Nerve & Vessels of Medical Compartment of Thigh
advertisement

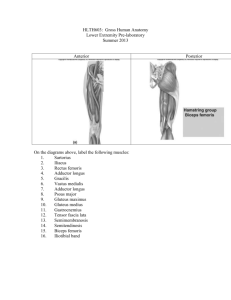
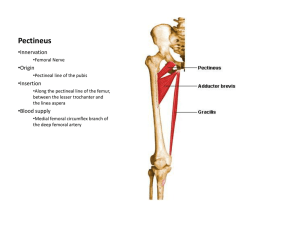
S-II-LM-096 Nerve and vessels of medial compartment thigh Learning Objectives : At the end of the lecture student will able : To define the medial compartment. To enlist the vessels of the medial compartment. To describe the nerve of the medial compartment. Clinical correlations of the medial compartment. Profunda Femoris Is a branch of femoral artery in the femoral triangle. Descends in the interval between the adductor longus and adductor brevis and then lies on the adductor magnus, ends as the fourth perforating artery Branches Branches: - lateral circumflex - medial circumflex femoral artery - branch to adductor magnus - perforating branches - terminal branch (4 th perforator) Medial femoral circumflex artery: Give muscular branches to medial compartment-Takes part cruciate anastomosis Lateral femoral circumflex artery: 4 Perforating branches: 3 arise as branches of the profunda femoris artery; the fourth perforating artery is the terminal part of the profunda artery Trauma to Profunda: - ischemia of foot is uncommon unless there is underlying significant atherosclerotic disease of superficial femoral artery; - many injuries to the profunda are initially not detected & present as late false aneurysms; - profunda femoris artery is at risk of injury during orthopedic procedures from perforation by metallic screws; - ligation of vessel for proximal injuries is contraindicated because this may be important collateral pathway, esp in atherosclerotic population Obturator Nerve Anatomy: - formed from anterior branches of L2, L3, L4 (see innervation of muscles of the lower limb) - largest nerve formed from anterior divisons of lumbar plexus ; - roots unite within the posterior part of psoas, & then descends thru psoas & runs downward over sacral ala into lesser pelvis, lying lateral to ureter & internal iliac vessels; - enters the upper part of the obturator foramen and then subsequently divides into anterior and posterior branches; - Anterior Branch: - runs in front of obturator externus & adductor brevis ; - it runs behind the pectineus and adductor longus muscles; - gives off articular twig that enters hip joint thru acetabular notch; - supplies muscular branches to hip adductors & then divides into cutaneous, vascular, and communicating vessels; - Cutaneous Branch: - when present, it assists in innervation of skin and fascia over distal 2/3 of thigh; - Posterior Branch: - pierces anterior part of obturator externus; - nerve then runs downward behind the adductor brevis & and in front of the adductor magnus; - it then splits into branches that are distributed to upper (adductor) part of adductor magnus & sometimes to adductor brevis;