Using Inspiration (v6)
advertisement

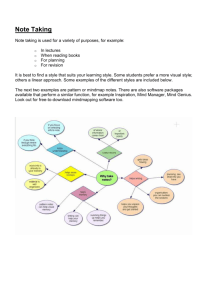
Using Inspiration (v7) Contents: Using Inspiration (v7) Uses of Diagrams Applications of Inspiration Starting and Stopping Inspiration Conventions used in this Userguide Help Diagram View Diagram Toolbar Adding and Customising Boxes Adding Symbols from the Symbols Palette Changing text Adding Notes in the diagram View Changing Arrows and Links Printing Diagrams/Outlines Advanced Features Using Inspiration (v7) Inspiration is a mind mapping program that helps with the planning and organising information. It has two main views or environments: Diagram view – To create a graphical organizer or a map showing how ideas or concepts interconnect. Outline view - Converts your diagram to a linear plan. This is useful for writing a report. As you work, both views keep track of your work. Uses of Diagrams You can create many types of visual diagrams. The kind of diagram you create in Inspiration depends on the idea you want to develop. A diagram that will be used to help structure an essay could be very different from a diagram used to help you remember ideas as part of the revision process. Below are two examples of the different types of diagrams you can easily build using Inspiration. 1 Example Mind Map (1) You may wish to use more visual aids for revision that help things stick in your mind (visual imagery). The example above was created to help a student learn about how substances can enter a cell. 2 Example Mind Map (2) Inspiration can help you plan and create quite complicated documents (essays, dissertation theses, and reports). The Add Note facility means that you can enter paragraphs of text for each key idea and build-up an entire essay that can then be copied into Word for final editing. The example above was created to help a student plan a 300 word essay on ‘the mind-body problem’ i.e. the question of whether the mind is separate from the body (drawing on Philosophy and Psychology theories). This plan would enable the student to build up a complex document piece by piece. It would also help them to remember what their ideas are and how the ideas relate to each other. 3 Applications of Inspiration o Essay and Project Planning from Scratch helping students to brainstorm their initial essay or project title, and build up model into paragraph and section headings. o Organising Existing Lecture Notes helping students revise what has been learned and check that there are no gaps. o Mental modeling helping students to understand difficult concepts, especially good for math/science concepts which may have been presented in a linear form initially. o Timeliness showing how ideas have developed over time, e.g. ‘what was the impact of Piaget or Montessori on the British education system?’ o Exam Revision students can devise content-free diagrams and use them to revise exam subjects, e.g. revising chemical or physical processes; impact of climate change on European tourism market. o Web Page Design students can construct a web page from an Inspiration brainstorm. o Diagrams for Presentations students can create flow diagrams or overview mind maps which can be copied and pasted into Word or PowerPoint for presentations. 4 Starting and Stopping Inspiration To start Inspiration: Click on Start ► All Programs ► Accessibility. Click Inspiration. You will see the Tip of the Day window. Click on Close to close the window and access Inspiration. To Stop Inspiration: On the Menu bar, click File ► Exit. Conventions used in this Userguide Inspiration offers many ways to do things, from toolbar buttons to menu commands or keyboard shortcuts. While all these options are readily available, this userguide usually shows one way to do the task. To see other ways to do each task, you can look at on line Help. Help To access the Help system while you are using Inspiration, choose Inspiration Help on the Help menu. 5 Diagram View This is a brief guide to some of the main features available in the Design view in Inspiration. Inspiration opens in Diagram view. You will see a white screen with a Diagram toolbar across the top, the Formatting toolbar at the bottom, and the Symbol palette on the left. The main idea in Inspiration is to use boxes, arrows and symbols to represent your ideas and the relationships or links between them. These can then be converted to a linear outline or plan. You would usually work in diagram view to create boxes then join them up. Entering the Main Idea or Topic When you open Inspiration, a symbol appears in the centre of the screen, with the placeholder text, Main Idea, selected. Just enter a topic to get started. 6 Diagram Toolbar RapidFire: Enter linked ideas quickly Outline: Go to Outline View Create: Add a new linked symbol in a particular direction Link: Create a link between two symbols Arrange: Arrange a diagram into selected layouts 7 Hyperlink: Create a hyperlink to another item such as a web page, a document, or an email address Note: Add or edit a note attached to a symbol Spell: Check the spelling in a document Listen: Listen to the computer read the information in your document Adding and customising boxes There are three main ways of adding new boxes or symbols to the diagram. By clicking the Create button, a cell can be produced from an existing symbol or box in the direction of the pointer. Select the box or symbol by clicking on it. On the Create button, click on the Pointer in the direction you want to create the new box or symbol. RapidFire is used to produce lots of cells from an existing idea (symbol or box). These are positioned around the original idea and can be picked up and moved. Select the box or symbol by clicking on it. Click the RapidFire button. Type your text and press Enter. As long as the RapidFire button is on, whenever you type text and press Enter a new box will appear. To turn the RapidFire tool off, click on the RapidFire button. Boxes can also be placed using the cursor key anywhere on the screen. First click with the mouse to position the cursor and then click on the type of symbol required. Different types of boxes or colours can be used to make cells stand out or to show that they are related. To change the shape of a box Select the box by clicking it. Click on the desired shape on the symbol palate. 