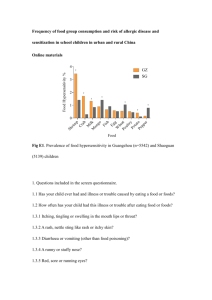
Sex Linked Traits Lab
advertisement

Names_____________________________ Sex-linked traits: The gene for a sex-linked trait can be located either on the X or Y chromosome and contains many more genes; most sex-linked traits are on the X chromosome. Females carry two X chromosomes while males carry the X and Y chromosomes. The Y chromosome carries a gene that shifts fetal development into a male. Red-green colorblindness is inherited as a sex-linked recessive trait. This experiment will demonstrate the effects and probability of sex-linked traits. We will use beans to represent the chromosomes. Red beans represent the dominant ability to see red-green color (normal vision), white beans represent the X chromosome with the recessive gene for colorblindness (b), and black beans represent the Y chromosome that does not carry the gene. Materials: 5 containers (labeled A-E) red beans, white beans and black beans Maternal A. Mix 20 red beans and 20 white beans for maternal genotype. XXb What is the phenotype for this mom? ___ ___________________ B. Have a container with 10 red beans for maternal genotype XX What is the phenotype for this mom? ______________________ C. Have a container with 10 white beans for maternal genotype XbXb What is the phenotype for this mom? ___ __________________ Paternal D. Mix 20 red beans and 20 black beans for paternal genotype XY What is the phenotype for this dad? ______________________ E. Mix 20 white beans and 20 black beans for paternal genotype XbY What is the phenotype for this dad? ____________ __________ Now, you will simulate Punnett Squares and determine the genotype and phenotype. Procedure 1. Without looking, pull one bean from A and one bean from D. Write down the result (XBXB, XBXb, XBY, XbY) AND record the sex of the offspring and the phenotype in the table below. Place the beans back into the bag from which you selected. 2. Repeat the above step until you have made 20 trials. Record your results and get percentage of each genotype occurrence. (Example: 5 normal females out of 20 total offspring = 25%) 3. Do the same thing for each possible mix. Ultimately you will mix all of the maternal with the paternal gene pool. These are the gene pool combination you should have: AD, AE, BD, BE, CD, and CE. Names_____________________________ Data Table Gene XX Phenotype NORMAL Sex FEMALE AD #s AD % AE #s AE % BD #s BD % BE #s BE % CD #s CD % CE #s CE % XXb NORMAL (carrier for colorblindness) FEMALE XbXb XY XbY Names_____________________________ Questions: 1. What is the probability of a female child inheriting colorblind genes from parents A and D based on your data? 2. What is the probability of a male child inheriting colorblind genes from parents C and D based on your data? 3. What is the probability of a female child inheriting colorblind genes from parents A and E based on your data? 4. What is the probability of a male child inheriting colorblind genes from parents B and E based on your data? 5. Do the probabilities you calculated match those from a Punnett Square? Why or why not? 6. Could a female child inherit colorblindness from parents who were not colorblind? Could a male child? 7. Check your data table and results with one other group. How did their probabilities compare to yours? 8. What are some of the reasons why the probabilities were different (or the same) among groups.