A CULTURAL COMPETENCE CURRICULUM MODEL
advertisement

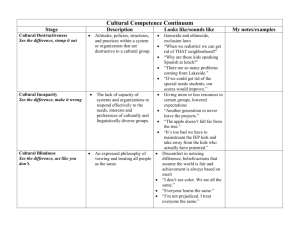
A CULTURAL COMPETENCE CURRICULUM MODEL Sheryl Ness, MA, RN Deborah Jefferson, MSN, RN Sandra Leinonen, MA, RN Kathy Ferguson, MS, RN Theresa Gannon, BSN, RN Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota This poster depicts a cultural competence curriculum model for nursing staff in a large medical center. In an environment of changing demographics and healthcare disparities, it is essential that nurses continue to develop competence in providing care across cultures. It is recognized that nurses are at different levels on their journey of becoming culturally competent. An extensive literature search supports that education can enhance the level of competence. The curriculum was designed to provide nursing staff with knowledge, skills, and tools to provide culturally and linguistically appropriate healthcare. We define cultural competence as the acquisition and integration of awareness, knowledge, and skills of cultural beliefs, values, and behaviors needed to provide individualized patient care. Expected outcomes include: Awareness of one’s own cultural background and nursing practice implications Recognition of the importance that culture plays in health promotion and treatment of illness Acquisition of skills to communicate with patients with diverse language and cultural backgrounds Knowledge and skills to complete a comprehensive cultural assessment Identification of resources to provide culturally and linguistically appropriate care The curriculum focuses on self awareness, culture general, and culture specific content. A variety of teaching strategies address the affective, cognitive, and psychomotor learning domains. The curriculum was implemented in 2007 with classes offered quarterly and content integrated into existing staff development. Outcome evaluation methodologies include: A pre and post assessment tool to determine the level of cultural competence A competency to demonstrate the effective use of an interpreter Cultural assessment chart audits Monitor use of the transcultural resources website Community-based focus groups assessing perceptions on the provision of culturally appropriate care This cultural competence curriculum model may be readily modified to address the learning needs in other healthcare institutions. This education initiative is supported by members of the Mayo Clinic Transcultural Patient Care Subcommittee - Education Workgroup. 1 Elements of the Cultural Competence Curriculum Student Characteristics or Intended Audience- Department of Nursing Staff at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, MN. Department of Nursing includes the role of primary RN, Nursing Education Specialists, Clinical Nurse Specialists, Nurse Researchers, Nursing Assistants and Unit Secretaries. Description of Program- The purposes of this program are to expand the participant’s a) definition of culture, b) knowledge and acquisition of skills to perform a cultural assessment, c) awareness of tools available to assist in providing culturally competent care to all patients, and d) use of the institution’s language department services in the provision of care. Overview of Program- Learning gained in this program will contribute to excellence and quality in nursing practice and patient care in all areas and departments. In this program, participants will explore the meaning of culture in a variety of contexts, including presentations, video and web-based modules, group discussions, simulation exercises, case presentations and dialogue regarding current clinical practice and institutional standards and resources. This program contains four core sessions (units of study) of one hour each. The entire program can be taken during the period of a year during staff development time or as a four hour block in a half-day session. It is recommended that nurses attend class module 1 first and then sequence in order of module numbers. The first module contains core elements of learning about culture and health care along with definitions that will be utilized in the other three courses. Program ObjectivesBy the end of this program, the learner will be able to do the following: 1. Define culture. 2. Identify techniques to overcome cultural barriers related to patient care. 2 3. Describe how to utilize the institution’s transcultural resources and language services. 4. Perform a cultural assessment as part of the patient plan of care. Syllabus Information Class Module 1 Title: What’s Culture Got to Do with It? Goal: To promote the understanding of cultural competence and demonstrate impact on quality of care. Summary: Culture is an essential part of who we are and shapes our beliefs, practices, and traditions. Participants will explore their own cultural heritage, issues related to health disparities, and implications for health care providers. Objectives: Identify how health beliefs are formed Recognize how assumptions may hinder development of a culturally based plan of care Identify one’s own culture Give examples of health disparities State three reasons why a health care provider needs to be culturally competent Teaching Strategies: A variety of teaching methodologies will be used in this class to address all learning domains (cognitive, affective and psychomotor). Role playing, lecture with discussion, as well as a short cultural simulation will be featured in this class. Evaluation: Participants will provide feedback after session is completed on general satisfaction. Class participation in role playing, simulation and group discussion will show evidence of 3 objective completion. A self-report survey three months after the class evaluates application of knowledge into practice. These questions are measured on a likert scale with opportunities