Wind PPT Notes
advertisement

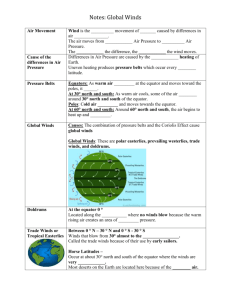
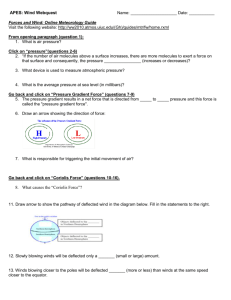
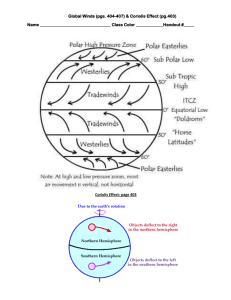
Name: _____________________________________ Period: ______________ Wind PPT Notes Wind occurs when the_______ of air over the Earth's surface is ______________ heated. Warm air __________, becoming lighter. When this happens, the air __________. As the warm air ________, cooler air rushes in to fill the __________ left by the rising warm air. This movement is called _____________________. Wind speed can be measured with an _________________________. At _________________ elevations, the air gets _______________ and there is less air pressure. This reduction in air pressure reduces _______________________ and wind speed increases. The rotation of the Earth also affects ________________. There are _______ major wind belts around the Earth (easterlies, westerlies, and trade winds in both the northern and southern hemispheres) that form by _______________. How Wind Forms Wind moves from an area of ___________ pressure to an area of ___________ pressure. Sunlight ___________ heats an area of the ground. The ground heats the air. The warm air rises, and an area of low ____________ forms. Sunlight heats an area of ground ________ strongly. The cooler, dense air ____________ slowly and an area of low pressure forms. Air moves as wind across the ______________, it moves from higher to lower pressure. Land and Sea Breezes • _____________________ heating of air over land and water results in breezes near shorelines. • While the land is warm during the day, air above it ________, and a cool breeze blows in from the ________. • As the land ______________ off at night, air pressure over it _________________, and a cool land breeze blows out to the sea. • Global Wind Belts • The ____________ wind travels varies. • Global winds travel _______________________ of kilometers in steady patterns. • Formed by two main factors: – unequal heating of the earth by ___________ – the earth's _______________. • The unequal heating makes the tropical regions ______________ than the Polar Regions. As a result, there is generally higher _____________ at the poles and lower at the equator. Wind flows from _____________ to ___________ pressure. • So the atmosphere tries to send the cold air toward the _____________ at the surface and send warm air ______________________ toward the pole at higher levels. • The spin of the earth _______________ this from being a direct route, and the flow in the atmosphere breaks into three zones between the equator and each pole. • A series of wind belts ________ Earth. Between the wind belts are calm areas where air is rising or _________________. Bands of calm air separate global wind belts • • The earth’s _________________ and the uneven heating of its surface cause a pattern of wind belts separated by ______________ regions. Calm Regions – Air ______________ stays calm; winds are __________________. – Doldrums – Horse _______________ Name: _____________________________________ Period: ______________ • Wind Belts – Curve to the east or west because of _______________________ Effect. – Coriolis Effect: if the earth did not _____________, the wind would flow directly from the poles to the equator. The earth’s rotation changes the _______________ of wind and they curve to the east or west. – Name after the direction from which they blow – Trade winds – Westerlies – Easterlies Coriolis Effect • As ________________ rotates, the Coriolis Effect turns winds in the Northern Hemisphere toward the _______________________. Wind Belts • • • • 6 total: 3 in the Northern Hemisphere (NH) & 3 in the Southern (SH). ____________________: Blow from the east moving from the horse latitudes toward the equator. The strong, steady winds die out as they come near the equator. ____________________: blow from the west, moving from the horse latitudes toward the equator. They bring storms across much of the US. Most of North America fits into this belt and that is why our weather usually comes from west. _____________________: which blow from the east, moving from the polar regions toward the middle latitudes. Stormy weather often occurs when the cold air of the easterlies meets the warmer air of the westerlies. Calm Regions • _____________________: Low-pressure zone near the equator. • – Warm air rises to the top of _____________________________ – Since much of the air movement is _________________, winds are light. – The air and then spreads out toward the __________________. – The rising, moist air produces clouds and ______________ _____________. – During the hottest months, heavy evaporation from warm ocean water in the region _______________ tropical storms. – Sailors noticed the stillness of the rising (and not blowing) air near the equator and gave the region the __________________________ name "doldrums." • _________________: High-pressure zones located about 30 ° north and 30 ° of the equator. – Warm air traveling away from the equator _________________ and ______________ in these regions. – Again, since much of the air movement is ________________, winds are light. – The weather tends to be clear and dry. 30 degrees from the equator, cool air sinks. – Tradition states that sailors gave the region of the subtropical high the name "horse latitudes" because ships relying on wind power stalled; fearful of running out of food and water, sailors threw their ________________ and ______________ overboard to save on provisions.