Circuit Symbols - Michigan State University
advertisement

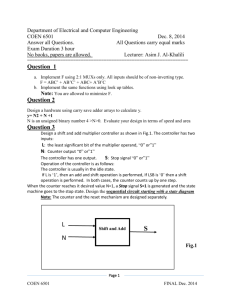
Constructing Circuit Schematics Using MS Word Prepared by: P. David Fisher and John A. Kelley Department of Electrical Engineering Michigan State University File: circut_symbols_3.doc Revised: 8/30/99 Overview Students and faculty often need to document electric, electronic, and digital-logic circuits by incorporating schematics into documents. To assist individuals in constructing circuits, we have consulted the appropriate IEEE standards for graphic symbols and then generated symbol sets that can be rapidly assembled to construct both simple and complex circuits. To construct circuit schematics using these symbols, one needs to know a little about how to copy, move, group, and rotate objects using MS Word. A good exercise for a beginner would be to copy the sample circuit given on page 7 of this report and paste this copy on the workspace provided on page 8. Select the object, ungroup it and then take apart the circuit. Once it has been taken apart, then re-assemble it in the workspace. Finally, group the individual elements (icons) to form a single object—i.e., the original circuit schematic. Finally, copy this object and paste it into a frame in a sample document. Once these skills have been acquired, the quality of the document will be enhanced significantly. It is recommended that circuit schematics drawn for one document be saved in a “circuit-template file.” By following this practice, one leverages writing projects off one another, and this saves time. This is so because future reports are much easier to generate since existing circuits can be reused. For example, search the template file for similar circuit architectures and components, and then cut and paste to obtain the new circuit. Please send comments and suggestions to P. David Fisher at fisher@egr.msu.edu. Table of Contents Circuit symbols and useful schematic icons ............................................................... Page 1 Discrete semiconductor devices .................................................................................. Page 2 Integrated semiconductor devices ............................................................................... Page 3 Logic gates .................................................................................................................. Page 4 Flip flops ..................................................................................................................... Page 5 Miscellaneous icons .................................................................................................... Page 6 Sample circuit ............................................................................................................. Page 7 Workspace to practice and create circuit schematics .................................................. Page 8 Circuit Symbols R, L, C & Switches Special Symbols Voltage and Current Sources Units V kV mV V A kA mA A k m H mH H nH F mF F nF v11 V11 i11 I11 Example: V11 = 2.23 mV Example: V11 = 2.23 mV Note: Set your snap to 0.05” for these icons 1 Discrete Semiconductor Devices PNP BJT NPN BJT N-channel JFET P-channel JFET N-channel insulated-gate, depletion-type, internallyterminated MOSFET N-channel insulated-gate, enhancement-type, four terminal MOSFET P-channel insulated-gate, depletion-type, four-terminal MOSFET P-channel insulated-gate, enhancement-type, fourterminal MOSFET PN Junction Diode Zaner Diode Photo-detector Diode Light-emitting Diode Note: Set your snap to 0.05” for these icons 2 Integrated Semiconductor Devices PNP BJT NPN BJT N-channel JFET P-channel JFET N-channel insulated-gate, depletion-type, internally terminated MOSFET N-channel insulated-gate, enhancement-type, fourterminal MOSFET P-channel insulated-gate, depletion-type, four-terminal MOSFET P-channel insulated-gate, enhancement-type, fourMOSFET PN Junction Diode Zaner Diode Photo-detector Diode Light-emitting Diode Note: Set your snap to 0.05” for these icons 3 Logic Gates Note: Set your snap to 0.05” for these icons 4 Flip Flops 1-LEVEL SR JK D T 0-LEVEL RISING FALLING S S S Clk S S S R R R R J J J J Clk Clk Clk S Clk Clk Clk K K K D D D D Clk Clk T Clk Clk Clk S 1S Clk 1R R S J S J Clk T Clk K R S D S D Clk S SR Flip Flop R Clk R R S T S T Clk Clk R Unclocked Clk K R Clk T FALLING/ ASYNCH S 1S Clk 1R R Clk K T RISING/ ASYNCH Clk R S R Note: Set your snap to 0.05” for these icons 5 Miscellaneous Load load 6 Coil unit Example Circuit For practice, you might want to try replacing circuit components with other components, or adding on to this circuit. Note: the individual icons have been grouped to form a simple “object”. The object has been grouped with an invisible “framing” rectangle that then allows you to move the object and wrap text with increased ease. The figure caption has been constructed using a “text frame”. t=0 R1 = 1.2 k R2 = 2.2 k VS = 4 V L1 = 3.8 mH C1 = 4.8 F Figure 1. A simple RLC circuit schematic demonstrating the application of the circuit symbols to construct a circuit. This figure caption also serves as a model. 7 8