Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential
advertisement
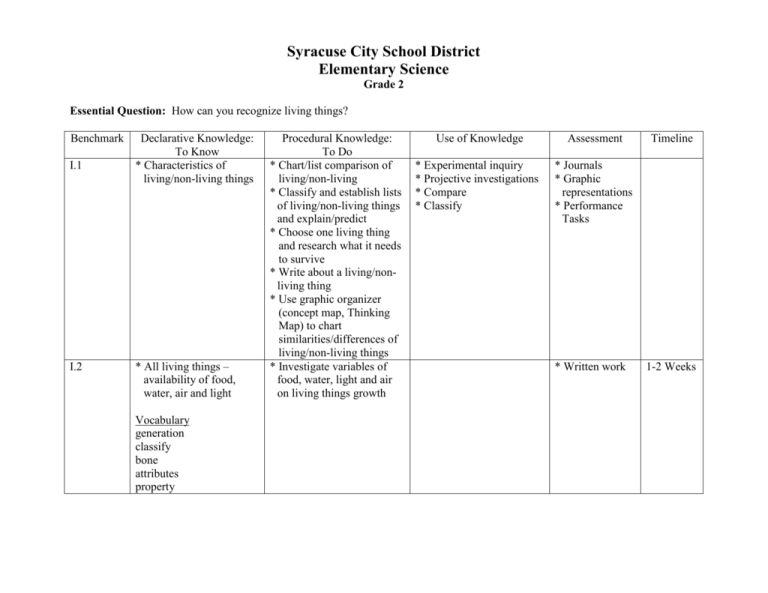
Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: How can you recognize living things? Benchmark I.1 I.2 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Characteristics of living/non-living things * All living things – availability of food, water, air and light Vocabulary generation classify bone attributes property Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Chart/list comparison of living/non-living * Classify and establish lists of living/non-living things and explain/predict * Choose one living thing and research what it needs to survive * Write about a living/nonliving thing * Use graphic organizer (concept map, Thinking Map) to chart similarities/differences of living/non-living things * Investigate variables of food, water, light and air on living things growth Use of Knowledge Assessment * Experimental inquiry * Projective investigations * Compare * Classify * Journals * Graphic representations * Performance Tasks * Written work Timeline 1-2 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: How is one generation similar to the previous or the following generation? Benchmark II.1 II.2 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Differences and similarities of plant types * Characteristics of animal groups with and without bones, hair color, size * Offspring do or do not resemble parent Vocabulary generation classify bone attributes property Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Classify plants by - leaf types - plant size - evergreen/not * Classify animals by bones/no bones, hair color, size * Compare/contrast offspring to parent plant or animal * Investigate similarities in family and write how you are like your parents, grandparents, brothers/sisters, and how you are different Use of Knowledge * Compare * Classify Assessment Timeline * Journals * Graphic representations * Performance Tasks 2-4 Weeks * Written work 1-2 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: How do living things adapt to survive in their environment? Benchmark Declarative Knowledge: Procedural Knowledge: Use of Knowledge To Know To Do III.1 * Animal body structures * Identify and match body * Compare perform given functions parts to function * Body parts and * Observe, coloration complement compare/contrast various environment animal’s body parts and * Plant structures perform coloration to their different growth, environment survival, reproductive * Identify, match and functions observe plant structures to function III.2 * Individual species of * Investigate variables of * Experimental inquiry plants and animals food, water, shelter, success is determined by mates on given animals competition for and plants - food * Use graphic organizer - water (concept map, Thinking - mates Map) to chart adaptations - shelter that animals or plants make to survive Vocabulary * Read and explain how function animals adapt or change success to survive (man vs. environment nature) * Write a paragraph explaining how a character or animal had to change to survive Assessment Timeline * Journals * Graphic representations * Performance tasks 2-4 Weeks * Written work 2-3 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: What sustains the continuity of life? Benchmark IV.1 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Life cycle of birds * Life cycle of various mammals * Life cycle’s success is determined by availability of food, water, space, light and temperature Vocabulary life cycle bird mammal Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Observe and record the sequence of life cycles of birds and mammals * Investigate variables of temperature, light, food, water, space upon said life cycles * Predict and chart variables and the effects on continuity of life (food, water, space) * Experiment with plants, changing the variables of light, water, nutrients, space) Use of Knowledge * Experimental inquiry * Compare Assessment Timeline * Journals 2-4 Weeks * Graphic representations * Performance tasks * Written explanation of what happens in the absence of variables needed for life Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: How do plants and animals respond to their environment? Benchmark V.1 V.2 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Organism depends on availability of food, water, light space, air Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Investigate variables of food, water, light, space and air upon organisms growth * Parts of plants and animals adapt to meet needs for food, water, shelter, space, light and temperature * Animals move from place to place to meet needs * Animal behaviors are influenced by environmental conditions * Observe and record changes in plant or animal parts to meet its needs - measure - journal - draw * Investigate and explain animal behaviors and characteristics influenced by environmental changes - migration - hibernation - nest building - shedding fur - fat storage - hunting * Read and explain a story about a person or