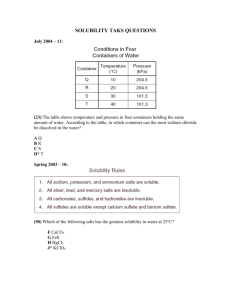
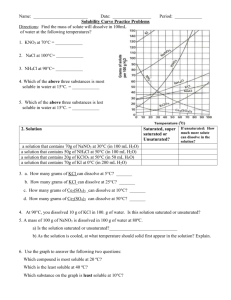
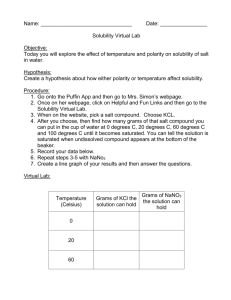
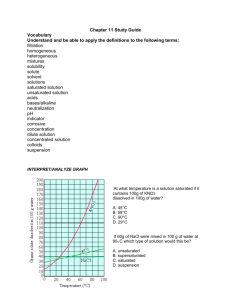
Data table #1: Group mass, volume, solubility
advertisement

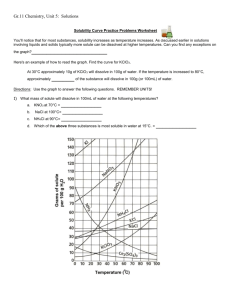
Name___________________________ Lab Station________ Lab Activity: Preparing Saturated Solutions & Measuring Solubility Objective: You will prepare a saturated solution of two substances and measure the solubility (concentration of the solute when it is saturated). Substances: Copper Sulfate (CuSO4) and one other assigned substance Directions: Day #1: Prepare Saturated Solution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Measure & record the mass of an empty evaporation dish. Put 10.0 mL of water in a test tube. Add 1 scoop of copper sulfate. Shake the test tube until all of the solid has dissolved. If all is dissolved, proceed to step # 7. Add another scoop of copper sulfate, and shake until it has all dissolved. If all is dissolved, proceed to step # 7. Continue to add scoops and shake until you have prepared a solution that is beyond saturated. It is beyond saturated when you can see solid particles on the bottom. Record the number of scoops in your lab notebook. The liquid portion of your solution is saturated. Decant (pour out the liquid portion) into a graduated solution and record the volume. Pour the solution into an evaporation dish, label and let sit out for the night. Repeat this procedure with the other assigned substance. Day #2: Measuring and Calculate Solubility. 1. If all the liquid has evaporated, measure the mass of the evaporation dish and the dry solid. 2. If there is still some liquid left, gently heat the solution until all of the liquid has evaporated. 3. Calculate the mass of the dry solid and calculate solubility. Data table #1: Group Data - mass & volume Substance Mass empty evaporation dish Volume of Solution Mass dish & dry solid Data table #2: Concentration & Solubility Substance Mass Dissolved Solid Volume Solution Concentration (m / v) Solubility (m / v) x 100 Measurements & Calculations: 1. Measure the volume of saturated solution in a graduated cylinder. 2. Calculate the mass of the dissolved solid: mass of crucible with dry solid – mass of empty crucible. 3. Calculate the concentration: divide the mass of the solid dissolved by the volume of the water boiled away 4. Calculated the solubility. Multiply the concentration of the saturated solution by 100. In other words, if you had used 100 mL of water, what would be the maximum amount of this solid you could have dissolved? Data table #3: Class data comparing solubility Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Group #1 Group #2 Group #3 Group #4 Group #5 Sodium Nitrate (NaNO3) Glucose (C6H12O6)