and either CD11b, CD45.1 or CD45.2. Open arrow heads indicate peripheral CD45.1+CD45.2– stimulatory DCs (lyDC/ myDC). Closed arrow heads indicate peripheral CD45.1+CD45.2– inflDCs. Arrows indicate CNS-derived CD45.1–CD45.2+ inflDCs. Figure S9 ‘Instructive effect’ of inhibitory CNS-DCs. Flat-bottom 96 well plates were coated with 3 μg/ml anti-CD3 antibody. Plates were washed and CD4+ T cells were cultured in the presence or absence of DCs (DC:T cell ratio 1:10). After 2 days the proliferation was measured by pulsing the culture for 16 hrs with 3H-thymidine. CNS-derived inflDCs have an ’instructive’ effect on other DCs that enforces inhibition: T cell proliferation in the presence of plate-bound anti-CD3 antibody can also be inhibited by inflDCs. In the presence of mature BM-derived DCs anti-CD3stimulated T cells proliferate even more strongly. However, when adding CNSderived inflDCs in combination with mature BM-DCs the inhibition of T cell proliferation by inflDCs is even more pronounced, i.e. there is stronger inhibition in the presence of otherwise non-inhibitory DCs.