8 To change the colour of a box Select the box by clicking it. Click on Effects on the Menu bar. Move to the Fill Color option. Pause slightly and a box of different colours will appear off the side of the main menu. Move the mouse pointer over the desired colour and click once. Note: The outline colour of the box and the text colour can be changed in the same way using the Line Colour and Text Colour options on the Effect menu. Changing the Colours Using the Format toolbar (bottom of screen): Select the box and click on the Fill Colour button to change the colour of the box, or the Line Color button to change the line colour. Line Color button Fill Color button To Change the Colour of a Multicolour Symbol Select the symbol by clicking on it. The colours in the symbol appear on the Formatting toolbar, after the Fill Color and Line Color buttons (see above diagram). Click on a colour and select a new colour from the palette. This new colour will replace the existing colour. 9 Adding Symbols from the Symbols Palette Symbols can be selected from the symbols palate to make a particular point or idea particularly distinctive. Some of the possible symbols are shown below. To select a symbol Click on the screen where you would like the new symbol to appear This may be an existing symbol or box. Select an appropriate palate displaying the desired symbol (either scroll through the palates using the left and right arrows, or select a palate from the list displayed by clicking the middle arrow). You will now see your symbol appear. 10 Changing Text Mind-maps can also be customised using different text. The following elements can be changed. Font (style) Size Colour Italics Bold e.g. Times, Courier, Bookman old style e.g. Small, Medium, Large or Extra Large e.g. Red, Blue, Green, Pink or any other e.g. This is where the words slant e.g. The letters are thicker and darker These options are found on the Format menu on the Menu toolbar. Different types of text can be used alongside different colour and shaped boxes to colour code ideas and groups of ideas. Coding makes things stand out and visually makes it easier to pick out different parts of the map. Colour and differentiation can also help make ideas more memorable so that they stick in the mind better. Adding Notes in the Diagram View The Add Note feature allows you to extend a mind map with extra information, while continuing to work in a visual format. This note is added into the outline and appears when the ‘map’ is looked at in outline view. Select a symbol by clicking on it. Click the Note button. A note opens below the symbol, and you can type your text. 11 Notes are very useful when writing essays or reports as they can be built up in steps e.g. Mind map the ideas. Note any references using Add Notes. Expand any definition of terms, explanations of ideas, or descriptions of theories using the Add Notes feature. Edit each Add Note box into full sentences and paragraphs to form the content of the essay/report. Check/change the order of the paragraphs using outline view. Copy and paste the whole essay/report into Word for final editing. Notes can also be added in Outline view In the Outline view, click at the point where the note is to be added. Click the Add Note button. Changing arrows and links This menu item allows you to connect two boxes together using an arrow. Linking Symbols Links show the connections and relationships between ideas. Select the symbol by clicking on it. This is the start of the link. Click the Link button to turn on the Link tool. The mouse cursor will turn into a double circle and arrow. Click the box or symbol you want as the end of the link. You can carry on linking symbols until you turn the Link tool off. To turn the Link too off, click on the Link button again. 12 Changing the Links format The way arrows look can be changed using the Link menu The type of arrow head at the start or end of the link can be changed. The arrow can be straight or curved. The direction it is pointing can also be reversed. Select the arrow to change by clicking on it. Click on Link on the Menu bar and select from the options displayed. There are two types of curved links o Curved link (3 pts) has one bend (like a ‘u’ or a ‘c’) o Curved link (4 pts) has two bends (like an ‘s’) One or two boxes will appear on the arrow selected. Click on these with the mouse and drag (holding down the mouse button) to see the arrow bend. Printing Diagrams/Outlines Diagrams or Outlines can be printed out from the File menu on the Menu toolbar. o To print a diagram you must be in the Diagram view i.e. looking at the diagram on the screen. o To print an outline you must be in the Outline view i.e. looking at the outline on the screen. A diagram may fit on the page better if the page is tuned lengthways (landscape). If you have changed the colour of the background, you may wish to return this to white before printing, especially if you are printing on to coloured paper. To view the map or the outline as it will look when it is printed, click on Print Preview under the File menu. When you are happy with the way that the diagram looks in the print preview, print it out by selecting Print from the File menu, followed by a click on the Okay button. 13 Advanced Features BACKGROUND COLOUR The colour of the background can be changed to make the screen easier to look at and the text easier to read. Click on Effects ► Background colour and pick colour. ZOOM The mountains in the bottom-left corner of the screen allow you to zoom in and out of your diagram. CHANGING THE ORDER IN OUTLINE VIEW The boxes from Diagram view are converted to main headings in Outline view in the order in which the boxes were created. This order can be changed by clicking on the number or letter next to the bold heading and dragging it up or down (keeping the mouse button pressed down). Moving the mouse from left to right changes main headings into sub-headings. The new position of the box is shown by a dotted outline. Release the mouse button to insert the heading into its new position. COPY INTO WORD The whole picture can be copied into another program like Word or PowerPoint. Chose Select All from the Edit menu and then Copy Open a blank document in Word or PowerPoint Select Paste or Paste Special from the Edit menu. GRID SNAP This is turned on or off using the Tools menu. When on, the boxes jump so that they are aligned with the grey grid squares displayed. 14