What Causes Our Weather Study Guide Questions
advertisement

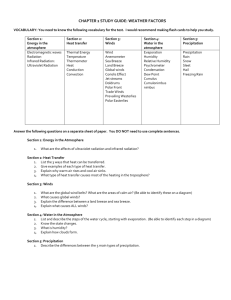
What Causes Our Weather Study Guide Questions 1. What are the 4 factors that cause weather to change? Temperature, Air Pressure, Wind, Humidity or moisture in the air. 2. What are the 3 factors that determine air pressure? Temperature of the air. A.) The higher the temperature, the lower the air pressure. Density of the air. (Elevation) A.) The higher the density, the higher the pressure. The amount of water vapor. (Humidity) A.) The higher the humidity, the lower the pressure. 3. What are the 3 ways heat can be transferred? 1.Radiation -Energy that comes off of the sun and is absorbed by the earth. 2. Conduction- The transfer of heat when molecules collide into each other. 3. Convection- The transfer of heat through convection currents. (Only through a fluid) 4. Why did the balloon inside the bell jar get larger during the air pressure lab? When the air was taken out of the jar, the pressure decreased because the lower the density of the air the lower the pressure. The balloon gets bigger because the air pressure inside of the balloon is stronger, which makes it bigger. 5. What are the three types of winds and what causes them to blow the way they do? Global wind, local wind and monsoon winds. Since all winds blow from high pressure to low pressure they all are affected by air pressure changes. Also the bigger the wind system the more it is effected by coriolis. Global winds are most affected by coriolis, monsoon winds are affected a little, and local winds are not affected much at all by coriolis. Winds can also change because of the temperature difference you can have from season to season or day to day. Monsoon and Local winds are affected the most by temperature changes. Global winds are affected a little. 6. Why do we get land breezes and sea breezes? Sea Breeze- Cold winds blowing from the water to the land. It is a convection current of wind caused by the land warming faster during the day than the water does. Land Breeze- Cold winds blowing from the land to the water. It is a convection current of wind caused by the land cooling faster at night than water does. 7. Completely describe the process of the water cycle. Water starts off in some kind of a water source. When heated, it evaporates or changes into a gas. As soon as the air cools enough the air becomes saturated. This causes condensation to take place. This process will form clouds. When the clouds become to heavy precipitation occurs. The precipitation falls to the ground or another water source. If it hits the ground it can work its way back to another water source by ground water or runoff. This will start the process all over again. 8. What is the relationship between air temperature and air’s capacity to hold water? Warm air can hold more moisture than cold air. As temperature of air increases, the capacity to hold water vapor increases. 9. Why is relative humidity a more useful measurement than humidity? By being expressed as a % it tells you how close the air is to becoming saturated. Humidity will only tell you how much water is in the air. You would not know how close the air would be from making clouds. 10. What two things determine relative humidity and when will it be the highest? Temperature of the air & the amount of moisture determine relative humidity, And it will be highest at Cold temperatures & High Water levels in the air. 11. DESCRIBE the 5 forms of precipitation. RAIN-Drops of H2O falling into areas of above freezing temps, SNOW-H2O that falls as a frozen six sided, flake, SLEET-Forms when snow falls through a warm area of air, melts, and then freezes back into an ice pellet smaller than 5mm, HAIL-Warm weather falling lumps of ice larger than 5mm, & FREEZING RAIN-Rain drops that are “super cooled” that freezes as soon as it touches a solid surface.