to enter qualitative feedback as well. Class Module 2 Title: Use of Mayo Intranet Resources for Providing Culturally Competent Care. Goal: To promote awareness of the resources and tools available to nurses working with patients within the Mayo healthcare system. Summary: This class is an online interactive tutorial designed to focus on how to locate and use information on the Mayo internet related to providing care across cultures. Objectives: Participants will identify key location within the Mayo internet where transcultural resources are located Demonstrate appropriate use of transcultural resources related to the care of patients within the institution Teaching Strategies: This class is an online tutorial designed with interactive teaching strategies including case studies and examples of actual patient scenarios along with the use of Mayo resources. Evaluation: Participants provide feedback after session is completed on general satisfaction within the online tutorial. Quarterly monitoring of the use of the Mayo Transcultural Resources website is reported and measured. Class Module 3 Title: Effective Use of Medical Interpreter Goal: To provide information and knowledge on how to effectively utilize the medical interpreter services at Mayo. Summary: In order to provide culturally appropriate care, health care providers need to be able to communicate effectively across cultures. Discussions will include when to call 4 an interpreter and how to use interpreter when communicating with non-English speaking, limited English speaking, and deaf and hard of hearing patients. Objectives: Participant will identify key resources that assist accessing medical interpreter services Discuss rationale for appropriate use of medical interpreter services within the health care setting Teaching Strategies: This class is taught in the classroom and includes lecture with case studies and group discussion. It is taught in partnership with an actual medical interpreter who will provide case examples and be available for participant questions. Evaluation: Participants provide feedback after session is completed on general satisfaction within the class. Class participation in case studies and group discussion will show evidence of objective completion. Quarterly monitoring of the actual use of medical interpreters is be reported and measured. Class Module 4 Title: Cultural Assessment: Use of Storytelling Technique Goal: To promote the key elements for completing a cultural assessment as part of the initial patient assessment while accessing healthcare at Mayo. Summary: To address the needs of individual patients, nurses need to be able to complete a cultural assessment identifying the beliefs, values and practices specific to their culture. Elements of a cultural assessment will be reviewed along with the documentation process for the patient record. Objectives: Identify three key elements within a cultural assessment. 5 Discuss how individual beliefs and values can influence individual health practices. Teaching Strategies: This class is taught through storytelling technique. A video of a patient scenario is viewed with group discussion following. Key elements of the assessment process are outlined with actual time for input into the patient chart. Evaluation: Participants provide feedback after session is completed on general satisfaction within the class. Class participation in group discussion and assessment process will show evidence of objective completion. Quarterly monitoring of the completion of the components of the cultural assessment (percentage completed) is reported and measured for all inpatient units. Summary of Teaching Strategies The four class modules for this course are designed to provide and enhance learning in all domains, including cognitive, affective and psychomotor. An emphasis was placed on active learning methods through a variety of strategies. Cultural simulation- promotes active learning strategies. Role playing- integrates knowledge and critical thinking skills. Storytelling – integrates imagery with a patient situation to support assessment and practical experiences. Lecture with group discussion – teaches new knowledge along with opportunities to learn and share with others. 6 Reference List American Organization of Nurse Executives (September, 2005). Position Statement on Diversity. The Voice of Nursing Leadership, 10-12. Billings, D.M. & Halstead, J.A. (2005). Teaching in Nursing: A guide for faculty. (2nd ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier. Campinha-Bacote, J. (2007). The Process of Cultural Competence in the Delivery of Healthcare Services. Retrieved on November 1, 2007 from: http://www.transculturalcare.net/Cultural_Competence_Model.htm Cooper Brathwaite, A. (2006). Influence of nurse characteristics on the acquisition of cultural competence. International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship 3(1), 1-10. Retrieved on October 27, 2007 from http://www.bpress.com/ijnes/vol3/iss1/art3 Iwasiw, C., Goldenberg, D. & Andrusyszyn, M. A. (2005). Curriculum Development in Nursing Education. Sudbury, MA: Jones & Bartlett. Kirkpatrick, D.L. (1994). Evaluating Training Programs: The Four Levels. San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler. Leineinger, M. (1995). Transcultural Nursing: Concepts, Theories, Research and Practices. (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. Mayo Clinic (2007). Mission and Vision Statement. Retrieved November 22, 2007 from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/about/missionvalues.html National Center for Cultural Competence, (2005). Retrieved November 12, 2007 from: http://www11.georgetown.edu/research/gucchd/nccc/ Taylor, R. (2005). Addressing barriers to cultural competence. Journal for Nurses in Staff Development 12 (4) 135-142. 7