Origin of Life on Earth
advertisement

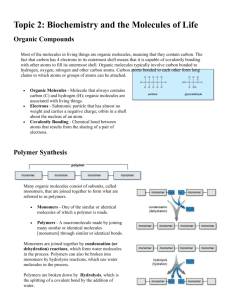
Nate Skeen Origin of Life on Earth Processes of spontaneous origin o abiotic synthesis and accumulation of small organic molecules or monomers o synthesis of polymers from monomers o aggregation of abiotically produced molecules into droplets, called protobionts, (jumble of organic molecules like RNA inside a membrane or membrane like structure) o self-replicating molecules o synthesis of organic molecules o water tends to depolymerize molecules (makes it difficult for molecules to become polymers) but is necessary for life), but is necessary for life o joining of these monomers into polymers o origin of heredity (may have been under way before ‘droplet’ stage Miller & Urey o Conducted experiment that simulated hypothetical conditions of Early Earth o Two flasks, one for the ocean and the other for the atmosphere, were connected into a loop with glass tubes o The ocean flask was placed above a heating source which would warm the liquid water to evaporation o Water vapor would then travel through the tubing system until it reached the second flask, simulating atmosphere. o The atmosphere flask contained water vapor, methane, ammonia, and carbon monoxide, as well as two electrodes that would spark to simulate lightning o The water vapor would then travel through a condenser and be reduced to liquid water, which would travel through a sampling probe and back into the ‘ocean’ flask to restart the cycle o After one week of continuous cycling, Miller and Urey reported that 10%15% of the carbon in the system was in the form of organic compounds like amino acids, sugars, lipids, and some building blocks for nucleotide bases Comets o Comets can carry organic compounds o Earth was bombarded with comets and asteroids 4 billion years ago o Impact could help polymerize amino acids into polypeptides Locations of synthesis o Space Scientists have created amino acids in low pressure and low temperature conditions o Alternating wet/dry conditions Seashores Drying clay particles could have catalyzed reactions to form organic molecules stromatolites o Near volcanoes Eruptions spit out water vapor, gases, and minerals which could form organic compounds Raw materials + heat could have provided conditions for amino acids and sugars o Deep oceans thermal vents release heated water that picks up minerals along the way Properties of RNA that could’ve allowed it to play a role in abiogenesis o RNA can self replicate o RNA can act as a catalyst (ribozyme), helping reactions Coacervates and Microspheres in origins of life o Coacervate A tiny spherical droplet of assorted organic molecules (specifically, lipid molecules) which is held together by hydrophobic forces from a surrounding liquid. o Microsphere Protein protocell (RNA) Polypeptides dissolved in hot water can form small spherical structures when dried and cooled Providing a membrane-enclosed volume which is similar to that of a cell Can grow and contain a double membrane which undergoes diffusion of materials and osmosis. Prokaryotic contribution to oxygen rich atmosphere o 3.5 bya bacteria developed the ability to photosynthesize o Helped convert iron dissolved in ocean water, into precipitates of iron oxide = rust-colored layers of rock o Waste production of photosynthesis is oxygen o Photosynthetic bacteria proliferated and produced more and more oxygen Endosymbiotic theory and eukaryotes o Eukaryotes came about as a result of symbiotic relationships between prokaryotes One engulfed by other i.e. chloroplasts and mitochondrion