Photosynthesis Lab: Light & Starch Production
advertisement

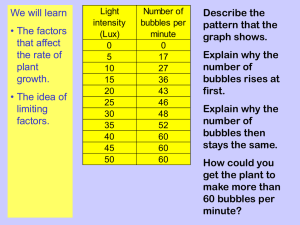
Light and Starch Production in Photosynthesis Background Photosynthesis is the process by which light energy is harvested by chlorophyll and used to convert inorganic raw materials - carbon dioxide and water to the products glucose and oxygen. Most photosynthesis takes places in the green parts of plants, in particular the leaves. . One of the products of photosynthesis is C6H12O6, or glucose. As the plant receives sunlight it is constantly producing glucose and then transporting it outside of the chloroplast. However, the plant cannot transport glucose out of the chloroplast as fast as it is produced. To solve this problem the plant combines the glucose molecules into a larger molecule called starch. The glucose molecule is a monosaccharide that through the process of dehydration synthesis can form a larger molecule called a polysaccharide. This polysaccharide, starch, is stored inside the chloroplast until it can be transported. Iodine is a specific stain for starch, producing a black color (actually a very dark blue) where starch is present. Safety: Students should wear eye protection when working with ethanol or iodine solution. Iodine solution is corrosive and care should be taken to prevent skin exposure. Ethanol is flammable and should never be used near an open flame. Take care with hot liquids. Be aware that plant sap may irritate the skin. Materials o hot plate o ethanol o beakers o tweezers or tongs o paper towels o o o o iodine solution petri dishes large leaf plant tape or paperclips and paper Procedure 1. Day 1: Using an opaque tape, cover a portion of the top of a leaf that will be exposed to sunlight. Alternatively, you can paperclip or otherwise attach a template with small cutouts to a leaf. Leave plant in a sunny area where photosynthesis may occur. 2. Day 2: Remove tape and/or paper from leaf. 3. Using forceps hold your leaf in boiling water for about 1 minute. This softens and kills the leaf. 4. Remove the leaf from the water (noting how it has changed) and place in test tube (pushing the leaf to the bottom. 5. Cover the leaf with ethanol and add to the beaker of hot water, or in the hot water bath. 6. Watch as the ethanol boils and the green coloring (chlorophyll) is removed from the leaf. This will take a few minutes. 7. When the leaf is white, remove the leaf from the alcohol and place it once again in the hot water for a few seconds. The leaf will be brittle when you take it out of the alcohol and the hot water softens it. Place the leaf in the petri disk over a sheet of white paper and cover with iodine. 8. Within a few minutes, record the presence of a blue/black color to indicate the presence of starch. Results Draw a picture of your leaf indicating the different shades you observe. Discussion Discuss the following questions with your lab partners and include in your analysis. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Why are certain parts of the leaf darker than others? Is there a relationship between the areas that received light and the areas of starch production? Think about what you have learned about photosynthesis to fully explain the relationship you observe. Explain two reasons that covering the underside of a leaf would not produce these same results. Which organic substance does iodine detect the presence of? What colors indicate a positive test? Plants don’t absorb all sunlight equally. Chlorophyll is a green pigment that absorbs light in the blue and red regions of the visible spectrum. Plants are green because they have a pigment (chlorophyll) that absorbs blue and red light and reflects green light. What do you think you would have observed about starch production if the leaf received only: a. Green light __________________________________________________________________ b. Red light___________________________________________________________________ c. Blue light__________________________________________________________________ Follow Up: Design Your Own Experiment In the lab, we demonstrated how light influences starch production in plants. What are some other factors that might influence starch production? Pick one factor. Hypothesize about how this factor might influence starch production. How might you test this hypothesis? Together with your lab group design an experiment to test your hypothesis. Turn in this sheet to your teacher when you have completed your experiment. Title: Hypothesis: Procedure: (Be sure to specify which plants are your variable and control plants) Results: What happened to the control plants? What happened to your variable plants? Discussion: Do your results support your hypothesis? Why or why not? In doing an experiment scientists often begin to think about other questions. After doing your experiment, write down two questions you thought about while carrying out your experiment: 1. 2. TEACHER NOTES Photosynthesis involves 2 stages - the Light-dependent Stage and the Light-independent stage. In the lightdependent stage, water is photolyzed by sunlight into Hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen enters the second stage, oxygen is gaseous by-product. In the light - independent stage enzymes are catalyzed the reduction of carbon dioxide by hydrogen. The carbohydrate, glucose is first formed. Glucose may be immediately used, translocated in the form of fructose or sucrose or stored as starch granules. Explain the significance of boiling the leaf in water. Boiling the leaf in water: o Removes the waxy cuticle which prevents entry of iodine/potassium iodide solution. o Ruptures cell membranes to make starch granules in cytoplasm and chloroplasts accessible to iodine/potassium iodide solutiion. Cell membranes are selectively permeable and do not readily allow the penetration of iodine. o Denatures enzymes, particularly those which convert starch to glucose e.g. diastase. Boiling arrests all chemical reactions, since enzymes which catalyse the reactions are denatured. Denatured enzymes have altered or destroyed active sites due to heat, pH, ionic concentration Account for the texture of the leaf after being boiled in water. The leaf was flaccid (soft) as cell membranes were ruptured and turgor pressure was lost. Explain the significance of boiling the leaf in ethanol. Chlorophyll is a green pigment and so masks the color change of the iodine test for starch. Chlorophyll needs to be removed from the leaf i.e. the leaf needs to be ' decolorized' for changes to be observed. A decolorized leaf is pale yellow or green. Ethanol is an organic solvent and so extracts chlorophyll from the leaf. Account for the texture of the leaf after being boiled in ethanol. The leaf was brittle as ethanol dehydrated (extracted water) from the leaf. Explain the significance of rinsing the leaf in water. The leaf was rinsed in water to rehydrate it. Iodine solution is an aqueous solution of iodine/potassium iodine - potassium tri-iodide; water is needed inside the leaf to enable penetration by diffusion. Which products of photosynthesis may be present but not revealed by the iodine test? Glucose, fructose and sucrose are all carbohydrate products of photosynthesis not revealed by the iodine test for starch. Do your results indicate that starch is the first product of photosynthesis? The results do not indicate whether starch is the initial, intermediate or final product of photosynthesis. How can this experiment be extended to demonstrate conclusively that photosynthesis has taken place? We do not know whether starch has accumulated in the leaf as a result of photosynthesis or whether the starch is permanently present in the leaf. To improve this experiment, the plant needs to be de-starched, and the leaves tested for the presence of starch. o Once it is demonstrated that all starch has been utilized or removed, photosynthesis is allowed to take place by exposing the plant to sunlight. o The leaves of the plant are now tested for the presence of starch. o If starch is present, then it has been synthesized by photosynthesis. We can then conclude that the presence of starch indicates that photosynthesis has taken place.