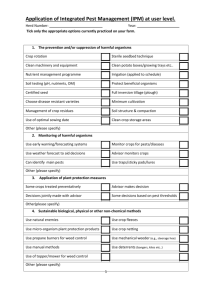
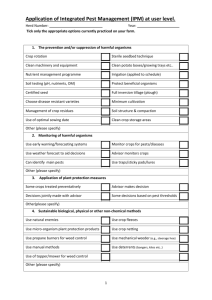
Select an integrated pest and disease management
advertisement

2810 version 4 Page 1 of 4 Select an integrated pest and disease management programme in production horticulture Level 5 Credits 7 Purpose This unit standard is for people working, or intending to work in horticulture. People credited with this unit standard are able to: identify life cycles of pests which affect a defined crop; identify diseases which are likely to affect the defined crop; assess a range of pest control measures; assess a range of disease control measures; and select a control programme for pests and diseases in a defined crop. Subfield Horticulture Domain Production Horticulture Status Registered Status date 25 July 2006 Date version published 25 July 2006 Planned review date 31 December 2011 Entry information Open, but it is recommended that before seeking credit for this unit standard learners gain knowledge and skills in pest, disease, and disorder identification. Accreditation Evaluation of documentation and visit by NZQA, industry and teaching professional in the same field from another provider. Standard setting body (SSB) Primary Industry Training Organisation Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP) reference 0032 This AMAP can be accessed at http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/framework/search/index.do. Special notes 1 Case studies may be used as the basis of this unit standard. 2 A defined crop may include any commercial horticulture crop from the following sectors: amenity, arboriculture, floriculture, fruit, landscape, nursery, vegetable, or viticulture. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 2810 version 4 Page 2 of 4 Elements and performance criteria Element 1 Identify life cycles of pests, which affect a defined crop. Performance criteria 1.1 Pests, which affect the defined crop, are identified, and the life cycle of each pest is described. Range minimum of five pests. 1.2 Signs and symptoms, which identify the presence and life cycle stage of each pest in a crop, are described. 1.3 Stages in the life cycle of each pest, where application of control measures are likely to be most effective, are defined. 1.4 Factors, which influence effectiveness of control measures, are identified. Range environmental conditions, stage of crop development, alternative host plants available to the pests. Element 2 Identify diseases, which are likely to affect the defined crop. Performance criteria 2.1 Diseases, which may occur, are identified, and the characteristics and life cycles are described. Range minimum of five diseases. 2.2 Signs and symptoms, which identify the presence and life cycle stage of each disease in a crop, are described. 2.3 Stages in the development of the disease, when control application is likely to be most effective, are identified. 2.4 Factors, which influence effectiveness of control measures, are identified. Range environmental conditions, stage of crop development. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 2810 version 4 Page 3 of 4 Element 3 Assess a range of pest control measures. Performance criteria 3.1 Biological pest control is explained and illustrated with five examples of ways in which common predators, parasites, and pathogens work. Range 3.2 Cultural pest control methods are explained, and the ways in which each controls pests are identified. Range 3.3 hygiene, crop rotation, soil water management, environmental modification, prevention of plant damage, use of resistant cultivars, use of quarantine. Characteristics of pesticides used to control production plant pests are identified. Range 3.4 may include but is not limited to – ladybirds, lacewing larvae, hover fly larvae, praying mantis, predatory mites. pest controlled, chemical group, formulation, toxicity, mode of action, resistance potential. Integrated pest control principles are identified and three proven methods are described as to their effectiveness in the horticulture industry. Element 4 Assess a range of disease control measures. Performance criteria 4.1 Cultural control methods are identified, and the ways in which each controls disease are described. Range 4.2 hygiene, crop rotation, soil water management, environmental modification, prevention of plant injury, use of resistant cultivars, use of quarantine. Principles of biological control of diseases are explained and two methods of control used in the commercial horticulture industry are described. Range may include but are not limited to – Agrobacterium radiobacter, Trichoderma viride. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 2810 version 4 Page 4 of 4 4.3 Characteristics of chemicals used to control plant diseases in production horticulture are identified. Range disease or disorder controlled, chemical group, formulation, toxicity, mode of action, resistance potential. Element 5 Select a control programme for pests and diseases in a defined crop. Performance criteria 5.1 Cultural and biological methods used for a specific crop are explained. 5.2 Chemical methods used for a specific crop are explained. Please note Providers must be accredited by the Qualifications Authority, or an inter-institutional body with delegated authority for quality assurance, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be accredited by the Qualifications Authority before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Accredited providers and Industry Training Organisations assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. Accreditation requirements and an outline of the moderation system that applies to this standard are outlined in the Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP). The AMAP also includes useful information about special requirements for organisations wishing to develop education and training programmes, such as minimum qualifications for tutors and assessors, and special resource requirements. Comments on this unit standard Please contact the Primary Industry Training Organisation via their website www.primaryito.ac.nz if you wish to suggest changes to the content of this unit standard. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016