Lymphatic System – Lecture 4
advertisement

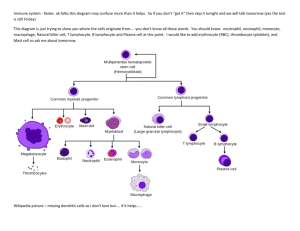
1 Objective for the Lymphatic System 1. Describe the function of the lymph system 2. Review the terminology of the lymph system 3. List the agents of infectious diseases and their process 4. Discuss the lymphatic vascular structure and flow 5. Compare the T-cells, B-cells, and Natural Killer Cells 6. Describe the structure of antibody molecules and their function 7. Explain the function and structure of the lymphoid organs 8. Discuss the hormones involved in lymphatic system 9. Compare humoral (antibody) and cell-mediated immunity 10. Compare active and passive immunity 11. Explain the phases of the acute inflammatory response 12. Describe the mediators in the inflammatory response 13. Discuss fever, it’s origin, benefits & complications 14. Discuss the allergic & autoimmune responses 15. Review the emerging infectious diseases 16. Discuss the immune system in regards to age 2 Lymphatic System – Lecture 5 I. Lymphatic System A. Make-up 1. Lymphocytes = major cells a. Responders to bacteria, viruses, abnormal cells, toxins 2. Vessels – lymphatic vessels connect to vascular system vena cava 3. Fluid a. Plasma like 4. Organs (lymph nodes, spleen, thymus) B. Function 1. Production, maintenance, distribution of lymphocytes a. Storage b. Organ production 2. Return of fluid & solutes from peripheral to blood a. 3.6 liters/day volume 3. Move hormones, nutrients, wastes from tissue to venous C. Terminology 1. Host – organism capable supporting nutritional & growth needs of Another 2. Infection – presence of multiplication of organism within host 3. Natural flora – harmless, natural bacteria present in humans 4. Virulence – disease producing potential 5. Pathogen – microorganisms rarely found without presence of a disease 6. Opportunistic pathogen – normal flora produces disease when host immunity is weakened 7. Antigen (immunogen)- foreign substance can stimulate immune response a. Receptor recognition 8. Antibody (immunoglobulin)- protein that recognize foreign antigen 9. Phagocyte 10. Antigen Presenting cells 11. Natural Killer cells 3 D. Agents of Infectious Disease 1. Prions – protein normally in neurons that becomes resistant to the enzyme that breaks polypeptide chain & produces neuronal damage a. Slow progression, non-inflammatory neuronal degeneration b. Acquired by transplantation, injection, contaminated devices, food c. Not responsive to antibacterial/antiviral agents, heat, radiation, disinfectants 2. Viruses a. No organized cell structures b. Protein coat surrounding acid core & RNA or DNA not both c. Incapable of duplicating outside living cells d. Use the cell for reproduction 3. Bacteria a. Autonomously replicating unicellular organisms b. Unorganized nucleus with DNA & RNA c. Cytoplasmic membrane – flexible lipid membrane d. Membrane enclosed in rigid cell wall e. Can be mobile – flagella f. Pili – hair like structures for attachments g. Reproduce by cellular division asexually h. Growth rates vary i. Exist as colonies usually 4. Rickettsiae – host dependent, passed to human by insect bites 5. Chlamydiae – transmitted without a vector 6. Fungi – (yeast & mold) – free living a. Asexual or sexual reproduction b. Yeast = waxy or creamy c. Molds = cottony or powdery d. Must grow at human temperature 7. Parasites – benefit from biologic relationship with another organism a. Wormlike (roundworms, tapeworms) – helminthes – eggs b. Vectors – ticks, mosquitoes c. Ectoparasite – mites, chiggers, lice, fleas 4 C. Mechanisms of Infection – portal of entry 1. Penetration 2. Direct Contact 3. Ingestion 4. Inhalation D. Lymphatic Vessels – carry lymph from peripheral tissue to venous in all parts body except nervous system 1. Lymphatics – carry lymph 2. Lymphatic capillaries – permits