20121215-212429
advertisement

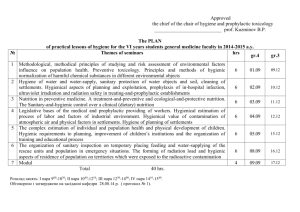
MODULE NO. 1 FOR THE 3-YEAR STUDENTS OF MEDICAL FACULTY TOPIC: ‘GENERAL QUESTIONS OF HYGIENE’ Sections: ‘MUNICIPAL HYGIENE’ and ‘NUTRITION HYGIENE’ PURPOSE: Assessment of theoretical knowledge level and practical skills in the questions of Municipal Hygiene and Nutrition Hygiene. QUESTIONS FOR THEORETICAL PREPARATION: ‘MUNICIPAL HYGIENE’ 1. Spectrum of solar radiation: biomedical implication of its basic parts, equipment and units. 2. Ultraviolet radiation: physical properties and biological effect. Natural and artificial sources of ultraviolet radiation. Methods and equipment for sanitary inspection of ultraviolet radiation, units. Disorders and diseases as a result of deficit or surplus of doses of ultraviolet radiation and their prevention. 3. Visual spectrum of solar radiation: characteristic, peculiarities of biological effect, Methods and equipment for sanitary inspection of visual light, units. 4. Infrared radiation, physical properties and biological effect, equipment for sanitary inspection of infrared radiation, units. Disorders and diseases as a result of deficit or surplus of infrared radiation. 5. Microclimate: definition. Medical significance of microclimate. Kinds of attemperation. Complex evaluation of microclimatic factors influence. Classification of microclimate. Disorders and diseases as a result of uncomfortable overcooling and uncomfortable overheating type of microclimate. 6. Hygienic requirements to the natural illumination and methods of its evaluation. Disorders and diseases due to inefficiency of illumination and ways of their prevention. 7. Methods of evaluation of natural illumination: basic criterions and hygienic standards for the different types of premises (learning, medical, etc.). 8. Hygienic requirements to the artificial illumination and methods of its evaluation. 9. Methods of evaluation of artificial illumination: basic criterions and hygienic standards for the different types of premises (learning, medical, etc.). 10.Methods of assessment of the air condition and ventilation in premises. 11. Basic sources of the air pollution, outputs and prevention of their negative influence on the human organism. 12.Hygienic requirements to the drinkable water. 13.Direct and indirect criterions of water pollution. 14.Ammonia, nitrites and nitrates in water, possible pathology because of their presence. Determination of water pollution terms on basis of types of nitrogen compounds. 15.Diseases as a result of using of not-qualitative water. Biogeochemical endemic diseases, definition, basic kinds, prevention. 16.Kinds and methods of water quality’s improvement. 17.Water purification: methods, devises, reactants, criterions of effectiveness. 18.Microbiological decontamination of water: methods, reactants, criterions of evaluation of microbial decontamination’s reliability. 19.Chemical decontamination of water: methods, reactants, criterions of evaluation of microbial decontamination’s reliability. 20.Radiological decontamination of water: methods, reactants, criterions of evaluation of microbial decontamination’s reliability. 21.Basic zones of sanitary maintenance of water sources and stages of improvement of water’s quality. 22.Hygienic requirements to the different types of wells. 23.Basic sources of water pollution, outputs of their influence and prevention of this influence. ‘NUTRITION HYGIENE’ 24. Physiological significance, basic functions of nutrition. 25. Principles and conditions of the rational nutrition. 26. Nutrition as a social and hygienic problem. 27. Physiological and hygienic substantiation of rational nutrition for people of different age-specific groups, professions, sportsmen. 28. The basic kinds of nutrition. Physiological norms of nutrition for different categories of population (age-specific groups, professional groups and others). 29. The physical activity coefficient. 30. Biomedical value of proteins, fats, carbohydrates in human organism, their daily needs. 