notes
advertisement
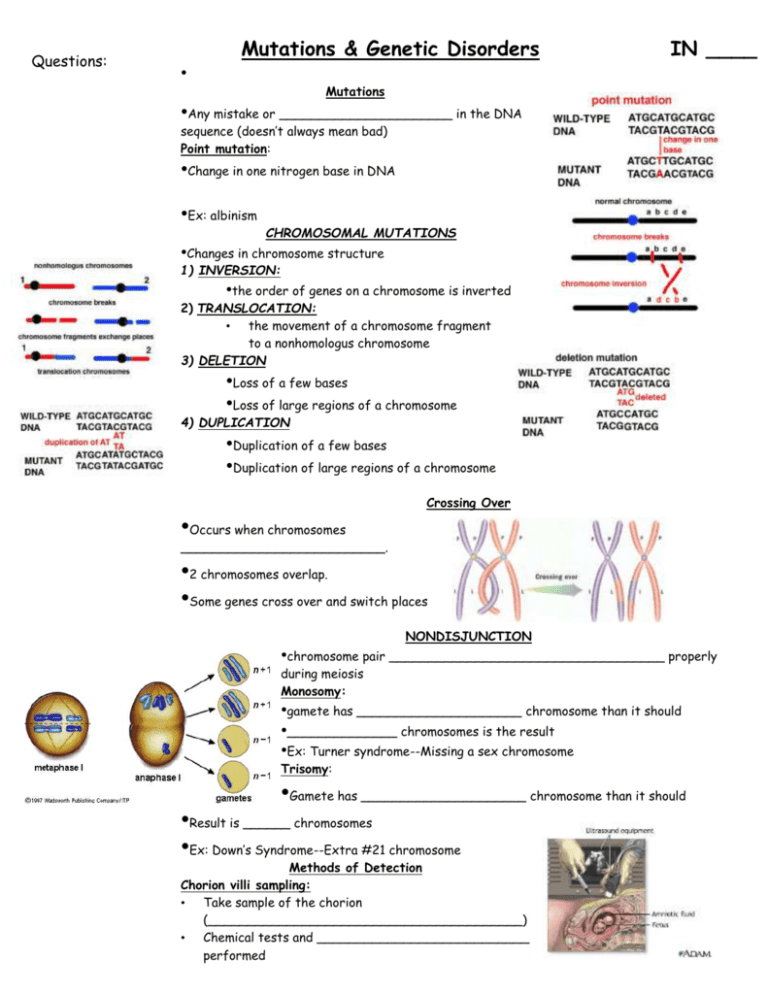
Questions: Mutations & Genetic Disorders • IN ____ Mutations •Any mistake or ______________________ in the DNA sequence (doesn’t always mean bad) Point mutation: •Change in one nitrogen base in DNA •Ex: albinism CHROMOSOMAL MUTATIONS •Changes in chromosome structure 1) INVERSION: •the order of genes on a chromosome is inverted 2) TRANSLOCATION: • the movement of a chromosome fragment to a nonhomologus chromosome 3) DELETION •Loss of a few bases •Loss of large regions of a chromosome 4) DUPLICATION •Duplication of a few bases •Duplication of large regions of a chromosome Crossing Over •Occurs when chromosomes __________________________. •2 chromosomes overlap. •Some genes cross over and switch places NONDISJUNCTION •chromosome pair ___________________________________ properly during meiosis Monosomy: •gamete has _____________________ chromosome than it should •______________ chromosomes is the result •Ex: Turner syndrome--Missing a sex chromosome Trisomy: •Gamete has _____________________ chromosome than it should •Result is ______ chromosomes •Ex: Down’s Syndrome--Extra #21 chromosome Methods of Detection Chorion villi sampling: • Take sample of the chorion (________________________________________) • Chemical tests and ___________________________ performed Logan Warren Ultrasound Questions: Ultrasound: •_____________________________ are used to generate an image of the unborn child. •Used to detect abnormalities of limbs, organs, etc. Amniocentesis: • __________________________surrounding the fetus is drawn out by needle • ___________________________________ are collected and grown in a lab. • Chromosomes can be then Karyotyped Autosomal Disorders Down’s Syndrome(Trisomy 21)/Patau’s Syndrome(Trisomy 13)/Edward’s Syndrome(Trisomy 18) Down’s Syndrome (DS) Excess ____________ chromosome Prenatal testing can be done Result of chromosomal mutation 1 in _______________ people born with this Likelihood of having a child with DS ________________ with advancing maternal age Symptoms: mental retardation, upward slant to eyes, small mouth, abnormal ear shape, decreased muscle tone _________________ Patau’s Syndrome & Edward’s Syndrome _________________ abnormalities Very severe conditions Most affected _________________ during first few weeks of life Deletion Disorders Angelman Syndrome/Prader-Willi Syndrome Angelman Syndrome Inappropriate laughter with convulsions ________________________________ Mental retardation Prader-Willi Syndrome Extremely floppy ___________________________ Mild mental retardation Sex Chromosome Disorders Klinefelter’s Syndrome/Turner’s Syndrome/Fragile X Syndrome Klinefelter’s Syndrome 47, ___________ 1 in 1000 ____________ live births Mild learning difficulties Taller than average with long lower limbs Show mild enlargement of breasts _______________________ (absence of sperm) Treat with testosterone Turner’s Syndrome 45, X Low incidence ________________________ Ovarian failure Normal intelligence Short stature Estrogen therapy Questions: Fragile X Syndrome Most common inherited cause of mental retardation 1 in _______________ males High forehead, prominent jaw, autism Gap in __________ chromosome Single Gene Disorders Cystic Fibrosis/Hemophilia/Sickle Cell Anemia/Phenylketonuria Cystic Fibrosis (CF) _______________________ disorder Mutation stops production of protein in lung cells, pancreas Thick _________________, bacterial infections in lung “sweat test” Most common in _____________________ (1 in 3300) Chest percussions, diet supplements _______________________ life expectancy Hemophilia ___________________ Failure of blood to clot _______________ in females Injections with clotting factors to stop bleeding episodes _____________________ a year in treatment Sickle Cell Anemia Mutation in _________________________ “sickle” shape to RBC Screening tests Most common in _______________________ Pain associated with blocked vessels, causes Summary: (1 in 375) ______________________ (fatigue) Common where mosquito-borne malaria is present PKU Mutation disrupts function of _________________ Leads to high phenylalanine levels in brain (poisons) Mental retardation, epilepsy Screening newborns (__________________) 1 in ___________________ Caucasian births Extremely ____________ in African-Americans Look normal Need low-protein diet, smelly formulas