fluid flow in but not backward a. Smallest vessels b. Blind pockets 3. Flow pattern a. Interstitial tissue to lymphatic capillaries to larger lymph vessels towards trunk – similar to venous b. Thoracic duct – collects lymph abdomen, pelvis, lower limbs, left half head, neck, chest 1) Located c. Right lymphatic duct – right side body drainage above diaphragm d. Final empty into circulation at subclavian & internal jugular 1) Blockage leads to lymphedema 4. Structure (like veins) a. Valves b. Low pressure c. Travel with arteriole or venule d. Single layer at terminal ends – like capillaries e. Lack tight junctions ( permit entry large substances) f. Layer structure 1) Intima – elastic tissue & endothelial layer 2) Medial – smooth muscle in larger vessels 3) Adventitial – endothelial layer g. Fluid movement 1) External compression 2) Vascular pulsations 3) Active & passive body movements 4) Fluid movement 120 ml/hour & influenced by Interstitial fluid pressure & lymph pumps 5) Edema – excess interstitial fluid in tissue 5 E. Lymphocytes (bone marrow & thymus ) – visitors & migrators 1. Types a. T-cells (thymus-dependent) – cell mediated immunity (80%) 1) Activated in viral infections, foreign tissue grafts, Delayed hypersensitivity 2) Regulates self-recognition – recognize antigen bound to receptors a) Macrophages – monokines secreted (1) Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) b) T-cells recognize c) Cluster of differentiation (CD) 3) Amplifies response B & T lymphocytes 4) Formation – bone marrow stem cells 5) Maturation – thymus a) Genes rearranged for expression T-cell antigen 6) Helper T Cells (CD4+) – master regulator a) Recognition of antigen activates b) Secrete cytokines c) Cytokine regulates B cells, cytotoxic T, & natural killer, macrophages (cell-mediated & antibody mediated) (1) Interleukins – chemical messenger (a) Increase B & T cells (b) Produce fever, pain , rash, arthritis 7) T Cytotoxic Cells (CD8+) – activated by viruses or Cancer a) Destroy by releasing cytolytic enzymes, toxic cytokines, pore forming molecules b) Destroy by membrane molecules or apoptosis 6 8) Memory T cells – reserve a) Second exposure differentiate into cytotoxic T quicker 9) Suppressor T cells – depresses action B & T a) Suppression factors b) Limit degree of response b. Natural Killer Cells (tumor, viruses, intracellular microbes) (5-10%) 1) Do not need to recognize specific antigen to activate 2) Kill automatically 3) Inhibited by cell membrane contact with self Molecules 4) Pore forming proteins, enzymes, toxic cytokines 5) Enhanced response with Interleukin 2 6) Immune surveillance for cancer & viruses c. B-cells (humoral immunity) – bacterial, neutralize toxins, prevent viral, allergic responses (10-15%) 1) Membrane immunoglobulin antigen receptor, class II MHC proteins, complement receptors, CD Molecules 2) B cells mature in bone marrow (precursor B) 3) Unique membrane receptor & effector antibody (antibiotic independent) 4) Migrates from bone marrow to lymph tissue 5) Activated by antigen complementary to surface immunoglobulin receptor a) Antigen – chemical targets (1) Pathogen, foreign compounds, parts of pathogens b) Antigen binding sites – variable segments 6) T-cell help undergoes transformation for B cells to secrete antibody plasma cells (immunoglobulins) 7) Immunoglobulins – antibody class of protein a) IgG (gamma globulin) – most abundant (1) Crosses placenta (2) Protects bacteria, toxins, viruses 7 b) IgA – saliva, tear, colostrums, bronchial, GI, prostatic, vaginal secretions (1) Local infections mucosal tissue (2) Prevents attachment viruses & bacterial epithelial cells c) IgM – first responder to antigen d) IgD – cell membrane of B lymphocyte (1) Initiates differentiation of B cells e) IgE – inflammatory, allergic responses (1) Binds to