31. Diseases of Protein Insufficiency and Excess, Fat Insufficiency and Excess, Carbohydrate Insufficiency and Excess, Microelements Insufficiency and Excess, Macroelements Insufficiency and Excess. Biogeochemical endemias. 32. , Vitamin Insufficiency and Excess. Problems of hypo-, avitaminosis, hypervitaminosis. 33. Alimentary and alimentary conditioned diseases, their classification, etiology, main principles of prevention. 34. Food poisonings, their classification, origin, epidemiological particularities. 35. Bacterial food poisonings (toxicoinfections, bacterial toxicoses, mycotoxicoses), their origin, basis of prevention. 36. Amicrobial Food Poisonings, their origin, prevention. 37. Food poisonings of unknown origin. 38. Medical control methods for nutrition adequacy and balance. 39. Methods and criteria of assessment of the individual nutritional status and organism provision with vitamins. 40. Energy expenditure of the organism, its components as the base of the ration’s caloric content. 41. Methods of determination of the energy expenditure. The Physical Activity Coefficient, its dependence from the hardness and intensity of work, social, geographical and climatic living conditions. 42. Calculation of the organism nutrient needs. 43. Methods of determination of the ration caloric value and nutrient content – balance, budget, questioning, weighting. 44. Calculation methods of determination and assessment of the ration’s quantitative and qualitative content according to the menu-contents. 45. Biomedical value of milk, dairy food, meat, fish, bread, flour, cereals, beverages. 46. Food additives, their classification, hygienic characteristic. 47. Food Sanitary Inspection (organoleptic, sanitary-chemical, bacteriological, helminthological methods, etc.). 48. Basic and Additional Food Quality Degrees. 49. Methods of diagnosis and prevention of the alimentary diseases. 50. Methods of food poisoning investigation and prevention, directive, methodical and legislative documents used during this procedure. 51. Hygienic foundations of the nutrition organization at the hospital. MedicalDietary and Medical-Preventive Nutrition. PRACTICAL SKILLS: ‘MUNICIPAL HYGIENE’ - determination of biodose, preventive, maximum and optimum doses of ultraviolet radiation; - determination of infrared radiation intensity; - hygienic assessment of natural and artificial illumination by different methods and basis of hygienic conclusion; - hygienic assessment of microclimate in premises; - charting of the wind rose and basis of hygienic conclusion and recommendations; - determination of natural and artificial ventilation parameters by different methods and their hygienic evaluation; - hygienic assessment of water laboratory analysis; - performing of water disinfection with Chlorine compounds; - hygienic assessment of soil laboratory analysis. ‘NUTRITION HYGIENE’ - determination of Basal Metabolism; - determination of nutrition adequacy and balance; - determination of human nutritional status; - evaluation of human organism provision with vitamins (and diagnosis of different vitamin insufficiencies); - diagnosis of alimentary diseases and food poisonings; - determination of Basic and Additional Food Product (Aliment) Quality Degrees - revelation of food adulteration. MANDATORY READING: for section ‘MUNICIPAL HYGIENE’ Hygiene and ecology: Textbook for Higher Education Institutions / Ed. by V.G. Bardov. – Vinnytsya: Nova Kniga, 2009. – PP. 14-130, 141-240. for section ‘NUTRITION HYGIENE’ Hygiene and ecology: Textbook for Higher Education Institutions / Ed. by V.G. Bardov. – Vinnytsya: Nova Kniga, 2009. – PP. 246-313. RECOMMENDED READING: for section ‘MUNICIPAL HYGIENE’ Hygiene and Ecology: Text-book / Vladimir A. Korobchanskiy, Michael P. Vorontsov, Alisa A. Musulbas. — Kharcov, 2006. — PP. 7-63. for section ‘NUTRITION HYGIENE’ Hygiene and Ecology / Vladimir A. Korobchanskiy, Michael P. Vorontsov, Alisa A. Musulbas. — Kharcov. — 2006. — PP. 87-123.