Cellular Transport Vocabulary: Definitions & Concepts
advertisement

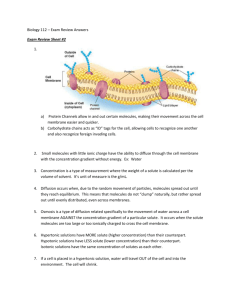
Cellular Transport Vocabulary Words 1. Passive Transport- General transport mechanism that requires no energy expenditure by the cell, molecules move with the concentration gradient…… molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration (energy that moves the molecules is provided by Brownian Movement)…… as in colliding pool balls in billiards. 2. Diffusion-Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. (passive) 3. Osmosis-Movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration (passive) (a special form of diffusion) 4. Facilitated Diffusion-Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration, sped up by openings in the cell membrane (passive) 5. Active Transport-Movement of molecules that requires a cell to expend energy. (riding a bike uphill) 6. Exocytosis-Active transport of molecules out of a cell. Usually against the concentration gradient. (low to high) 7. Endocytosis-Active transport of molecules into a cell. Usually against the concentration gradient. (low to high) 8. Pinocytosis-“Cell drinking” Active transport of tiny amounts of water into a cell. Usually against the concentration gradient. (low to high) 9. Phagocytosis- “Cell eating” Active transport of molecules into a cell. White blood cells “eat” foreign particles such as bacteria, viruses… **Solution-A liquid mixture that involves the combination of a solvent with a solute. *Solute-the substance dissolved in the liquid part of a solution *Solvent-the liquid into which the solute is dissolved. 10. Hypotonic Solution-More solute inside the cell than the water environment that it is living in. Water will enter the cell in an effort to equalize (dilute) the water concentration inside the cell and outside of the cell. (osmosis) 11. Hypertonic Solution-More solute outside the cell than inside the cell. Water will leave the cell in an effort to equalize (dilute) the water concentration outside the cell and inside the cell. 12. Isotonic Solution-There is an equal amount of solute inside the cell and in the environment the cell is living in. Water is entering and leaving the cell at an equal rate. (at equilibrium) 13. Equilibrium-To be in balance or in a state of equality 14. Concentration Gradient-A difference in concentration across a cell’s membrane. 15. Brownian Movement- The phenomenon that states that molecules are in random motion at all times except under the condition of “absolute zero,” when all molecular movement ceases.