mast & basophils (2) Binding releases histamine 8) Antibody Function a) Neutralization b) Agglutination c) Activation of complement d) Attraction of phagocytes e) Enhancement of phagocytosis f) Stimulation of inflammation 9) Antibody Structure a) Parallel pair of polypeptide (heavy & light) (1) Constant – same as every other antibody in that type b) Antigen Binding Sites – variable segments (1) Give is specific shape (2) Account for different antibodies c) Antigen-antibody complex – binding of antigen/antibody d. Normal flora e. Tumor necrosis factors (TNF) 1) Slow tumor growth & kill tumor cells 2) Stimulate Neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil 8 3) Promote eosinophil activity 4) Cause fever f. Phagocytic regulators – cytokine 1) Specific & nonspecific response 2) Attract macrophages & microphages g. Colony-stimulating factors (CSF) 1) Activate T cells, monocyte-macrophage, fibroblasts 2) Stimulate RBC production in bone marrow 3) Stimulate lymphocyte production lymph organs 2. Origin & Circulation a. Lymphocytes are visitors b. Wander through c. Long life spans up to 20 years d. Divisions of stem cells in bone marrow & lymph tissue e. Bone marrow & thymus = production 1) Hemocytoblasts – bone marrow a) Bone marrow – NK & B cells b) Thymus – Thymosin - hormone F. Lymphoid Organs 1. Lymph nodes – small oval lymphoid organ covered by fibrous capsule a. Filters & purifies lymph prior to release in venous system b. Antigen detection stimulates B & T cell responses c. Protect vital organs d. Flow 1) Afferent channel entry 2) Lymphocytes & macrophages flow slowly through 3) 99% destruction prior to leaving 4) Efferent channel exit 2. Spleen – upper abdominal cavity left side – largest lymph tissue a. Filter for blood and systemic infection response b. Composition 1) Red pulp – arterial supplied, RBC breakdown 9 2) White pulp – B & T lymphocytes with macrophages & dendritic cells c. Function 1) Remove abnormal cells 2) Initiate immune response 3) Store iron reserves 3. Thymus – behind sternum and decreases in size a. T-cell mature b. T-cells migrate to medulla c. Hormone thymosin 4. Secondary Lymphoid Tissues a. Membrane entry lined with mucosa lymphoid tissue b. Line respiratory, digestive, urogenital tracts 1) Peyer patches – intestinal c. Tonsils (5) – pharyngeal or adenoids, palatine, lingual 1) Pathogen not destroyed embed in nodule - infection G. Hormones 1. Interleukins – cytokine (chemical messengers) – 23 types a. Increase T & B cell sensitivity differentiation b. Enhance inflammatory defenses like fever c. Stimulate blood cell production d. Stimulate NK cells e. Types 1) IL-1 2) IL-2 3) IL-3 4) IL-4 5) IL-5 6) IL-6 7) IL-7 8) IL-8 9) IL-9 10) IL-10 11) IL-11 12) IL-12 13) IL-13 14) IL-17 15) IL-18 16) IL-23 10 2. Interferons – a. Prevent viral entry & replication b. Stimulate NK cells & macrophages c. Alpha d. RNA viral infection 3. Tumor necrosis factors (TNF) a. Kill tumor cells b. Stimulate T cells, eosinophil, inhibit parasites & viruses c. Actions 1) Stimulate release corticotrophin releasing 2) Suppresses appetite 3) Fever 4) Increase release C-reactive protein 5) Attracts neutrophils 6) Production IL-1, stimulates phagocytosis 7) Increase insulin resistance 8) Causes S&S inflammation d. Autoimmune disorders 4. Phagocytic regulators a. Attracts monocytes & activates them to macrophages b. Prevents macrophage migration from area 5. Colony-stimulating factors (CSF) a. Stimulate activity of moncyte to macrophage b. Stimulate production blood cells in bone marrow II Immune Response A. Non-specific – birth, genetic 1. Defenses a. Physical barrier 1) Hair, Sweat glands, bacterial chemicals Lysozymes, Antibodies, Mucus b. Phagocyts 1) Microphages ( eosinophil & neutrophils) 2) Macrophages (monocyte-macrophage system) c. Immunological