animal who moved and the differences be/she encounters (country to city, another country to America) * discuss adaptations students have made if they have moved Vocabulary adapt shelter migration hibernation shed germ Use of Knowledge * Experimental inquiry * Compare * Deductive reasoning Assessment * Journals * Graphic representations * Performance assessments Timeline 1-2 Weeks 2-4 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: What is the relationship between plants, animals and their environment? Benchmark VI.1 VI.2 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Animals move from place to place to meet needs * Animal behaviors are influenced by environmental conditions * The sequence of various food chains, land and water * Producer and consumer * Decomposers are necessary to recycle nutrients in food chain Vocabulary sequence producer consumer decomposer recycle nutrients food chain migration hibernation mate Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Investigate animal behaviors and characteristics influenced by environmental changes - migration - hibernation - nest building - hunting - shedding fur or reverse * Create models of various land and water food chains including decomposers * Read stories about plants or animals and discuss/write about how the environment affects them * Chart cause and effect for various plants and animals during seasonal changes Use of Knowledge * Experimental inquiry * Invention * Deductive reasoning Assessment * Journal * Performance tasks * Graphic representation Timeline 1-2 Weeks 2-4 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: Are human decisions and activities helpful or harmful? Benchmark VII.1 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Humans depend on their natural environments for food, clean water, clean air * Animal and plant growth and survival are influenced by human interactions * Understands that germs are found everywhere Vocabulary human natural environment Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Observe and give examples of ways people get food, clean water and air from natural world * Observe and give examples of how actions of people have negative results on natural environment * Identify sources of germs and sequence how they are transferred * Investigate various situations/disasters that have harmed the environment (landfills, wet lands, industrial pollution * Investigate NYS preservation and protection of environment (may use ESF presenters, living schoolbook, Onondaga Park Museums, Onondaga Lake Watershed website) * Write an essay on How has a human decision or activity helped or harmed the environment? Use of Knowledge * Deduction reasoning * Investigation Assessment Timeline * Performance tasks * Project * Group projects * Investigative reports * Written documents 2-3 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Physical Setting Essential Question: How can the movement of the Earth and celestial bodies be observed and measured over time? What impact does this movement have on daily life? Benchmark I.1 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Earth rotates once every 24 hours causing night and day * One day = 24 hours * Sun and stars remain constant – Earth rotates creating apparent movement * Length of day light and darkness varies with seasons * Weather changes daily and seasonally * Appearance of Moon changes daily * Stars appear in patterns or groups called constellations Vocabulary rotate constellation daily sunrise sunset myth Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Explain and model Earth’s daily rotation causing day and night * Observe sun and stars movement in the sky * Periodically record time of sunrise and sunset * Graphically record Moon’s changing phases on a monthly basis * Recognize Big Dipper and other major constellations * Read and retell myth of constellation, moon, sun, etc. * Identify one constellation for each season * Model/simulate movement of Earth and celestial bodies over time (make a mobile) * Write an explanation of the impact of Earth and celestial movement on daily life Use of Knowledge * Inductive reasoning Assessment * Performance assessment * Graphs and charts * Journals Timeline 2-4 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grades 2 Essential Question: How do air, water, and land interact? Benchmark II.1 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Thermometer reflects temperature * Degrees are the unit of temperature * Thermometer rises with heat, falls with cold * Precipitation can be measured * Sky conditions vary (cloudy, sunny) Vocabulary thermometer temperature degree precipitation Procedural Knowledge: Use of Knowledge To Do * Read thermometer to * Compare nearest 5 degrees * Classify * Observe and graph thermometer’s reaction to hot and cold * Observe and record daily precipitation * Observe and record daily sky conditions * Using the newspaper as a model, construct a weather map * Write a cause/effect essay on precipitation or temperature Assessment *Performance tasks * Journals * Graphs * Charts * Written response Timeline 