Sample Essay Questions
advertisement

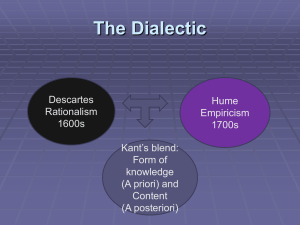
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What does Kant mean by Din an sich? What does Hegel mean by “Geist” “To think in existence” for Kierkegaard meant: What does Kant mean by noumenal reality? Who coined the term “Theodicy”? According to Kierkegaard the term “existence” was reserved for: For Descartes, what is res cognitans? To say that event A causes B, we mean that A is… to B For Kierkegaard, what knowledge can help Abraham to decide whether to obey God or not? 10. Humanism emphasizes: 11. What is the meaning of the term theodicy? 12. Who awakened Immanuel Kant from his “dogmatic slumber”? 13. The following are all traits/characteristic of the tough-minded according to William James except: 14. The Pragmatic Method according to William James settles…disputes 15. Hume argues that causality is a complex idea made of three foundational ideas. What are these ideas? 16. Which Thomistic arguments are known as the “Cosmological Arguments” for God’s existence? 17. Truth for Søren Kierkegaard is: 18. Hume’s “Copy Thesis” suggests that the content of all ideas is ultimately copied from: 19. What is “Fides Quarens Intellectum”? 20. Which philosopher first introduced the concept and the term pragmatism into philosophy? 21. For Kant, phenomenal reality is: 22. What is the cause of man’s own estrangement from his essential being according to Kierkegaard? 23. The three faculties of the human mind according to Kant are.. 24. Some major characteristic of the tender-minded according to William James are: 25. How did David define a miracle Hume? 26. For Kant, the faculty of the human mind that produces pure concepts such as God is… 27. Which philosopher equated God with nature? 28. In Thomas Aquinas’ 1st, 2nd and 5th ways of arguing for the existence of God, he begins with: 29. Spinoza calls Thought or Extension… 30. What is Pantheistic Monism? 31. The three kinds of laws for John Locke are… 32. The three types of knowledge for Spinoza include the following: 33. For David Hume all the perceptions of the human mind resolve themselves into two distinct kinds, which he calls: 1 34. Karol Wojtyla was satisfied with St. Thomas for correctly situating the human person in terms of : 35. What doctrine did Wojtyla identified as the Achille’s heel of the Communist regime in Poland? 36. What weakness did John Paul II identify in Thomistic philosophy? 37. For Wojytla “the law of the gift” or the human person as ex-centric provides the…grounding for the paradoxical sayings of Jesus in the Gospel 38. For John Paul II “Christianity” is… 39. According to Avery Cardinal Dulles the “key” to unlocking the distinctiveness of pontificate Paul II as a thinker is : 40. What lies at the very heart of his pontificate and message? 41. What distinctive way does John Paul II present the dogmatic heritage of the church? 42. What weaknesses did Karol Wojtyla note of the philosophy of St. Thomas Aquinas? (Hint: “Thomistic Personalism”) 43. How did St. Thomas Aquinas situate the human person in terms of ‘…the general categories of being’? How did Wojtyla differ in this perspective? 44. What does Wojtyla mean by “the law of the gift”? 45. What provides the anthropological grounding for the paradoxical sayings of Jesus? 46. Briefly comment on Dignitatis Humanae, No 1 in view of Wojtyla’s contribution to the Second Vatican Council. 47. What does JPII mean by “authentic freedom”? 48. Summarize John Paul II’s address to the General Assembly of the United Nations in 1995? 49. How does Libertarianism severs the bonds between freedom and responsibility? 50. What account/s for the extraordinary brutality of the 20th century according to John Paul II? 51. What did the human person receive from God? (Hint: Centesimus Annus, No.38.1) 52. How did Wojtyla criticize Marxist collectivism, libertarian individualism and anarchist alienation in his piece The Acting Person? 53. What is NOT Christianity? And what is Christianity? 54. What is the primary source of wealth today according to Wojtyla? 55. Why is dialogue an exchange of gifts? 56. What does the Pope mean by “tribunal of mercy”? 57. What is “Bone pastor, panis vere…”? 58. Why is ‘solidarity defined as a virtue’? 59. Take Note of the following encyclicals (Year of Publication, author, the English o o o translation/name) Redemptoris Missio Novo Millennio Ineunte Eccesia de Eucharistia 2 o o Ut Unum Sint Laborem Exercens Take note of the following the Kantian Categories: a) Quantity b) As to Quality c) As to Relation d) As to Modality 60. Unity 61. Totality 62. Substance 63. Possibility 64. Plurality 65. Reality 66. Limitation 67. Necessity 68. Existence Sample Essay Questions Discuss Pope John Paul II’s conception of personalism. What is the significance of personalism in the themes of his papacy/pontificate? How did he relate it (personalism) to: I. a) Missionary activity a) Ecclesiology b) Ecumenism and interreligious dialogue c) Social teachings of the Church 2. How does Karol Wojtyla’s personalist perspective stand in tension with previous church traditions such as: a. Natural theology b. Natural law c. Contraception d. Death Penalty e. Just War f. Social Order g. Kingship of Christ h. Last Judgment i. Purgatory 1. 3. Why is Kant’s philosophy called “critical philosophy”? In simple terms, what is meant by a priori knowledge? Give an example What is meant by Kant’s Copernican revolution? Kant says that all knowledge begins with experience but that it does not follow that it all arises out of experience. What does he mean by that? e) What is pragmatism? f) What is the pragmatic method? g) Discuss Thomas Aquinas’ Five Ways a) b) c) d) 3 h) How does St. Anselm differ from St. Thomas Aquinas’ proof for God’s existence? i) What is theodicy? Explain the following: moral, metaphysical and physical evils with relevant examples. 4. a) Write a comprehensive essay on Soren Kierkegaard’s Ways of Life Stages with relevant examples. 4