lpn-student-notes-1-9-09
advertisement

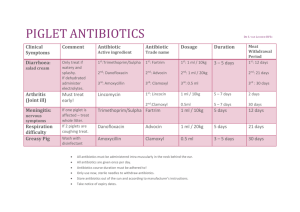
PHARM 1-9-09 GOLD-may be used as an anti-inflammatory READ ABOUT STEROIDS PG 333 READ ALL YELLOW PAGES (NURSING IMPLICATIONS) CH 7 ANTIMIBROBIALS Most antibiotics are made in a lab synthetically now. AGE-the young have an immature immune system and the elderly have multiple things going on. Their cells can’t rejuvenate. These would be things to consider when giving antibiotics/ or infections -immune compromised (HIV) -chemotherapy -WBC -BODY can’t have a good immune system if it doesn’t have good nutrition, is underweight or anemic. CLASSIFICATIONS OF KINDS BACTERIA-uses antibiotics FUNGI- uses antifungal VIRUSES –uses antivirus (antibiotics do not help viruses) ADMINISTERING ANTIBIOTICS If its for the eye, would use eye drops If its for the ear, would use ear drops Skin-triple antibiotic -always read the label 3x when handling dropper as the med can be dangerous if used vise versa, ex, using ear drops in the eye can burn the eye. -Need to have a good kidney and liver to be able to excrete toxins GENTAMYASIN- can lose hearing problem if you don’t have a good liver that can help excrete. This type of med is used as a last resort antibiotic. -If large and obese-need higher dose of meds -overuse of antibiotics causes resistance. (ex MRSA is more common in hospitals now) -if an antibiotic is not effective and not caught in time, it might lead to septic shock. Sometimes waste products of antibiotic may cause problems pg. 153. cells rupture CLASSIFICAIONSCidal- to kill (kill bacteria) ex- cephalosporin’s, penicillin, vancomyacin Bacteria static- slows it down, slows down growth ex- tetracycline, sulfamides, erythromycin Know adverse effects-side effects, allergies FOR TEST: Should know about penicillin, tetracycline’s, should know classifications SULFAMIDES-should know that bacteria static treats UTI PENICILLAN mainly cephalosporins, used to treat ghonorea pg 154 STREPTOCOCCUS- used for strep throat ADVERSE EFFECTS: mostly diarrhea. Allergic reactions happen as a dermotalogic reaction first, then anacaphalic. Would need epi pen as a counteract QUIZ REVIEW: Ch 10- know gate theory, anageslics pg 260 Pg 261 opiods, pg 262-all, 267-skin. Fentanyl 268, Diluadid- 268, methadone, codeine, (tynelol) Vicodyn, oxicodne, opiod antagnost (narcan) pg 270. naltrexone. Read about non-opiod anageslics. Pg 271 salicylates. Imatrix pg 278. LPN’S don’t need to be concerned about epidurals. Pg 326-330 (gold, briefly) pg 332. cortisteroids pg 333-334. MEDSURG Different hospital departments or medical specialties may have similar abbrev. That do not mean the same thing. Ex- BM-may mea bowel movement, may also mean baby has taken breast milk w/o complications in the OB department. -drugs have an effect on lab values -some drugs are taken because you take other drugs -know the therapeutic classifications of drugs -CUMUDIN- requires greater lab values. Ex PTT and APTT lab test -MOST questions from Nclex about drugs, quantities, etc would be based on the current drug book. -when a person comes in with burns, they are not just at risk for infection, but also a decrease of fluids and electrolytes. FAMILIESAre an important part of healthcare. (ex, when in a coma, the last sense that would leave would be the hearing. The family could be a support to the patient even during this time) -the more info shared w/ families, the better in most cases. -nurses need to learn to multitask and keep in sight all dimensions of nursing holistic care. FACTORS AFFECTING FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTESDiaphoresis Liver function Kidney function Pancreatic function Nutrition, Exercise level If the pancreatic function has a problem with insulin production, it does not necessarily mean that it has affected the production of other enzymes. PEDS -NO questions on test about immunizations as they are ever changing. PASSIVE IMMUNITY- passing, its going to go away. ROTOVIRUS- taken mostly at 2, 4 6 months. Review pg 394-398. IRON- very important to the infant up to 12 months. HONEY- do not give as its associated with infant botulism, infant gets infected. DEVELOPMENT- hold head up prone, hands remain tightly fisted SAFETY- you want a baby to be both 22 pounds and 1 year before changing the car seat. Make sure you check water heater temp. SIDS- get rid of bumper pads on crib. Smoking. Family bedding CH. 17. DEVELOPMENT ERICKSON 2-3 yrs. – bladder control by 2.5 years. Depends on the myelin sheath on spinal cord Autonomy vs shame and doubt. -children recognize they are a separate individual. They become confident and secure in themselves if successful. If not- become overly concerned, etc. LANGUAGES- study guide on quia TIME OUT- recommended 1 min per year of age TOILET TRAINING_- autonomy. May see poop and urine as part of themselves and be scared to separate with that part of themselves. NUTRITIONFinger foods- be cautious of choking Ritualization- may need special spoon/utensil. Infection- are at risk for high anemia Need food high in vitamin C. LEAD POISONING STUDIES- PG 348-359 DISCLAIMER: THESE ARE STUDENT NOTES TAKEN OF LECTURE INFORMATION PRESENTED IN CLASS AND IS NOT AN OFFICIAL DOCUMENT FROM THE INSTRUCTORS OR THE FACULTY OF RTC. THE INFORMATION PRESENTED MAY NOT BE 100% COMPLETE OF WHAT WAS LECTURED IN CLASS AND SHOULD NOT BE USED AS AN ONLY SOURCE OF INFORMATION FOR ANY TESTS, QUIZ, OR FINAL EXAMS.