Surveillance – NK cells – constant monitor d. Interferons – proteins released by lymphocytes 1) Interfer with viral replication 11 2) Stimulate macrophage & NK 3) Type of cytokine – hormones of immune system e. Complement – supplement antibodies – complement proteins = chain reaction 1) Attract phagocytes 2) Enhance phagocytosis 3) Destroy cell membrane 4) Promote inflammation f. Inflammation 1) Mast cells – heparin & histamine 2) Regeneration g. Fever – hypothalamus 1) Pyrogen - proteins 2) Pathogen, bacteria, antigen-antibody act as pyrogen B. Specific (cell mediated & humoral) – threats on individual basis - immunity 1. Forms of Immunity a. Innate – genetic- birth and not prior exposure b. Acquired – active or passive 1) Active – exposure to antigen - antibodies a) Natural – environmental exposure b) Induced – administer antigen immunization 2) Passive – transfer from one person to another a) Natural – mom to baby b) Induced – administer antibodies immunization 12 2. Properties a. Specificity b. Versatility c. Memory d. Tolerance 3. Immune Response a. Cell-mediated Immunity – T cells & macrophages 1) Protect viruses, intracellular bacteria & cancer 2) Macrophage activated by T cell cytokine (IFN-y) 3) Antigen display cell introduce to antigen peptide to helper T 4) Antigen recognition = T cell activation 5) Cytotoxic activity with engulfment & killing by macrophages b. Humoral Immunity – B cells ( chemical attack- antibodies) 1) Maturation of B cells 2) Antigen/antibody response 3) Bacteria & viruses via antibodies C. Regulation of Response 1. Inadequate = immunodeficiency 2. Excessive = allergic 3. Self – limited 4. Feedback system 5. Tolerance – non-reactive to self antigen III. Inflammation & Fever A. Acute Inflammation 1. Phases a. Cardinal (rubor –red; tumor- swelling; calor- heat; dolor – pain) 13 b. Vascular Stage 1) Vasoconstriction 2) Vasodilation 3) Vascular permeability - edema a) Loss protein fluid – fluid loss into tissue b) Pressure changes c) Chemical mediators c. Cellular Stage – movement of WBC’s 1) Granulocytes (neutrophil, eosinophil, monocytes ) a) Neutrophils – first (1) Role of neutrophils b) Eosinophils – chemical mediators, allergic c) Basophils – histamine & mast cells 2) Mononuclear Phagocytes – destroyer 3) Leukocyte response a) Margination & adhesion – leukocytes accumulation and sticky b) Emigration – leukocytes change shape squeeze into break c) Chemotaxis- chemical release attraction of leukocytes d) Activation & phagocytosis - d. Outcome 1) Resolution 2) Suppuration 3) Organisation 14 4) Chronic Inflammation 2. Mediators a. Histamine – mast cells; dilatation arterioles, permeability venules b. Serotonin – platelets similar to histamine c. Arachidonic acid (phospholipids) (blocked by NSAID) 1) Leukotrienes 2) Prostaglandins (1) P1 (2) P2 (3) Arachidonic Acid 3) Thromboxane d. Platelet-activating factor 1) Platelet aggregation 2) Eosinophil chemoattractant 3) Enhances function of neutrophil & monocyte e. Cytokines (lymphocytes & macrophages) 1) Interleukins (IL), interferons (IFN), tumor necrosis f. Nitric oxide 1) Relaxes vascular smooth muscle 2) Reduces platelet aggregation 3) Regulator leukocyte recruitment 4) Aids in killing microbial agents g. Kinin (bradykinin) h. C-reactive protein 1) Located on chromosome 1 2) Increase in inflammation 3) Complement binding to foreign & damage cells 4) Humoral response 5) Marker for inflammation 6) Increase risk diabetes & Coronary artery disease B. Chronic – long lasting 1. Infiltration of macrophages & lymphocytes instead of neutrophils 2. Fibroblasts = scarring & deformity 15 C. Fever 1. Thermoregulatory Center – hypothalamus a. Nervous system feedback from surface 2. Thermostatic Set Point – body temperature regulated so core is normal a. Above Set Point – heat dissipating activity