Copper (II) Oxide Lab Report
advertisement

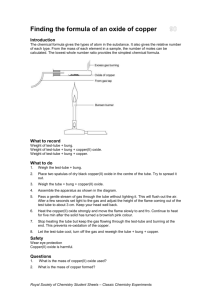
Block: ___ Teacher: ________________ Date: _______ Name: ____________________ Partner(s): ______________________________________________________________ Record your data as Group I: collect and record data from 4 other groups Group # 1(you) 2 3 4 5 Mass of copper(II) oxide Mass of copper Mass of oxygen Ratio, mass Cu/mass 0 % Cu in the oxide Record your data and calculations below. A. Mass of test tube. _____g. B. Mass of test tube plus copper(II) oxide ______ g. C. Mass of copper(II) oxide used: _____ g. D. Mass of test tube plus copper: ______ g. E. Mass of copper produced: _____ g. G. % of Cu in your copper(II) oxide: _____ % Cu F. Mass of oxygen lost: _____g. H. Mass ratio, Cu/O:______ gCu/gO I. Moles of copper produced. Show set-up. __________ mol Cu J. Moles of oxygen removed. show set-up _________ mol O K. Mole ratio, moles Cu to moles 0, in copper(II) oxide. _________ molCu/molO QUESTIONS. 1. Based upon your tabulated class data, does copper(II) oxide have a constant composition, within experimental error? What is that composition? 2. Based upon your answer in line K above, rounded to a whole number ratio, what is the formula of copper(II) oxide? Remember, a formula is simply a ratio of atoms or moles. 3. Using your formula from Q2, write a balanced equation for the reaction of methane with copper(II) oxide producing copper, carbon dioxide, and water. 4. If we assume that copper(II) oxide had the simplest possible formula, CuO, regardless of what we may have determined in Q2, calculate the atomic mass of copper, based upon this formula, that the atomic mass of oxygen is 16.00 g/mol, and your experimental data for masses of copper and oxygen in the copper(II) oxide. Show work. 5. A common observation during this experiment is a green coloration of the flame from the test tube. What might cause this? 6. What would be the effect of the following experimental errors on the % of Cu in copper(II) oxide? Would the calculated result be too high or too low? a. Blowing some copper(II) oxide out of the test tube. b. Using a wet test tube or damp copper(II) oxide. c. Not reacting all the copper(II) oxide.