Reporting verbs
advertisement

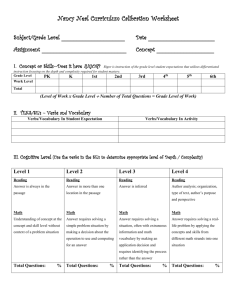
Reporting Verbs When introducing references into the text (citing) you should choose suitable 'reporting' verbs as these can: strengthen the arguments you are presenting help the reader understand why the source is relevant. Some verbs are neutral: Smith (2004) describes... Jones (1999, p 3) states... Green (2002) defines... Jackson (2003) reports... Some verbs draw attention to the author's viewpoint: Harris (2001) argues... O'Neill (1997) disputed... Some verbs give information about the author's work: Holmes (2000) investigated... Church (1998) evaluated... Some verbs highlight the author's viewpoint: Brown (2001) believes... McAllister (1996) recognised... Smith (2004) predicted... 1. Using other people's ideas in your writing How do you convey the ideas of other people in English academic writing? In some assignments it may be enough to use your own experiences, impression and responses. However for most of the writing you'll do at university you'll need to use the ideas, writings, and research of other people. This involves finding relevant materials, evaluating the ideas, and acknowledging the sources of this information. (Acknowledging is also known as referencing, documenting, or citing other people's work). You can use references. Using references is necessary to properly acknowledge other people's words/design/codes/results. References show the reader: where you obtained the information you have read widely your academic opinions are supported by research that you have recognised another person's efforts. 2. Quoting sources A direct quote is an exact copy of what someone else has said or written. The quotation will either be: in "quotation marks" if short (ie. less than three lines) indented and/or in a different font if longer than 3 lines. An indirect quote means taking someone else's idea or work and rewriting it into your own words or summarising it; it is also known as paraphrasing and/or summarising. For BOTH direct and indirect quotes you MUST acknowledge where you got the ideas from. In other words you need to cite the author and publication details using the referencing/citation style required by your Faculty, School or subject. APA in our school Messages conveyed by verbs The message Giving factual information Example: Martin (1994) documented various forms of plagiarism. What the author thought Example: It is clear that Chanock (2003) believes that much of what is written about plagiarism is ill-considered. The procedure How the author did it/what the author found. Example: Martin (1997) explains that there are a number of reasons why students plagiarise. What the author concludes Example: East (2005) concludes that lecturers and students can have different understandings of the role of referencing and advises lecturers to be explicit about their expectations. Words which show opinion – usually a negative evaluation Example: East (2004), who challenged existing ways of presenting information online, disregarded technical constraints. Words which show opinion – usually a positive evaluation Example: Chanock (2003) highlights the importance of presenting a range of views.