PSI Large Biological Molecules Multiple Choice
advertisement

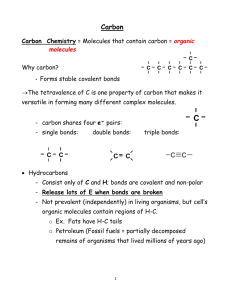
Large Biological Molecules Multiple Choice 1. Organic chemistry is a science based on the study of a. Inorganic compounds b. Water and its interactions with other molecules c. Functional groups d. Carbon compounds 2. How many electron pairs does carbon share to complete its valence shell a. 2 b. 4 c. 6 d. 8 3. Why are hydrocarbons not soluble in water? a. Hydrocarbons are hydrophilic b. Most bonds in hydrocarbons are non-polar covalent carbon to hydrogen bonds c. Most bonds in hydrocarbons are polar covalent carbon to hydrogen bonds d. Hydrocarbons are lighter than water 4. Hydrocarbons a. Contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms b. Are held together by hydrogen bonds c. Are polar d. Are held together by ionic bonds 5. Hydrocarbons containing only single bonds between the carbon atoms are called __________________. a. Saturated b. Unsaturated c. Non-polar d. Polar 6. Hydrocarbons containing double or triple bonds between some of the carbon atoms are called __________________. a. Saturated b. Unsaturated c. Non-polar d. Polar njctl.org Biology Large Biological Molecules 7. Gasoline and water do not mix because a. Gasoline is non-polar and water is polar b. Gasoline is less dense than water c. Gasoline is less viscous than water d. Gasoline is polar and water in non-polar 8. Nucleotides are to ________________________ as _____________________ are to proteins. a. Polymers; polypeptides b. Nucleic acids; amino acids c. Amino acids; polypeptides d. Nucleic acids; monosaccharides 9. Which of the following is not a component of an amino acid? a. Amine group b. R-group c. Carboxyl group d. Hydroxyl group 10. The 20 amino acids vary only in their? a. Amine group b. R-group c. Carboxyl group d. Hydroxyl group 11. Amino acids combine to make a. Enzymes b. Proteins c. Lipids d. Carbohydrates 12. The maximum number of structural levels that a protein can have is a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 13. At what structural level do proteins get their function a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Quaternary njctl.org Biology Large Biological Molecules 14. Denaturation causes proteins to a. Lose their shape and function b. Become new shapes with new functions c. Change from secondary to tertiary structure d. Change from tertiary to quaternary structure 15. The structural level of a protein least affected by a disruption in hydrogen bonding is the a. Primary level b. Secondary level c. Tertiary level d. Quaternary level 16. Which of the following is characteristic of the secondary structure of proteins? a. Alpha helix b. Pleated sheet c. Hydrogen bonding d. All of the above 17. At which structural level of proteins do bonds form between the R-groups? a. Primary level b. Secondary level c. Tertiary level d. Quaternary level 18. The tertiary structure of a protein refers to a. Its size b. The presence of pleated sheets c. Its overall 3-D structure d. The number of R-groups it contains 19. Which structural level of a protein consists of a chain of amino acids assembled in a specific order? a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Quaternary 20. Which of the following is not one of the seven classes of proteins? a. Digestive b. Structural c. Signaling d. Storage njctl.org Biology Large Biological Molecules 21. Hemoglobin is an example of what class of protein? a. Defense b. Enzymatic c. Contractile d. Transport 22. Hormones are an example of what class of protein? a. Transport b. Enzymatic c. Structural d. Signaling 23. Which of the following is not an example of a monosaccharide? a. Glucose b. Sucrose c. Fructose d. B & C 24. All sugars have several __________________ groups that make them soluble in water. a. Carboxyl b. Hydroxyl c. Amine d. R 25. Disaccharides are a. Glucose b. Fructose c. An example of a hydrolysis reaction d. An example of a dehydration synthesis reaction 26. Starch is used for a. Energy storage in animals b. Energy storage in plants c. Energy storage in plants and animals d. As a structural molecule in plants 27. Glycogen is used for a. Energy storage in animals b. Energy storage in plants c. Energy storage in plants and animals d. As a structural molecule in plants njctl.org Biology Large Biological Molecules 28. Cellulose is used for a. Energy storage in animals b. Energy storage in plants c. Energy storage in plants and animals d. As a structural molecule in plants 29. Which of the following is not true for both DNA and RNA? a. Both are made of a five carbon sugar b. Both have the base guanine c. Both have the base uracil d. Both have a phosphate group 30. Which of the following is not true about RNA? a. Can be many different shapes b. Contains thymine as a base c. Contains cytosine as a base d. Has one hydroxyl group more than DNA 31. Which of the following is true about DNA? a. Can be many different shapes b. Contains uracil as a base c. Contains cytosine as a base d. Has one hydroxyl group more than RNA 32. Which nucleotide base does guanine bond to? a. Adenine b. Thymine c. Uracil d. Cytosine 33. Which nucleotide base does Thymine bond to? a. Adenine b. Thymine c. Uracil d. Cytosine 34. Which class of biological molecules does not consist of polymers? a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Amino Acids d. Nucleic Acids njctl.org Biology Large Biological Molecules 35. Lipids are a. Hydrophobic b. Hydrophilic c. Amphiphilic d. A & C 36. Which of the following is not true about a hydrophilic group? a. Non-polar b. Found at the end of fatty acids c. Attracted to water d. The opposite of a hydrophobic group 37. Which of the following is an example of an amphiphilic molecule? a. Glycerol b. Saturated fatty acid c. Unsaturated fatty acid d. Phospholipid 38. Which of the following is true about saturated lipids? a. Liquid at room temperature b. Do not have the maximum number of hydrogen bonds possible c. Have double bonds in their carbon chain d. Have only single bonds in their carbon chain 39. Trans fats are made by a. Saturating unsaturated fatty acids b. Unsaturating saturated fatty acids c. Dehydration synthesis d. A natural process in a person’s stomach 40. Which of the following is not an example of a lipid? a. Phospholipid b. Waxes c. Glycogen d. Steroids njctl.org Biology Large Biological Molecules Answers 1. d 2. b 3. b 4. a 5. a 6. b 7. a 8. b 9. d 10. b 11. b 12. c 13. c 14. a 15. a 16. d 17. c 18. c 19. a 20. a 21. d 22. d 23. b 24. b 25. d 26. b 27. a 28. d 29. c 30. b 31. c 32. d 33. a 34. a 35. d 36. a 37. d 38. d 39. a 40. c njctl.org Biology Large Biological Molecules