ReviveABCManagementSjm
advertisement
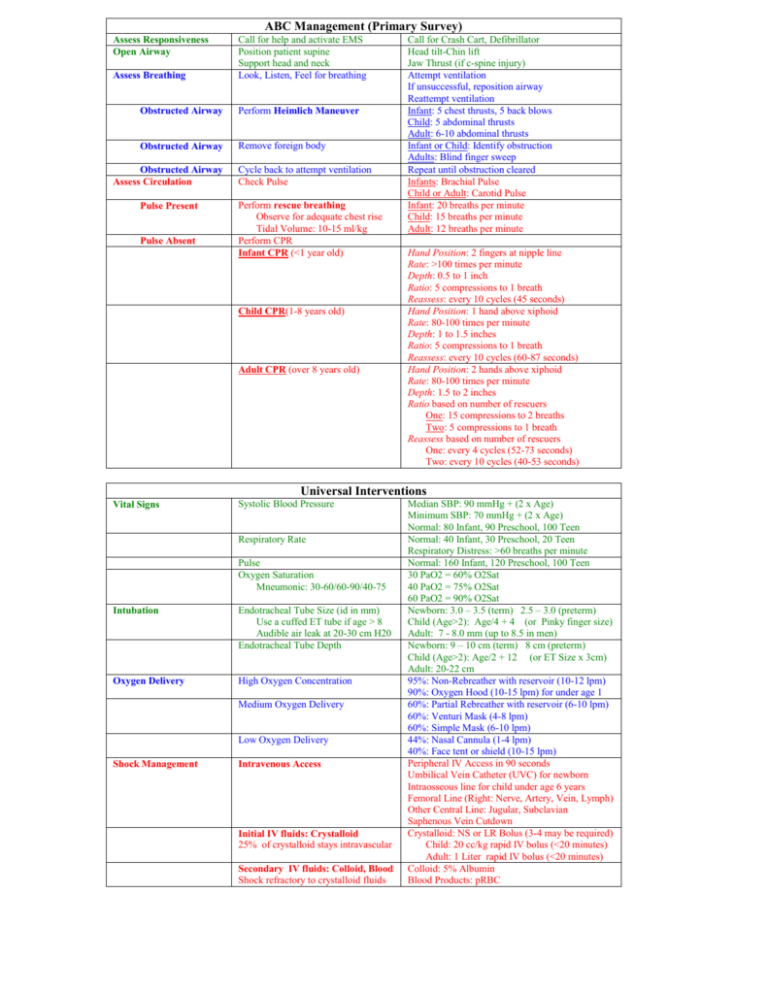
ABC Management (Primary Survey) Assess Responsiveness Open Airway Assess Breathing Call for help and activate EMS Position patient supine Support head and neck Look, Listen, Feel for breathing Obstructed Airway Perform Heimlich Maneuver Obstructed Airway Remove foreign body Obstructed Airway Assess Circulation Pulse Present Pulse Absent Cycle back to attempt ventilation Check Pulse Perform rescue breathing Observe for adequate chest rise Tidal Volume: 10-15 ml/kg Perform CPR Infant CPR (<1 year old) Child CPR(1-8 years old) Adult CPR (over 8 years old) Call for Crash Cart, Defibrillator Head tilt-Chin lift Jaw Thrust (if c-spine injury) Attempt ventilation If unsuccessful, reposition airway Reattempt ventilation Infant: 5 chest thrusts, 5 back blows Child: 5 abdominal thrusts Adult: 6-10 abdominal thrusts Infant or Child: Identify obstruction Adults: Blind finger sweep Repeat until obstruction cleared Infants: Brachial Pulse Child or Adult: Carotid Pulse Infant: 20 breaths per minute Child: 15 breaths per minute Adult: 12 breaths per minute Hand Position: 2 fingers at nipple line Rate: >100 times per minute Depth: 0.5 to 1 inch Ratio: 5 compressions to 1 breath Reassess: every 10 cycles (45 seconds) Hand Position: 1 hand above xiphoid Rate: 80-100 times per minute Depth: 1 to 1.5 inches Ratio: 5 compressions to 1 breath Reassess: every 10 cycles (60-87 seconds) Hand Position: 2 hands above xiphoid Rate: 80-100 times per minute Depth: 1.5 to 2 inches Ratio based on number of rescuers One: 15 compressions to 2 breaths Two: 5 compressions to 1 breath Reassess based on number of rescuers One: every 4 cycles (52-73 seconds) Two: every 10 cycles (40-53 seconds) Universal Interventions Vital Signs Systolic Blood Pressure Respiratory Rate Pulse Oxygen Saturation Mneumonic: 30-60/60-90/40-75 Intubation Endotracheal Tube Size (id in mm) Use a cuffed ET tube if age > 8 Audible air leak at 20-30 cm H20 Endotracheal Tube Depth Oxygen Delivery High Oxygen Concentration Medium Oxygen Delivery Low Oxygen Delivery Shock Management Intravenous Access Initial IV fluids: Crystalloid 25% of crystalloid stays intravascular Secondary IV fluids: Colloid, Blood Shock refractory to crystalloid fluids Median SBP: 90 mmHg + (2 x Age) Minimum SBP: 70 mmHg + (2 x Age) Normal: 80 Infant, 90 Preschool, 100 Teen Normal: 40 Infant, 30 Preschool, 20 Teen Respiratory Distress: >60 breaths per minute Normal: 160 Infant, 120 Preschool, 100 Teen 30 PaO2 = 60% O2Sat 40 PaO2 = 75% O2Sat 60 PaO2 = 90% O2Sat Newborn: 3.0 – 3.5 (term) 2.5 – 3.0 (preterm) Child (Age>2): Age/4 + 4 (or Pinky finger size) Adult: 7 - 8.0 mm (up to 8.5 in men) Newborn: 9 – 10 cm (term) 8 cm (preterm) Child (Age>2): Age/2 + 12 (or ET Size x 3cm) Adult: 20-22 cm 95%: Non-Rebreather with reservoir (10-12 lpm) 90%: Oxygen Hood (10-15 lpm) for under age 1 60%: Partial Rebreather with reservoir (6-10 lpm) 60%: Venturi Mask (4-8 lpm) 60%: Simple Mask (6-10 lpm) 44%: Nasal Cannula (1-4 lpm) 40%: Face tent or shield (10-15 lpm) Peripheral IV Access in 90 seconds Umbilical Vein Catheter (UVC) for newborn Intraosseous line for child under age 6 years Femoral Line (Right: Nerve, Artery, Vein, Lymph) Other Central Line: Jugular, Subclavian Saphenous Vein Cutdown Crystalloid: