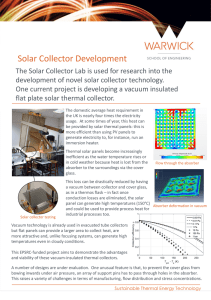
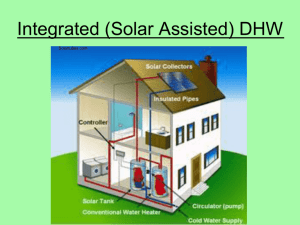
Which model of solar collector heats water best?
advertisement

Grade Level/Subject Unit Enduring Understanding SOL Objectives 6th grade Energy Solar power is a renewable energy resource with many applications. With engineering, creativity, and technology, solar energy use can be made even more practical. 6.2 The student will investigate and understand basic sources of energy, their origins, transformations, and uses. Key concepts include a) potential and kinetic energy; b) the role of the sun in the formation of most energy sources on Earth; c) nonrenewable energy sources; d) renewable energy sources; and e) energy transformations. 6.9 The student will investigate and understand public policy decisions relating to the environment. Key concepts include a) management of renewable resources; b) management of nonrenewable resources; c) the mitigation of land-use and environmental hazards through preventive measures; and d) cost/benefit tradeoffs in conservation policies. Title Lesson Objective Inquiry Level Materials Needed How is it Level 2/3? Which model of solar collector will heat water the best? Design and test three different models of solar collectors to show an application of solar energy. 2/3 Thermometers, cups, shoeboxes, timers, access to outdoor area OR desk lamps, other materials (will vary) Teacher provides the research question and the materials. The methodology is developed largely by the students, although the lab packet does provide some guidance. Students develop their own solar collector designs. Lab: Which model of solar collector will heat water the best? Task: Design and conduct an experiment that tests the ability of three different solar collectors to heat a cup of water. Which will get the hottest? Find out! Materials: - Shoeboxes - Aluminum foil - Plastic wrap - Construction paper - Tape - Cups - Thermometers - Lamp (optional) - Timer Research question: What is the effect of different types of _________________ on the temperature of water placed inside them? Independent variable What factor will you change? _________________________________ Dependent variable What factor will you measure? _________________________________ Hypothesis: __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ Sample hypothesis: If ice cubes are placed in containers made out of glass, plastic, and metal, then the ice cubes will melt fastest in the metal container. Preparation: Design three different solar collectors using the materials available. Discuss possible designs with your group BEFORE you begin assembling them. Feel free to look at pictures or do other research to get ideas. A cup of water with a thermometer must be able to fit inside each collector. Experimental groups: Draw a sketch of each solar collector your group designed. Briefly describe the important features of each design. Drawing Description 1 2 3 Control group: _______________ Constants (what three factors should be kept the same across all groups to ensure fairness?) 1. ___________________ 2. ____________________ 3. ___________________ Results TIME Design #1 __________ Design #2 __________ Design #3 __________ Control __________ Lab summary Directions: Please answer the questions below thoughtfully and in complete sentences. Purpose What question were you trying to answer by conducting this experiment? Method Explain (briefly) the steps that you followed to set up and conduct the experiment. Results State the results for each group. Tell which group (if any) had the highest value, and which had the lowest. Conclusion Compare the results to your hypothesis and state whether your hypothesis is supported or not. Explain why you believe you got the results that you did. Reflect on your methods. What could you do differently to make the results more valid (reliable) next time?