Regional Notes - Winston Knoll Collegiate
advertisement

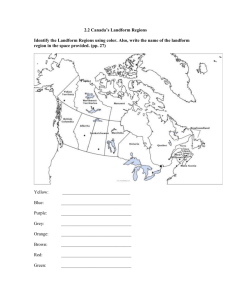
The Atlantic or Appalachian Highlands Region Water is truly plentiful in this region which includes the Gulf of St. Lawrence, as well, as the Canadian coastal waters of the Atlantic Ocean. Water always means tourism, as well, as transportation such as shipping industry, and hydroelectricity. The fishing industry has a rich heritage in the maritime provinces. Canadians have been fishing the Grand Banks since John Cabot's discovery in 1497. Cod, halibut, herring , flounder, mackerel, lobster, scallops, sole, crab, shrimp and mussels are just waiting for you to sample. Unfortunately, since we've been over-fishing these areas since 1497, we've run into some problems of endangered species. The cod fish were nearly wiped out. The Rocks of the Appalachian Highlands provide minerals for Canadians to mine. Iron, zinc, and gold are a few of the minerals utilized and mined in the Atlantic Region. The trees of this regions are important to tourism/recreation industry (hiking, camping) etc., as well as, they are used to produce pulp and paper. Most of the pulp eventually becomes our daily newspapers. Oil has been discovered under the ocean floor here. The Hibernia oil field has helped boost the sagging economy of Newfoundland and Labrador because many out of work fishermen can go and work on the floating oil derricks found out in the ocean. Great Lakes, St. Lawrence Lowlands Region This region has the best source of water in Canada because of the St. Lawrence River, Niagara Falls and the Great Lakes. Glaciers retreating, formed the lakes and rivers long ago. As the glaciers retreated, they dug huge holes that were filled by water. Manufacturing is the St. Lawrence, Great Lakes Lowlands biggest industry. Fifty percent of jobs in this region are related to manufacturing. Manufacturing plants are located in the golden horseshoe. Lots of things are produced here. People living within this region tend to build manufacturing plants close to the bodies of water, for hydro power (electricity); close to where the minerals are found; close to people for more workers; and on rock which can hold up buildings and heavy machinery. This region provides all of these necessities for successful manufacturing in Canada. Farming is another popular industry here. This region has the 2nd largest area in Canada used for farming because of it's rich soil, flat land and the climate is good (long growing season that is warm and humid). This is a very important region for growing crops in Canada. The St. Lawrence lowlands mine iron-ore, zinc, coal, silver, copper and lead. They retrieve the minerals by drilling into the rocks and using machinery. Many jobs are directly and indirectly linked to mining. Canadian Shield Region The Canadian Shield is the largest of Canada's 6 physical regions. It mainly is rock that was once mountains millions of years ago. Through the process of erosion, water, ice, glaciers from the Ice Age, and wind wore down this rock so that it became flatter. Over those millions of years, rivers, rapids, lakes and valleys have been carved out by the forces of nature. All these beautiful sources of water add to the tourism and recreation (camping) industry but at the same time it made it difficult to create a transportation system there. In the northern areas of the Shield bush planes are still commonly used to get around. When all of the erosion was finished, the rock was very close to the surface. As a matter of fact there isn’t a lot of depth to the soil. Trees like the fir, pine and spruce love it here but the shallowness of the soil wouldn't work for plants that have a deep root system. This is also an area where you couldn't survive very well as a farmer. Plains Region The Interior Plains landscape includes much more than just the prairie grasslands. You'll find that this entire region is generally flat in elevation. In fact there are 3 flat levels of elevation and each level is lower as you move to the east. If you can picture 3 steps on stairs that descend, then you sort of get what it looks like. Furthermore, found within these 3 levels of flat elevation, you may find hills, escarpments (cliffs), low mountains, forests, wide river valleys and there are even sand dunes! The Plains truly rely upon water, for the region's climate is generally dry. Water not only helps irrigate crops and livestock but it is also a source of transportation for our products, supplies, goods and services. In the past, these water routes were also major fur trading routes. These waterways also act as areas of recreation, tourism, as well, as resources like hydroelectricity for Canadians. It is important to discuss major industries found within this landscape, the first being farming. Both the crops and livestock produced in this area feed many Canadians, as well as, others around the world. Moreover, the agricultural industry is also linked with promoting the tourism industry. Many rodeos, stampedes and agricultural shows are held throughout this region for everyone to enjoy. Secondly the mining of fuel products like oil, natural gas, coal, potash copper, zinc, gold and uranium is crucial. Lastly many of the forest areas found in the Plains are harvested for the lumber industry or else admired by tourists for the tourism industry. The resources found in the Interior Plains are transported across Canada to other regions. Cordillera Region The climate of the Cordillera’s coast is mild, wet and rarely has snow that stays. The interior of the Cordillera is usually colder and dryer with larger amounts of snow. In the summer, it is warmer and there is less rain. The landscape of the Cordillera has long chains of high rugged mountains. This includes the Rocky Mountains and the Coastal Mountains. Parts of this region are covered with forests. The natural resources of the Cordillera are forestry (this is the biggest industry in the region), agriculture, mining (iron, lead, zinc, silver, copper and nickel) and fisheries (the west coast is famous for salmon). Most of the people in the Cordillera live in extreme south lowlands [Vancouver] and southern plateau due to the warmer climate. Northern Region Sometimes, when people think of Canada, they vision in their heads our northern region. In fact our northern region is the entire landscape of Canada, which is north of the 60 N parallel (latitude). This area is very unique compared to the rest of Canada. The unique tilt of our Earth's axis gives this region 6 months of constant sunlight and then 6 months of continual darkness. Because of the unique landscape and climate conditions (extremely cold in the winter months) this area of Canada has the lowest human population in Canada. As in the Interior Plains and the Cordillera the majority of the people will live where the land is level and /or where there is a water source nearby. As previously stated water is a source of food, communication, recreation as well as transportation. Hunting, trapping and fishing are also crucial to the Northern population as well as other Canadians. Since the Cordillera and the Canadian Shield are also 2 regions found in the North, remember these are rocks and we always mine our rocks to produce useful minerals as well as oil and gas which we use in our everyday life.