NS or LR Bolus (3-4 may be required) Child: 20 cc/kg rapid IV bolus (<20 minutes) Adult: 1 Liter rapid IV bolus (<20 minutes) Colloid: 5% Albumin Blood Products: pRBC Arrhythmia Management Universal Approach Arrhythmia: Too Fast Unstable Narrow Complex Wide Complex ABC Management IV-O2-Monitor CPR as indicated Consider Intubation Intravenous Access High-flow Oxygen Administration Cardiac Monitor Synchronized Cardioversion Indications: Narrow complex tachycardia Wide complex tachycardia Child First dose: 0.5 Joules/kg Subsequent doses: 1 Joules/kg Adult PSVT, Atrial Flutter: 50, 100, 200, 300, 360 J VT, Atrial Fibrillation: 100, 200, 300, 360 J Treat Underlying Cause Fever, Hypovolemia, Hypoxia, Anxiety, Pain Electrolyte abnormality, Drug Ingestion Pneumothorax, Cardiac Tamponade Vagal Maneuvers: Carotid massage or ice immersion Adenosine First: 0.1-0.2 mg/kg rapid IV (up to 6 mg) Next: 0.2-0.4 mg/kg rapid IV (up to 12 mg) Verapamil (Age over 8, no CHF or Hypotension) First: 0.1 mg/kg (up to 2.5 mg) IV over 3 min Next: 0.2 mg/kg (up tp 5.0 mg) IV over 3 min Synchronized Cardioversion (See above) Lidocaine Bolus: 1 mg/kg IV Infusion if bolus successful: 20-50 ug/kg/min Synchronized Cardioversion (See Above) Lidocaine First: 1.0 - 1.5 mg/kg IV push, wait 3-5 min Next: 0.5-0.75 mg/kg IV push (Max: 3 mg/kg) Procainamide 20-30 mg/min (max: 17 mg/kg) Bretylium 5-10 mg/kg over 10 minutes Synchronized Cardioversion (See Above) Epinephrine every 3-5 minutes IV Dose: 0.01 mg/kg (0.1 ml/kg 1:10,000) ET Dose: 0.1 mg/kg (0.1 ml/kg 1:1000) Atropine: 0.02 mg/kg IV/ET (0.1-0.5 mg) Transcutaneous Pacing Do not shock Sinus Tachycardia Sinus Tachycardia P Waves present and normal Constant PR interval Heart rate below PSVT Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT) P Waves Absent or abnormal Heart Rate above Sinus Tachycardia Infants > 220 beats/minute Children > 180 beats/minute Adults > 160 beats/minute Child Ventricular Tachycardia Adult Ventricular Tachycardia Arrhythmia: Too Slow Arrhythmia: Pulseless Shockable Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) Asystole Child Unstable Bradycardia Adult Unstable Bradycardia Atropine 0.5-1.0 mg IV/ET q5 min (to 0.04 mg/kg) Transcutaneous pacing Dopamine 5-20 ug/kg/min Epinephrine 2-10 ug/min Shockable Rhythms Ventricular Fibrillation Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia Defibrillate Child: 2 j/kg, 4 j/kg, 4 j/kg Adult: 200j, 300j, 360j Epinephrine (repeat every 3-5 minutes) Child: 0.01 mg/kg IV (0.1 mg/kg ET) Adult: 1 mg IV (2.5 mg in 10 cc NS ET) Defibrillate: 4 joules/kg (Adult: 360 Joules) Lidocaine 1 mg/kg IV/IO Defibrillate: 4 joules/kg (Adult: 360 Joules) Bretylium 5-10 mg/kg Defibrillate: 4 joules/kg (Adult: 360 Joules) Child: Same treatment as for Asystole Adult (Same treatment as for Asystole) Epinephrine 1 mg IV push q3-5 minutes Atropine 1 mg IV q3-5 minutes (max: 0.04 mg/kg) Treat Cause: 4H TAPE MD Hypoxemia, Hypovolemia, Hypothermia, Hypokalemia, Tension Pneumothorax, Tamponade, Pulmonary Embolus, Myocardial Infarction, Drug Overdose Treat Cause Hypoxia, Hypothermia, Hyperkalemia, Hypokalemia Preexisting acidosis Drug Overdose Child: (Same treatment as for PEA) Epinephrine first: 0.01 mg/kg IV (0.1 mg/kg ET) Epinephrine next: 0.1 mg/kg IV or ET Adult: Same Treatment as PEA (consider TCP)





