Name
advertisement
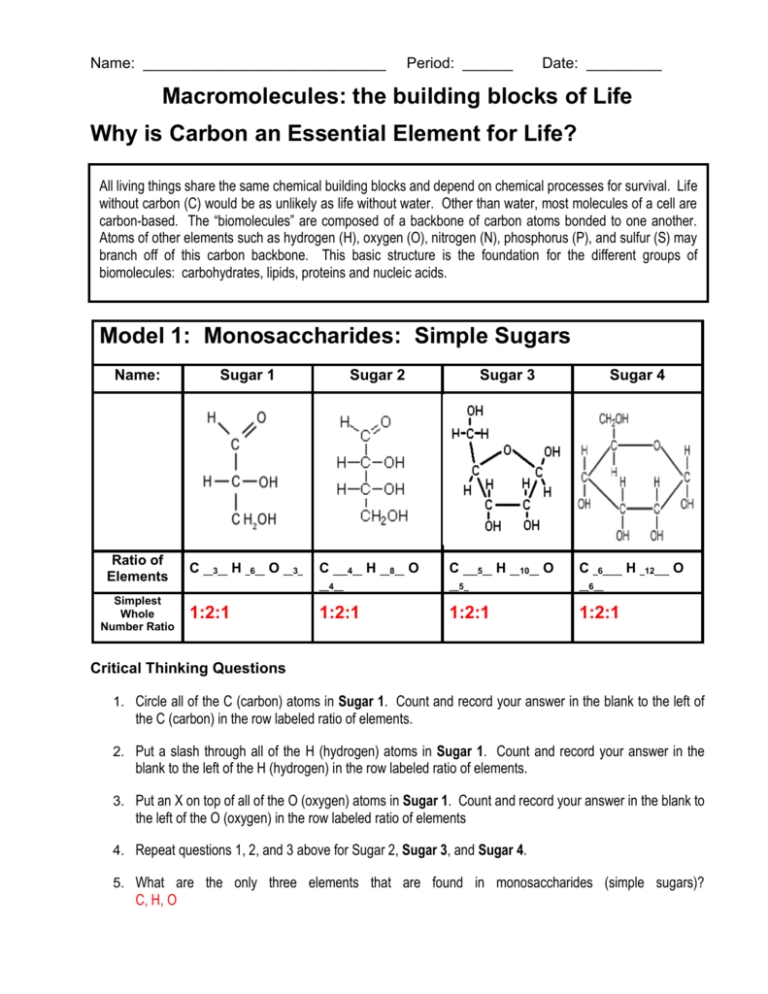
Name: _____________________________ Period: ______ Date: _________ Macromolecules: the building blocks of Life Why is Carbon an Essential Element for Life? All living things share the same chemical building blocks and depend on chemical processes for survival. Life without carbon (C) would be as unlikely as life without water. Other than water, most molecules of a cell are carbon-based. The “biomolecules” are composed of a backbone of carbon atoms bonded to one another. Atoms of other elements such as hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and sulfur (S) may branch off of this carbon backbone. This basic structure is the foundation for the different groups of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. Model 1: Monosaccharides: Simple Sugars Name: Sugar 1 Ratio of Elements C __3__ H _6__ O __3_ Simplest Whole Number Ratio 1:2:1 Sugar 2 Sugar 3 Sugar 4 C ___4__ H __8__ O C ___5__ H __10__ O C _6____ H _12___ O __4__ __5_ __6__ 1:2:1 1:2:1 1:2:1 Critical Thinking Questions 1. Circle all of the C (carbon) atoms in Sugar 1. Count and record your answer in the blank to the left of the C (carbon) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 2. Put a slash through all of the H (hydrogen) atoms in Sugar 1. Count and record your answer in the blank to the left of the H (hydrogen) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 3. Put an X on top of all of the O (oxygen) atoms in Sugar 1. Count and record your answer in the blank to the left of the O (oxygen) in the row labeled ratio of elements 4. Repeat questions 1, 2, and 3 above for Sugar 2, Sugar 3, and Sugar 4. 5. What are the only three elements that are found in monosaccharides (simple sugars)? C, H, O 6. What is the simplest whole number ratio for each of the above simple sugars? 1:2:1 7. Monosaccharides (simple sugars) are also called carbohydrates. Using what you have learned about the elements and their ratios in monosacharides, explain why the term carbohydrate is an appropriate term for this group of compounds. Carbo stands for a carbon molecule. Hydrate represents a water molecule which is two hydrogens and one oxygen. CH2O which represents the ratio Read This! Lipids or fats are made up of two kinds of units: glycerol and fatty acids. Lipids are produced when glycerol binds to fatty acids. A maximum of three fatty acids can bind to one glycerol molecule to form a lipid. Glycerol 8. What elements are present in glycerol? C HO 9. Are there any elements in glycerol that are not in carbohydrates? No 10. A monoglyceride contains 1 glycerol molecule and _____1____ fatty acids. A diglyceride contains 1 glycerol and ___2______ fatty acids. A triglyceride contains 1 glycerol and _____3____ fatty acids Model 2: Lipids: Fatty acids Name: Ratio of Elements Simplest whole number Ratio Fatty Acid 1 Fatty Acid 2 Fatty Acid 3 Fatty Acid 4 C __4___ H __8__ O C __6___ H _12___ O C __7___ H __14__ O C __8___ H __16__ O __2__ __2__ __2__ __2__ 2:4:1 3:4:1 7:14:2 4:8:1 11. Circle all the C (carbon) atoms in Fatty Acid 1. Count and record your answer in the blank to the left of the C (carbon) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 12. Put a slash through all of the H (hydrogen) atoms in Fatty Acid 1. Count and record your answer in the blank to the left of the H (hydrogen) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 13. Put a X through all of the O (oxygen) atoms in Fatty Acid 1. Count and record your answer in the blank to the left of the O (oxygen) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 14. Repeat questions 10, 11, and 12 above for Fatty Acid 1, Fatty Acid 2, and Fatty Acid 3. 