2-3 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: How can matter be described? Benchmark III.1 III.2 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Matter can be measured and observed * Mass is measured by a scale * Gram, pounds, ounces are units of weight or mass * Volume is the amount of space something takes up * Volume is measured by graduated cylinders, beakers, measuring cups – milliliter, liters, gallon, quart, pints are units of volume * Objects can be classified by given properties - know appropriate criteria to describe objects * Ruler, tape measure, yard or meter stick measure length * Environmental conditions affect some properties of objects - lighting affects color, shadows * Properties of a solid or liquid Vocabulary matter weight gram ounce mass scale pound volume Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Classify or measure objects by given criteria * Measure mass using pan balance and standard or non-standard units * Measure volume of liquids using beakers, graduated cylinders, or other standard volume containers * Sort objects by at least 2 properties (color, shape, size, texture, weight, volume, etc.) * Determine length of given objects to nearest centimeter, inch * Vary ambient light to determine affect on color, shadow size, length * Write up a lab experience * Determine properties of a liquid and solid - classify objects as liquids or solids * Observe liquids change of shape by pouring such into various shaped containers while maintaining volume Use of Knowledge * Classify * Compare * Experimental inquiry * Problem solving Assessment * Teacher observation * Performance tasks * Lab write-up Timeline 2-4 Weeks 1-2 Weeks beaker milliliter liter gallon quart pint ruler tape measure yard stick meter stick centimeter inch solid liquid graduated cylinder Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: How does energy change things? Benchmark Declarative Knowledge: Procedural Knowledge: Use of Knowledge To Know To Do IV.1 * Energy causes change * Give examples of how the * Deductive reasoning * Energy exists in these following cause change in * Experimental inquiry forms matter * Invention - heat - heat – change of state - electric - electricity – turn or - sound movement - mechanical - sound – vibration - light - mechanical - move things - light – grow plants IV.2 * Sun’s energy warms air * Observe, measure and and land record temperature of * Food provides energy objects warmed by Sun for animals to move * Recognize cause/effect of * Energy can be lack of food (no energy, transferred to matter tired) * Sequence and explain Vocabulary energy transfer energy light - electrical/sound heat transfer (electricity/boom box) electricity sound - mechanical/sound mechanical (musical instruments) * Write, draw, construct about energy transfer * Design a model and demonstrate energy transfer Assessment Timeline * Teacher assessments * Performance tasks 1-2 Weeks 1-2 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grade 2 Essential Question: How do energy and matter interact to create change in motion? Benchmark V.1 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Force is push or pull * Gravity pulls objects toward the Earth * Balance is an equalization of forces * Magnetic force can attract certain materials * Magnetism can attract objects through gases, liquids, solids * Magnetic poles Vocabulary force balance attract gravity weight Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Observe object’s change of direction or position due to application of force such as: wind, magnetism, gravity, human * Observe and chart gravity’s effect on various objects thus causing motion * Investigate factors such as weight, location, center of gravity, shape, size upon an object’s ability to balance * Classify objects that magnet does or does not attract * Observe a magnet’s attraction upon objects through air, water and various solids * Observe strength of attraction on various sites of a magnet * Write an explanation of effect of gravity or magnetism on an object * Predict effects of gravity or magnetism on objects Use of Knowledge * Experimental inquiry * Inductive reasoning * Classify * Compare Assessment Timeline * Journal * Teacher made assessments * Performance tasks * Demonstrate effects of gravity on various objects 2-4 Weeks Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grades PreK – 4 Scientific Inquiry/Mathematical Analysis Essential Question: What do I need to know? How can I find out? Benchmark I.1 II.1 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Formatting of questions who, what, where, when, why * Tools to record observations - graphs - charts - drawings and labeling - narratives * Recognize similarities and differences * Roles of cooperative groups - facilitator - materials manager - observer - recorder Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Develop and answer appropriate questions to seek greater understanding of observed objects and events * Record observations and develop relationships - graphs - charts - drawing & labeling - narratives * Compare and contrast personal observations with others * Work in cooperative groups * Scientific tools used for measuring - thermometer - beakers, cups, etc. - linear measurement - scales - time * Sequence of events of the plan * Create, share and carry out plans for explaining phenomena. Indicate - materials - procedure - data collection through observation and use of simple measurement tools Use of Knowledge * Compare * Classify * Experimental inquiry * Investigation * Invention * Problem solving * Inductive reasoning * Deductive reasoning * Constructing support * Comparison * Classification * Experimental inquiry * Projective investigation * Invention * Problem solving * Induction * Deduction * Constructing support Assessment * Teacher observation * Performance assessment * Teacher made/or program assessment * Records * Graphs * Charts * Labs Timeline On going Benchmark III.1 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * The format of graphic organizers * Inferences gained from data collection - patterns - sequences * Oral presentation skills, listening skills * Editing and revising Vocabulary observe label graph facilitator recorder compare contrast procedure data predict conclusion hypothesis edit revise diagram materials materials manager Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Organize observations through use of simple charts and tables * Develop conclusions based on interpretation of data * Share, listen and compare findings with others * Modify findings if necessary * Write observations, data, conclusions into lab reports Use of Knowledge * Compare * Classify * Experimental inquiry * Ivestigation * Invention * Problem solving * Inductive reasoning * Deductive reasoning * Constructing support Assessment * Teacher observation * Performance assessment * Teacher program assessment * Records * Graphs * Charts Timeline On going Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grades Pre-K – 4 Essential Question: How many? How much? How do you know? Benchmark Declarative Knowledge: Procedural Knowledge: To Know To Do I.1 * Understand appropriate * Select appropriate concepts of addition, operations and apply subtraction, mathematical skills multiplication and needed to solve problems division in the natural world and in science experiments/labs II.1 * The process of inductive * Develop conclusions and deductive reasoning based on simple logical reasoning III.1 * The correct use of scientific manipulative materials Vocabulary addition subtraction multiplication division tool thermometer scale ruler measurement * Select appropriate scientific tool to solve problems - thermometer - scale - ruler - microscope - balance scale - beaker - anemometer - meter stick Use of Knowledge * Compare * Abstract * Problem solving * Experimental inquiry * Inductive reasoning * Deductive reasoning * Constructing support * Abstracting * Invention * Experimental inquiry * Deductive reasoning * Compare Assessment * Teacher observation * Performance assessment * Teacher model or program assessment * Teacher observation * Science labs Timeline On going Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grades Pre-K – 4 Essential Question: How can matter be described? Benchmark PS III.1 PS III.2 Declarative Knowledge: To Know *Matter has properties * Objects can be sorted or classified according to their properties * Measurement can be made with standard and non-standard units * Matter can change Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Observe with eyes and magnifiers * Understand color hardness, weight and size * Match colors * Categorize hard/soft * Name colors * Sort by shape * Classify by color * Seriate height * Classify wet/dry, heavy/light * Sort objects by sink/float * Measure with standard and non-standard units * Use and observe rulers, thermometers balances, magnets and graduated cylinders * Participate in baking activities * Observe snow melting * Freeze water * Help make play dough * Dissolve Use of Knowledge * Observe * Classify * Compare * Induction Assessment * Teacher observation * Teacher observation Timeline Syracuse City School District Elementary Science Grades Pre-K – 4 Essential Question: What makes it work? How can I make it? Benchmark I.1-5 Declarative Knowledge: To Know * Attributes or features of given object that could be modified * Process of researching information * Process of prioritizing possible solutions * Process of design, construction, and model building Vocabulary attribute feature research design construct model solution efficient Procedural Knowledge: To Do * Identify objects and their features that could be improved upon making them more efficient; construct model * Research history behind the design of an object; write report * Brainstorm possible technical solutions, evaluate each and select best choice * Create age appropriate design, build and test model and revise if necessary Use of Knowledge * Decision making * Investigation * Experimental inquiry * Invention * Problem solving Assessment * Performance task * Reports/charts/ graphs/designs * Inventions Timeline On going