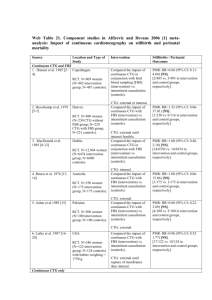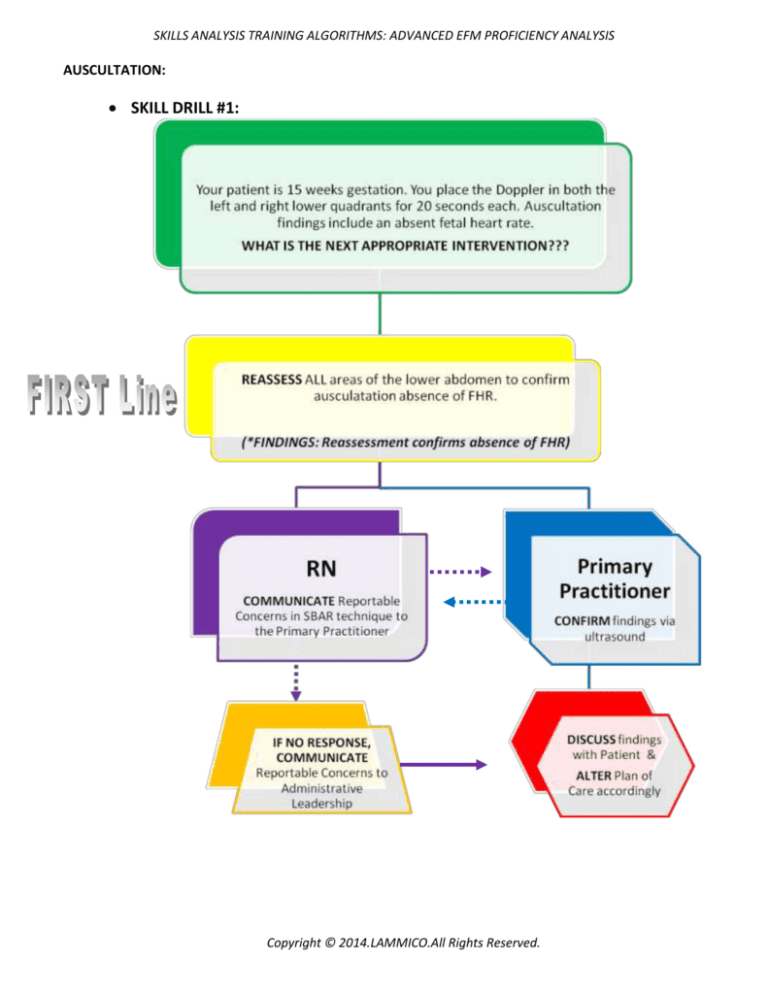
SKILLS ANALYSIS TRAINING ALGORITHMS: ADVANCED EFM PROFICIENCY ANALYSIS
AUSCULTATION:
SKILL DRILL #1:
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
AUSCULTATION:
SKILL DRILL #2:
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
AUSCULTATION:
SKILL DRILL #3:
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
ELECTRONIC FETAL MONITORING:
SKILL DRILL #1:
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
ELECTRONIC FETAL MONITORING:
SKILL DRILL #2:
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
ELECTRONIC FETAL MONITORING:
DRILL #3:
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
ELECTRONIC FETAL MONITORING:
DRILL #4:
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
References:
1. American Academy of Pediatrics and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
(2007).Guidelines for Perinatal Care, 6th ed.): Elk Grove Village, IL: Author.
2. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). (2009). Intrapartum fetal
heart rate monitoring: Nomenclature, interpretation, and general management principles
(Practice Bulletin #106). Washington DC: Author.
3. ACOG. (2006). Amnioinfusion does not prevent meconium aspiration syndrome (Committee
Opinion #346). Washington DC: ACOG
4. Association of Women’s Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses (AWHONN). (2008). Nursing
Care and Management of the Second Stage of Labor,(2nd ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
5. AWHONN. (2008). Fetal Heart Monitoring (Position Statement). Washington, DC: Author.
6. AWHONN. (2004). Amniotomy and Placement of Internal Fetal Spiral Electrode through
Intact Membranes (Clinical Position Statement). Washington, DC: Author.
7. AWHONN. (1998). Competence Validation for Perinatal Care Providers: Orientation,
Continuing Education, and Evaluation. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott.
8. Clark S, Simpson KR, Knox E, & Garite, T. (2009). Oxytocin: New perspective on an old
drug. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 200: 35e1-35e6.
9. Curran, C., & Torgersen, K. (2006). abcdEFM: The TEXTBook, Electronic Fetal Monitoring.
Virginia Beach, VA: Clinical Specialists Consulting, Inc.
10. Eslamian L, Marsoosi V, & Pakneeyat Y. (2006). Increased intravenous fluid intake and the
course of labor in nulliparous women. Int J Obstet Gynecol, 93:102-5.
11. Feinstein, N.F., Sprague, A. & Trepanier, M.J. (2008). Fetal Heart Rate Auscultation (2nd
ed.). Washington DC: Author.
12. Fraser WD, Hofmeyr J, Lede R, Faron G, Alexander S, Goffinet F, et al. (2005).
Amnioinfusion for the prevention of the meconium aspiration syndrome. Amnioinfusion Trial
Group. N Engl J Med; 353:909–17.
13. Freeman, R, Garite, T, & Nageotte, M. (2003). Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring (3rd Ed).
Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins.
14. Garite TJ, Weeks J, Peters-Phair K, Pattillo C, & Brewster WR. (2000). A randomized f
co;ntrolled trial of the effect of increased intravenous hydration on the course of labor in
nulliparous women. Am J Obstet Gynecol; 183:1544-8.
15. Lyndon, A., & Ali, L. U. (Eds.). (In press). Fetal Heart Monitoring: Principles and Practices
(4th Ed.). Dubuque, IA: Kendall Hunt Publishing.
16. Macones, G. A., Hankins, G. D., Spong, C. Y., Hauth, J., & Moore, T. (2008). The 2008
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Workshop Report on Electronic
Fetal Monitoring: Update on definitions, interpretation, and research guidelines. Obstet &
Gynecol ; 112(3):pp. 661-666.
17. Menihan, CA, & Zottoli, EK. (2007). Electronic Fetal Monitoring: Concepts and Applications
(2nd Ed). Philadelphia PA: Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins.
18. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) Research Planning
Workshop. (1997). Electronic fetal heart rate monitoring: Research guidelines for
interpretation. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 177(6):1385-1390, and J Obstet Gynecol Neonat Nurs,
26(6): 635-640.
19. Simpson, K.R. (2008). Cervical Ripening and Induction and Augmentation of Labor (3rd Ed.).
Washington, DC: AWHONN.
20. Simpson K, (2008). Intrauterine resuscitation during labor: Should maternal oxygen
administration be a first-line measure? Seminars in Fetal & Neonat Med, 13:362-367.
21. Simpson, K. (2007). Intrauterine resuscitation during labor: Review of current methods and
supportive evidence. J Midwifery Women’s Health, 52(3):229-237.