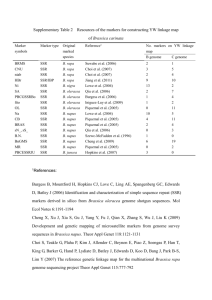
Supplemental References
advertisement

LITERATURE CITED IN SUPPLEMENTAL TABLES BROWN, G. R., E. E. KADEL III, D. A. BASSONI, K. L. KIEHNE, B. TEMESGEN et al., 2001 Anchored reference loci in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L. ) for integrating pine genomics. Genetics 159: 799-809. CHAGNÉ, D., G. R. BROWN, C. LALANNE, D. MADUR, D. POT et al., 2003 Comparative genome and QTL mapping between maritime and loblolly pines. Mol. Breed. 12: 185-195. DEVEY, M. E., K. D. JERMSTAD, C. G. TAUER and D. B. NEALE, 1991 Inheritance of RFLP loci in a loblolly pine three-generation pedigree. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83: 238-242. DEVEY, M. E., T. A. FIDDLER, B.-H. LIU, S. J. KNAPP and D. B. NEALE, 1994 An RFLP linkage map for loblolly pine based on a three-generation outbred pedigree. Theor. Appl. Genet. 88: 273-278. DEVEY, M. E., M. M. SEWELL, T. L. UREN and D. B. NEALE, 1999 Comparative mapping in loblolly and radiata pine using RFLP and microsatellite markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 99: 656-662. JARVIS, S. B., M. A. TAYLOR, M. R. MACLEOD and H. V. DAVIES, 1996 Cloning and characterisation of 3 cDNA clones of genes that are differentially expressed during dormancy-breakage in seeds of Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii). J. Plant Physiol. 147: 559-566. JERMSTAD, K. D., A. M. REEM, N. C. WHEELER and D. B. NEALE, 1994 Inheritance of restriction fragment length polymorphisms, random amplified polymorphic DNAs and isozymes in coastal Douglas-fir. Theor. Appl. Genet. 89: 758-766. JERMSTAD, K. D., D. L. BASSONI, N. C. WHEELER and D. B. NEALE, 1998a A sex-averaged linkage map in coastal Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii [Mirb.] Franco) based on RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97: 762-770. JERMSTAD, K. D., D. L. BASSONI, C. S. KINLAW and D. B. NEALE, 1998b Partial DNA sequencing of Douglas-fir cDNAs used for RFLP mapping. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97: 771776. PERRY D. J., and J. BOUSQUET, 1998a Sequence-Tagged-Site (STS) markers of arbitrary genes: development, characterization and analysis of linkage in Black spruce. Genetics 149: 10891098. PERRY, D. J., and BOUSQUET J., 1998b Sequence-Tagged-Site (STS) markers of arbitrary genes: the utility of black spruce-derived primers in other conifers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97: 735743. SCHUBERT, R., G. MUELLER-STARCK and R. RIEGEL, 2001 Development of EST-PCR markers and monitoring their intrapopulational genetic variation in Picea abies (L.) Karst. Theor. Appl. Genet. 103: 1223-1231. SLAVOV, G. T., G. T. HOWE, I. YAKOVLEV, K. J. EDWARDS, K. V. KRUTOVSKII et al., 2004 Highly variable SSR markers in Douglas-fir: Mendelian inheritance and map locations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 108: 873-880. TEMESGEN, B., G. R. BROWN, D. E. HARRY, C. S. KINLAW, M. M. SEWELL et al., 2001 Genetic mapping of expressed sequence tag polymorphism (ESTP) markers in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L. ). Theor. Appl. Genet. 102: 664-675. WANG, X. Q., D. C. TANK and T. SANG, 2000 Phylogeny and divergence times in Pinaceae: evidence from three genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 17: 773-781. WILLIAMS, J. G. K., A. R. KUBELIK, K. J. LIVAK, J. A. RAFALSKI and S. V. TINGEY, 1990 DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl. Acids Res. 18: 6531-6535.