CHEM 1311A FINAL EXAM PART 1A November 30, 2001
advertisement
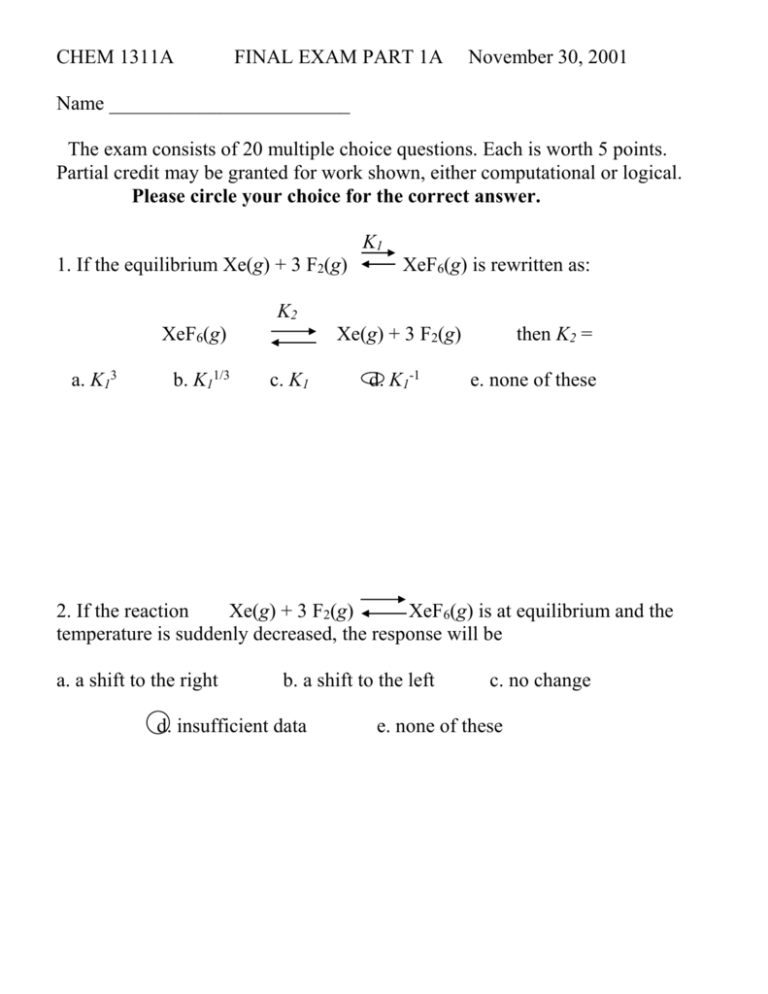
CHEM 1311A FINAL EXAM PART 1A November 30, 2001 Name ________________________ The exam consists of 20 multiple choice questions. Each is worth 5 points. Partial credit may be granted for work shown, either computational or logical. Please circle your choice for the correct answer. K1 1. If the equilibrium Xe(g) + 3 F2(g) XeF6(g) is rewritten as: K2 XeF6(g) a. K13 b. K11/3 Xe(g) + 3 F2(g) c. K1 d. K1-1 then K2 = e. none of these 2. If the reaction Xe(g) + 3 F2(g) XeF6(g) is at equilibrium and the temperature is suddenly decreased, the response will be a. a shift to the right b. a shift to the left d. insufficient data c. no change e. none of these 3. The reaction HCOOH(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + HCOO-(aq) has Ka = 1.8 x 10-4 @ 25oC. Using the following concentrations, calculate the reaction quotient and chose the direction the reaction will proceed. [HCOOH] = 0.10 molar [HCOO-] = 2 x 10-4 molar [H3O+] = 1 x 10-4 molar a. 1.6 x 10-3, left b. 2.0 x 10-7, left c. 2.0 x 10-7, right d. 1.6 x 10-3, right e. none of these 4. A buffer solution is prepared using H2S and HS- (Ka = 9.1 x 10-8). It has [H2S] = 0.15 M and [HS-] = 0.10 M . The resulting pH will be a. 6.86 b. 7.14 c. 8.96 d. 6.94 e. none of these 5. The [H3O+] of a solution prepared by mixing 500 mL of 0.10 M HBr with 450 mL of 0.10 M KOH is a. 5.26 x 10-7 b. 2.75 x 10-3 c. 2.35 x 10-2 e. none of these d. 5.26 x 10-3 6. Ka for NH4+ = 5.6 x 10-10; Kb for NH3 = a. 1.9 x 109 b. 1.8 x 10-5 c. 1.8 x 105 d. 3.6 x 10-5 e. none of these 7. 50 mL of 0.75 M hydrazoic acid (HN3; Ka = 1.9 x 10-5) is titrated with 0.10 M NaOH solution. The amount of NaOH solution needed to neutralize all HN3 is a. 25.0 ml b. 37.5 ml c. 50.2 ml d. 55.5 ml e. none of these 8. For the following reaction, if the volume of the reaction vessel is increased 3 NO(g) N2O(g) + NO2(g) Which statement is true? a. b. c. d. reaction shifts right yield decreases reaction shifts left yield increases definite problem with answers here; reaction should shift left and yield should decrease; b, c, and written explanation accepted e. both a and b f. both a and d 9. The ion, HCO3- is a. part of a Brønsted-Lowrey pair c. basic in some situations b. amphoteric d. acidic in some situations e. all of these 10. At equilibrium, the partial pressures for the following reaction are 3 Al2Cl6(g) 2 Al3Cl9 PAl2Cl6 = 1.00 atm and PAl3Cl9 = 1.02 x 10-2atm; the equilibrium constant is a. 1.52 x 10-3 b. 1.04 x 10-4 c. 1.03 x 