File
advertisement

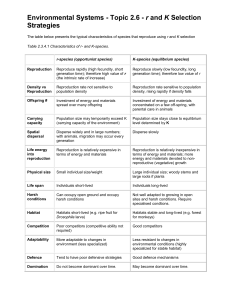
Process Underlying Social Learning And Application of Social Learning Theory By: Ricko John M. Mata I. Objectives At the end of this article, the students should: Analyze the different processes underlying Social Learning properly Value the importance of Social Learning effectively Explain the different fields of where to apply Social Learning Theory properly II. Preview This topic contains the four processes that form the basis of Social Learning Theory. These processes are Attention, Retention, Motivation, and Motor Reproduction. Also in this topic will discuss the different fields or scenario where Social Learning Theory can be applied. III. Content PROCESS UNDERLYING SOCIAL LEARNING Attention Attention has also been referred to as the allocation of limited processing resources. This process surrounds the acquisition of the attention of the learner. Acquisition can be based on such factors as sensory capacity, arousal level, and past reinforcement. In order for an individual to learn anything, he or she must pay attention to the features of the modeled behavior. Anything that distracts your attention is going to have a negative effect on observational learning. If the model is interesting or there is a novel aspect to the situation, you are far more likely to dedicate your full attention to learning. Retention Is the ability to remember everything you hear or learn. This process involves the learner accessing symbolic coding, mental image, cognitive organization, symbolic rehearsal, motor rehearsal that has caught their attention. Motor Reproduction This process includes the physical reproduction of the observed activity through physical capability, self-observation and feedback. Once you have paid attention to the model and retained the information, it is time to actually perform the behavior you observed. Further practice of the learned behavior leads to improvement and skill advancement. To reproduce a behavior, the observer must organize responses in accordance with the model. Observer characteristics affecting reproduction include physical and cognitive capabilities and previous performance. Motivation This process includes external vicarious and/or self-reinforced motivation. In order for observational learning to be successful, you have to be motivated to imitate the behavior that has been modeled. Reinforcement and punishment play an important role in motivation. While experiencing these motivators can be highly effective, so can observing other experience some type of reinforcement or punishment. For example, if you see another student rewarded with extra credit for being to class on time, you might start to show up a few minutes early each day. APPLICATION OF SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY Management Social Learning theory proposes that rewards aren't the sole force behind creating motivation. Thoughts, beliefs, morals, and feedback all help to motivate us. Three other ways in which we learn are vicarious experience, verbal persuasion, and physiological states. Modeling, or the scenario in which we see someone's behaviors and adopt them as our own, aide the learning process as well as mental states and the cognitive process. Media violence Media violence research Principles of social learning theory have been applied extensively to the study of media violence. Akers and Burgess hypothesized that observed or experienced positive rewards and lack of punishment for aggressive behaviors reinforces aggression. Many research studies have discovered significant correlations between viewing violent television and aggression later in life, as well as playing violent video games and aggressive behaviors. The role of observational learning has also been cited as an important factor in the rise of rating systems for TV, movies, and video games. School psychology Many classroom and teaching strategies draw on principles of social learning to enhance students' knowledge acquisition and retention. For example, using the technique of guided participation, a teacher says a phrase and asks the class to repeat the phrase. Thus, students both imitate and reproduce the teacher's action, aiding retention. An extension of guided participation is reciprocal learning, in which both student and teacher share responsibility in leading discussions. Additionally, teachers can shape the classroom behavior of students by modeling appropriate behavior and visibly rewarding students for good behavior. By emphasizing the teacher's role as model and encouraging the students to adopt the position of observer, the teacher can make knowledge and practices explicit to students, enhancing their learning outcomes. Other An easily envisioned example of social learning in the workplace is in an on-thejob training setting. Here a supervisor either explicitly or implicitly shows a new employee a physical task to be replicated for the employee's job performance. Often this physical performance may be quite foreign to the new employee However, in most cases after a few run through and attempts on the employee's part they are able to complete the task by envisioning the symbolic codes they developed consciously or unconsciously of the earlier observed model performance. IV. Lessons Learned: Our world is a social place. We could not avoid communicating with other people. We spend most of our time as a member of social group. And by learning socially, we could use this everywhere we go. Even though when we were children, we’re interacting with another children and play. I learned that we should act well because as what I have understood in Social Learning Theory, behaviors are gained through observation and imitation meaning that as an experienced person compare to children they imitate or mimic us whether what we do. Whether we are talking or not, and whether we are alone or in a group, we are thinking about what other people think, both about ourselves and about others. In order to figure out what we will say or do, we constantly consider our perspective and other individuals’ perspective. We are expected to think about our situation along with the other people involved in the social situation as we determine what to say or do. It is also important in classroom set-up. Social emotional learning competencies include self awareness, social awareness, self management, relationship skills, and responsible decision making. These characteristics need to be developed for children and young adults to be successful, not only in school but also in life. V. Exercise 1. This process surrounds the acquisition of the attention of the learner a. Attention c. Motor Reproduction b. Retention d. Motivation 2. This process includes the physical reproduction of the observe activity through physical capability, self-observation and feedback. a. Attention c. Motivation b. Retention d. Motor Reproduction 3. This process includes external vicarious and/or self-reinforced motivation. a. Attention c. Motor Reproduction b. Retention d. Motivation 4. This process involves the learner accessing symbolic coding of the behavior that has caught their attention. a. Attention c. Motor Reproduction b. Retention d. Motivation (TRUE OR FALSE) In social learning theory, OBSERVATION AND MODELING of behavior, attitudes, and emotional reactions of others is NOT the basis of social learning. ___________ 5.