15. What are the only three elements that are found in fatty acids? H,O,C 16. What is the simplest whole number ratio for each of the above fatty acids? Carbon and Hydrogen have a 1:2 ratio but there is no overall ratio because the number of oxygen molecules in a fatty acid is always two and does not increase, which does not allow for a uniform ratio1 17. Compare the molecules in Model 1 to the molecules in Model 2. In what ways are the molecules similar? In what ways are the molecules different? Similar They are made up of the same elements Those elements form the same number of bonds Different They are different structures The amount and ratio of the elements differs 18. Using what you know about the properties of water, which Model (1 or 2) contains molecules that are more likely to be polar and attracted to water (hydrophilic)? Explain your answer. The Monosaccharides are more likely to be polar and hydrophilic because they contain many O-H hydrogen bonds just like water 19. Using what you know about the properties of water, which Model (1 or 2) contains molecules that are more likely to be nonpolar and repel water (hydropbobic)? Explain your answer. The Lipids are likely to be nonpolar because they are long chains of hydrogen and carbon. Read This! Amino acid General Structure Amino acids are the basic building blocks or subunits of proteins. There are twenty amino acids, and each one of them is a little different. Each amino acid is composed of a “common group” and a “variable group“ designated as R. The “common group consists of all of the atoms except for those designated as “R.” All organisms need some proteins, whether they are used in muscles or as simple structures in the cell membrane. Model 3: Amino acids: the subunits of proteins Amino Acid 1 Name: Ratio of Elements Amino Acid 2 Amino Acid 3 C __2__ H __5__ O _2___ N C __3___ H __7__ O __2__ N C __6___ H __13__ O __2__ N __1__ __1__ __1__ 20. Use a pen or a pencil and draw a box around the “common group” of, Amino Acid 1, Amino Acid 2 and Amino Acid 3. 21. What elements are present in the “common group” of an amino acid? Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen 22. Circle the “R” group in each amino acid above. 23. Are there any elements in an amino acid that are not in carbohydrates or lipids? If so, what is / are they? Nitrogen 24. Circle all the C (carbon) atoms in Amino Acid 1 (common group and variable group). Count and record your answer in the blank to the left of the C (carbon) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 25. Put a slash through all of the H (hydrogen) atoms in Amino Acid 1 (common group and variable group). Count and record your answer in the blank to the left of the H (hydrogen) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 26. Put a X through all of the O (oxygen) atoms in Amino Acid 1 (common group and variable group). Count and record your answer in the blank to the left of the O (oxygen) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 27. Repeat questions 24, 25, and 26 above for Amino Acid 2 and Amino Acid 3. 28. Of the three amino acids given in Model 3, which one is the least complex in structure and which one is the most complex in structure. Explain your answer. Read This! Nucleotides are the basic building blocks or subunits of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). There are 2 types of nitrogen bases that form nucleotides; they can either have 1 ring in their nitrogen base or 2 rings in their nitrogen base. Nitrogen base Phosphate group sugar 29. What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? Phosphate Group, Sugar, Nitrogen base 30. What is the NEW element (one that has not been used in the three previous biomolecules) that we find in a nucleotide? Phosphorous Extension Question 1. Study the diagrams below. Indicate whether the diagram is an example of a carbohydrate, fatty acid, nucleotide or an amino acid. Elements and ratio of elements: Elements and ratio of elements: __________C5:H10:O1_____________ _________ C3:H7:O3N1_ a. ______Lipid b. _________Amino Acid Elements and ratio of elements: Elements and ratio of elements: ________ C1:H2:O1___________ ___C9:H12:O6:N5;P1 c. ____carbohydrate_________ d. Nucleotide