Glue this side into your Science Journal ROCK CYCLE There are 3
advertisement
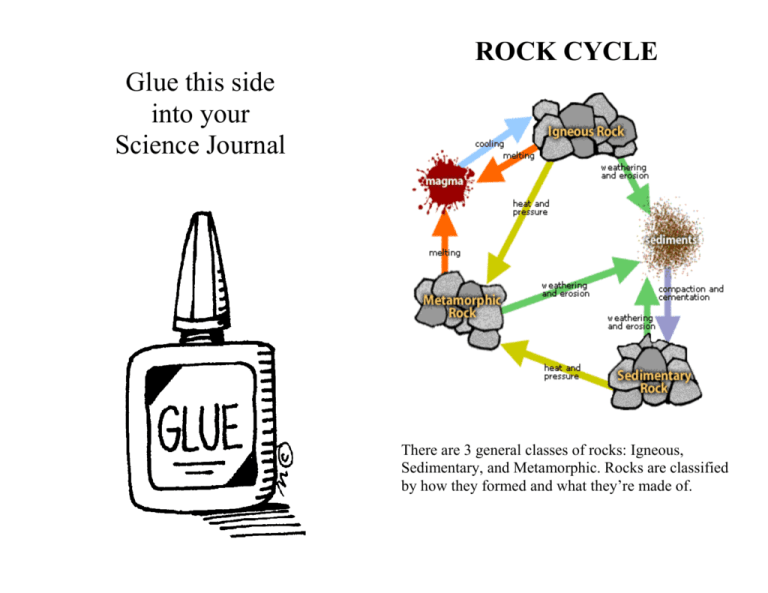
ROCK CYCLE Glue this side into your Science Journal There are 3 general classes of rocks: Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic. Rocks are classified by how they formed and what they’re made of. Geologists classify rocks by observing color, texture and mineral composition. These observations help identify what type of rock it is. • Texture: the size, shape, and pattern of the rock’s grain. • Color: the apparent color of the rock, on the inside and the outside. • Mineral composition: The minerals that make up the different parts of a rock. Metamorphic rocks are formed from Igneous and Sedimentary rocks under extreme: • Heat • Pressure FOSSILS Fossils…are any remains or imprints of living things of the past. Fossils are found in sedimentary rocks. Importance of Fossils Fossils provide information about life and conditions in the past. Plant fossils can tell us about the ancient environment. Animal fossils can tell us about past environments, what the animal ate, and how they lived. Scientists study them to learn about extinct plants and animals. IGNEOUS ROCKS Igneous Rocks… are formed when lava and magma crystallize to form solid rock. Igneous means “born of fire” Sedimentary Transformations Point A: Water or wind deposits sediments (Deposition) Point B: The heavy sediments press down on the layers beneath (Compaction) Point C: Dissolved minerals flow between the particles and cement them together (Cementation) METAMORPHIC ROCKS Metamorphic Rocks…are formed when an existing rock is partially melted, squeezed, or both. Metamorphic rocks were once igneous or sedimentary rocks that have "morphed" into another kind of rock because of heat and pressure. How do sedimentary and igneous rocks change? If you exam metamorphic rock samples closely, you'll discover how flattened some of the grains in the rock are. Magma vs. Lava • Magma is a hot liquid made of melted minerals. • When magma pours onto the earth’s surface it is called lava. • The longer it takes for the magma or lava to cool, the more time mineral crystals have to grow. The more time the crystals have to grow the coarser the texture of the resulting igneous rock. • Igneous rock can form underground, where the magma cools slowly. Or, igneous rock can form above ground, where the magma cools quickly. 3 Ways a Rock Can Melt Temperature – An increase in temperature deep within the Earth’s crust can cause the minerals in a rock to melt. Pressure – The high pressure deep within the Earth forces minerals melt from intense heat and pressure. Composition – Fluids like water and carbon dioxide enter a rock that is close to its melting point. When these fluids combine with the rock, they can lower the melting point of the rock enough for it to melt and form magma. 2 Types of Igneous Rocks • INTRUSIVE IGNEOUS ROCKS – When igneous rocks are formed by magma that cools BENEATH Earth’s surface. • EXTUSIVE IGNEOUS ROCKS – When igneous rocks are formed by LAVA ON Earth’s surface. SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Sedimentary Rocks…are formed when sediments (sand clay, and silt) are compressed and become solid rock 4 ways Sedimentary Rock can be formed? • Erosion • Deposition • Compaction • Cementation Lithification…The process by which sediment becomes sedimentary rock • 1st step : Erosion • 2nd step : Deposition • 3rd step : Compaction • 4th step : Cementation Sedimentary Rocks - Erosion...Destructive forces breaking up and wearing away all the rocks on Earth’s surface by heat and cold, rain, waves, and grinding ice. Erosion occurs when running water or wind loosens and carry away the fragments of rock. Sedimentary Rocks – Deposition…The process by which sediment settles out of the water or wind carrying it. • Moving water or wind slows and deposits the sediment. • Sediment may include shells, bones, leaves, stems, and other remains of living things. • Remains of living things in the sediment may slowly harden and change into fossils trapped in the rock. Sedimentary Rocks – Compaction…New sediments fit together loosely, but gradually, thick layers of sediment build up creating new layers. • Layers are heavy and press down on the layers beneath them. • Compaction is the process that presses sediments together. • Weight of the layers compacts the sediments, squeezing them tightly together. • The layers often remain visible in the sedimentary rock. Sedimentary Rocks – Cementation…The process in which dissolved minerals crystallize and glue particles of sediment together. • While compaction is taking place, the minerals in the rock slowly dissolve in the water. • The dissolved minerals seep into the spaces between particles of sediment. • It takes millions of years for compaction and cementation to transform loose sediments into solid sedimentary rock.