10-3 d. not enough data e. none of these 11. Ka = 6.5 x 10-5 for benzoic acid . A 0.80 molar aqueous solution will have a pH of a. 2.1 b. 4.2 c. 7.6 d. 6.5 e. none of these 12. Baking soda undergoes the following equilibrium when heated: 2 NaHCO3(s) Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(g) The equilibrium expression is: a. [NaHCO3]/[Na2CO3]PCO2PH2O c. [Na2CO3]PCO2PH2O/[NaHCO3] b. PCO2PH2O d. 1/PCO2PH2O e. none of these 13. An aqueous solution of 0.10 M K2SO4 will a. b. c. d. e. have a pH less than 7 due to the formation of HSO4-. have a pH of 7 since K2SO4 does not hydrolyze in water. have a pH greater than 7 due to the formation of KOH. have a pH less than 7 due to an increase in [H3O+]. None of these Written answer showing formation of OH- and c accepted 14. A buffer has 0.08 moles of weak acid (Ka = 1 x 10-4) and 0.08 moles of conjugate base. When strong acid is added to the solution a. b. c. d. e. The strong acid will react with the conjugate base to give weak acid. The strong acid will not react, but will dilute the solution and reduce the pH. The strong acid will neutralize the weak acid. Both b and c. None of these 15. For the reaction SO2Cl2(g) SO2(g) + Cl2(g) K = 2.4 at 100oC. At equilibrium at 100oC the partial pressures of SO2 and Cl2 are both 0.58 atm. The partial pressure of SO2Cl2 is ___ atm. a. 0.28 b. 1.4 x 10-4 c. 3.6 x 10-3 d. 0.14 e. none of these 16. For sulfuric acid, H2SO4, Ka1 = 1 x 102. This makes sulfuric acid a. a strong acid with Ka2 > 1 x 102 b. a weak acid with Ka2 < 1 x 102 c. a weak acid with Ka2 > 1 x 102 d. a strong acid with Ka2 < 1 x 102 e. none of these 17. This tt this curve represents a titration of a a. b. c. d. e. volume of titrant (ml) A. weak acid with a strong base. B. weak base with a strong acid. C. strong acid with a strong base. D. strong base with a strong acid. E. strong base with a salt. 18. At the equivalence point in the titration curve of question 17, the amount of titrant used is a. 50 ml b. 25 ml c. 30 ml d. 15 ml e. none of these 19. When equilibrium is described as dynamic, it means that a. b. c. d. e. the concentrations of the products are changing. the concentrations of the reactants are changing. The ratios of products and reactants are changing. Forward and reverse reactions continue to occur. Both a and b. 20. If a reaction in a sealed vessel is at equilibrium and the pressure is suddenly increased, a. b. c. d. e. the equilibrium constant increases. the equilibrium constant decreases. the reaction quotient increases. The reaction quotient decreases. Insufficient data.