molecule linkage
advertisement

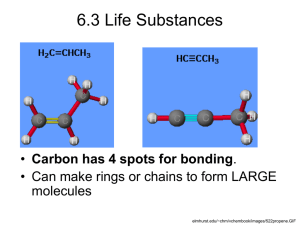
As pH gets smaller it means we are increasing the amount of H+ ions…. This is an acid As pH gets larger it means that we are increasing the amount of OH- ion concentration. This is more basic. The thing about logs is how many more H+ ions does a pH of 2 have than a pH of 4? 1000 times more H+ ion the 2 than the 4! pH of blood 7.4 and needs to be stable in order for our bodies so we have the presence of buffers.. combinations of h ion acceptors and donors, they are actually weak acids and weak bases.. COOH group in aqueous solution is a hydrogen donor so it is a weak acid… NH3 is the amino group which is a hydrogen ion acceptor, or weak base… END of CHAPTER 3 NOTES.. 1. How many valence electrons does a carbon atom contain? How many bonds can a single carbon atom make? What kinds of bonds does carbon make? 4 valence electrons…. 4 single bonds… Carbon makes Covalent Bonds 2. What molecular geometry does carbon make when bonded to 4 molecules? Draw a 3D projection of a methane molecule. Tetrahedral 3. What is a hydrocarbon? Name the 4 characteristics of Hydrocarbons? A compound where carbons and hydrogens are attached to each other. Length Branching Double Bong Location Presence of a Ring 4. Shape is very important in biological molecules, define the word isomer and name the 3 different kinds, describe each. Also name an example mentioned in class that illustrates how important molecular shape and arrangement is? Isomer- has the same molecular formula as another molecule but differs in connectivity and arrangement. 1. Structural Isomers – Same chemical composition, different connection and structure 2. Cis-Trans Isomers – Cis = same side Trans = different sides 3. Enantiomers – Right left hand… mirror images One isomer of albuterol is used to open up the airway of people having an asthma attack… however, the other isomer has no such effect on the body 5. What is a functional group? What are the 7 functional groups mentioned in class? Can you draw the chemical composition of each? Can you identify them if attached to a molecule? DON’T GET CAUGHT UP IN THE DETAILS… JUST BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY THE GROUPS ON STRUCTURES Hydroxyl- AKA alcohols have an Oxygen which causes the molecule it is attached too to be polar.. this means since like dissolves like that molecules with hydroxyl groups play well with water (is polar). Carbonyl - know the difference between a key tone and an aldehyde. Aldehyde is on the “outside”.. see that rhymes!! Carboxyl - contains 2 O’s so it is highly polar! has 2 ionized forms because it acts as an ACID! Found on amino acids. Amino - Also found on amino acids, acts as a BASE. Know its 2 ionized forms - NH2 ——> NH3+ Sufhydryl - AKA Thiol… used to stabilize protein structure.. Can covalently bond with another thiol group… when this occurs this is called a cross link Methyl- CH3… recently methylation has been discovered to silence genes and has developed a new field called epigenetics. Phosphate - important in energy and found in nucleic acids… contributes a negative charge to molecules… When water cleaves off a phosphate group from an ATP lots of energy is released. Functional units are important because even a single change in functional group can change a molecule as drastically from estradiol to testosterone 6. Name the 4 kinds of organic molecules. Which of these 4 is NOT a polymer? Why? Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins Carbohydrates… Lipids are not made up of repeating monomer units ,therefore, they are not polymers 7. Explain the difference between a dehydration and a hydrolysis reaction? A dehydration reaction (or the pulling out of water) forms bonds between molecules. A hydrolysis reaction (the adding of water) breaks bonds between molecules 8. What is the general ratio of a single sugar or monosaccharide? C1:H2:O1 = simple sugar or monosaccharide C3:H6:O3 Be able to work problems with polysaccharides every bond I make subtract a H20 molecule from the total chemical equation 9. What are the 2 main functions of Carbohydrates? 1. Short term energy storage (cells main source of energy) 2. Structural components of cells 10. A glucose will not be a ring in an aqueous solution? T or F False. Sugars like to form rings when solvated with water 11. What kind of reaction combines 2 monosaccharaides into a disaccharide? What kind of bond is formed by this reaction? Dehydration reaction. Glycosidic Linkage 12. Plants store glucose as ________ and Animals store glucose as ___________. Starch… Glycogen If you eat more carbs than you are supposed to eat… this is one way the body storing excess carbs… once you have filled up all your glycogen stores then you start to store carbs as fats! 13. What kind of reaction breaks down a disaccharide into 2 monosaccharaides? Hydrolysis Reaction 14. What is the name of the structural polysaccharide that contains Nitrogen? Where is it found? Chitin.. found in the exoskeleton of insects.. dissolvable stitches.. also found in cell wall of fungi 15. Name the 3 types of Lipids discussed in class? What is each molecularly comprised of? 1. Steroid – 4 fused rings 2. Triacylglyceride (Fatty Acids) – glycerol backbone and 3 fatty acid chains 3. Phospholipid – glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate 16. What kind of bond or linkage is formed in a dehydration reaction involving a glycerol backbone and a fatty acid chain? Ester Linkage 17. What is the difference in a Unsaturated FA chain and a Saturated FA chain? Unsaturated FA chains have double bonds and are found in liquid form. Saturated FA chains are linear with no double bonds and are solid. the word “saturation” refers to the saturation of the carbon skeleton with hydrogens. 18. Lipids are hydrophilic? T or F? False… lipids are for the most part NOT water soluble 19. What was so significant about the Urey and Miller experiment? The Urey and Miller experiment showed that organic molecules could be synthesized from nonorganic molecules. By simulating the early earth’s atmospheric conditions they sound that amino acids had been synthesized. 20. What is the structural difference in alpha and beta linkages in sugars? Alpha linkages are much more branched than Beta and are primarily used for energy purposes. Beta linkages are straight chained and used for structural purposes. Cellulose is the structural component found in plants they have a Beta linkage.. we do not have the enzymes to break down beta linkages so we cannot get nutrients from them.. THIS IS FIBER