Okazaki fragments
advertisement

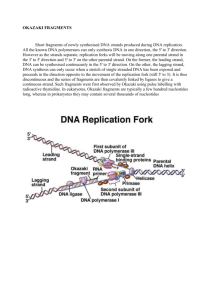
Okazaki fragments Short fragments of newly synthesised DNA strands produced during DNA replication. All the known DNA polymerases can only synthesis DNA in one direction, the 5' to 3' direction. However as the strands separate, replication forks will be moving along one parental strand in the 3' to 5' direction and 5' to 3' on the other parental strand. On the former, the leading strand, DNA can be synthesised continuously in the 5' to 3' direction. On the other, the lagging strand, DNA synthesis can only occur when a stretch of single stranded DNA has been exposed and proceeds in the direction opposite to the movement of the replication fork (still 5' to 3). It is thus discontinuous and the series of fragments are then covalently linked by ligases to give a continuous strand. Such fragments were first observed by Okazaki using pulse labelling with radioactive thymidine. In eukaryotes, Okazaki fragments are typically a few hundred nucleotides long, whereas in prokaryotes they may contain several thousands of nucleotides. Maturation of Okazaki Fragments (A) DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is released from the lagging strand when it collides into the previously synthesized downstream Okazaki fragment. Neighboring Okazaki fragments are thus separated by a nick. The RNA primer (red) portion of an Okazaki fragment is about 10 nucleotides long and the DNA (green) portion is 1,000 to 2,000 nucleotides long. (B) DNA polymerase I now binds to the nick and removes the RNA of the downstream Okazaki fragment by the 5'-to-3' exonuclease while simultaneously extending the DNA (brown) of the upstream Okazaki fragment. This is equivalent to the process of nick translation. The net result is that RNA primer (red) is replaced by DNA (brown). DNA polymerase I only synthesizes about 10 to 20 nucleotides before it falls off of the DNA. This is enough to do the job. (C) The remaining nick must be joined together with DNA ligase. E. coli DNA ligase uses NAD+ as the source of energy. The net result is that Okazaki fragments are joined together as longer, continuous DNA without any RNA sequences.