initiated b. Voluntary self regulation 3. Metabolism – main source of heat production a. Norepinephrine & epinephrine released b. Fine motor actions (shivering) c. Physical exertion 4. Heat loss a. Pilomotor muscles (goose bumps – reduce skin surface) b. Arteriovenous shunts – arterial to venous movement 1) Open – heat to surface 2) Closed – heat interior 3) Sympathetic nervous system c. Blood volume d. Radiation – heat transfer to air e. Conduction – direct transfer one to another f. Convection – heat transfer thru air g. Evaporation – heat transfer via water (sweat) 5. Fever – elevation body temperature above 99 F (hypothalamus) a. Beneficial – limited 1) Accelerate activities of immune system b. Causative factors 1) Pyrogen – circulating proteins reset thermometer cause rise in hypothalamus thermostat a) Causatives – pathogen, bacterial toxins, antigen-antibody complex c. Complications 1) CNS problems 2) Disorientation 3) Convulsions 4) Hallucinations 5) Nausea c. Stages 1) First (prodromal) 16 2) Second (chill) 3) Third (flush) 4) Fourth (sweating) d. Age related 1) Less than 3 months serious 2) Elder less response even low temps – medical need D. Alterations 1. Hypersensitivity (allergic) a. Inappropriate or excessive b. Triggers – allergens c. Types 1) Immediate hypersensitivity – first exposure T & B a) Large IgE antibody production b) First exposure not as extensive c) Repeat exposure now antibody attached to mast cells with release histamine, heparin, cytokines, prostaglandins & other chemicals d) Sudden inflammation of tissue 2) Cytotoxic Reaction (Type II) – a) IgG or IgM antibodies b) Reaction complement- mediated or antibody- mediated c) Reaction can also be on cell or in fluids d) Causative – Rh incompatibility, blood transfusion, drug reactions 3) Immune Complex-mediated (Type III) a) Reactions between IgG & IgM with blood borne immune complexes in tissues b) Leads to vascular injury c) Indirect injury (vasculitis) 4) Cell-mediated hypersensitivity (Type IV) a) Direct Cell-Mediated – direct kill of antigen by CD8+ T lymphocytes b) Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity – CD4+ T cells secrete cytokines that recruit & activate substances that secrete inflammatory cells 5) Latex allergy 6) Autoimmune Diseases 7) AIDS 17 2. Autoimmune – mistakes own system for foreign (lupus) a. Genetic or environmental factors b. Unknown trigger c. Response 1) Breakdown of T-cell responsiveness to antigen 2) Release of antibodies against self 3) Mimicry against normal tissue (look a-like) 4) Superantigen – short circuit responses excessive Production CD4+ (food poisoning) 3. Anaphylaxis – histamine dump a. Widespread vasodilation b. Capillary permeability c. Airway contriction d. Respiratory failure 4. Transplantation a. MHC & HLA - surface antigen that determines foreign substance b. Host-versus-Graft Disease 1) Immune cells of the transplant person attack tissue of donor cells 2) Lymphocytes required especially CD4 & CD8 3) Over production B cell antibodies & T-cell mediated hypersensitivity reactions 3) Organ rejection c. Graft-versus-Host Disease 1) Immunologically competent cells transplanted into Recipient who is immunologically compromised E. Bioterrorism 1. Anthrax 2. Smallpox 3. Plague 4. Botulinum 5. E-coli 6. Chemical 7. Nuclear 18 F. Emerging Infectious Diseases 1. TB 2. Hepatitis 3. AIDS 4. MRSA & VRSA 5. Influenza 6. Ebola 7. Avian Flu 8. Pandemic Flu G. Age relation & immune system 1. Newborn a. Naturally acquired immunity- mother’s milk b. Artificially acquired immunity – immunizations c. Natural passive immunity – placental passed 2. Advanced Age a. Less responsive b. Decrease in size thymus c. Reduction T-cell numbers d. Reduced antibody reaction without T-cells e. Increase CA surveillance & infection f. Decrease immune response 19