Erythropoiesis

E
rythropoiesis
Dr. Wasif Haq
Introduction
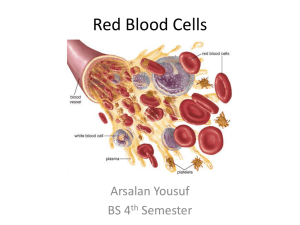
• Red blood cells also called as “Erythrocytes”.
• R.B.C. required for transportation of respiratory gases.
• Biconcave disc shaped.
• Mean diameter 7.5.-7.8 micrometer.
• Initially nucleated, later anucleated.
• Flexible cell membrane.
• Significance?
Count & Levels
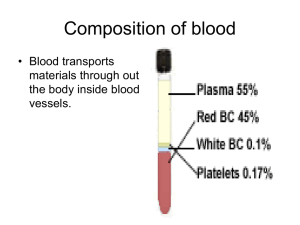
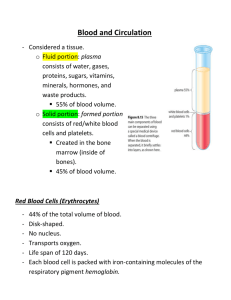
• Most numerous amongst all blood cell types.
• In males: 5,200,000 (+ 300,000) Million cells/cubic millimeter.
• In females: 4,700,000 (+ 300,000) Million cells/cubic millimeter.
• Why the count in males is greater?
Hemoglobin Levels
• Maximum concentrating ability of R.B.C.’s for
Hemoglobin is 34 g/dl.
• Every deciliter of blood in men carry 16 grams of
Hemoglobin, while in females; 14 grams.
• 1 single gram of Hemoglobin is capable of combining with 1.39 milliliters of Oxygen.
Functions of R.B.C.’s
• Transportation of Oxygen bound with
Hemoglobin: 97% Hemoglobin.
• Carbonic anhydrase enzyme: Transportation of
CO
2 from tissues back to lungs in form of
‘bicarbonate’ ions.
• Acid-base buffering.
R.B.C.’s Production
• Also known as “Erythropoiesis” or
“Erythrogenesis”.
Intra-embryonic/
Intra-uterine life
Postnatal life
Intra-Embryonic Life
• Initially: Yolk sac.
• Second trimester: Mainly liver along with Spleen
& lymph nodes.
• Third trimester and after birth : Only in bone marrow.
Post-natal Life
• Bone marrow of all the bones till 5 years of life.
• Relation between age & R.B.C.’s production?
• Vertebrae, sternum, ribs and ilia produce R.B.C.’s throughout life.
Erythropoiesis
• Pluripotent Hematopoetic stem cells in bone marrow
(also called as Hemocytoblast) are source for R.B.C.’s.
• Any type of blood cell type can be formed by
Hemocytoblasts.
• Certain number of Pluripotent Hematopoetic stem cells will become committed to form only R.B.C.’s , hence called “Committed stem cells”.
• Commitment occurs before any structural differences observed.
• Growth & differentiation inducers.
H aematopoetic stem cell
P roerythroblasts
B asophil erythroblasts
P olychromatophil erythroblasts
O rthochromatic erythroblasts
R eticulocytes
E rythrocyte
Nutrients Required
• Vitamin B12, Folic Acid & Iron.
• Deficiency of Vitamin B 12 & Folic Acid-
Maturation failure.
• Larger than normal size R.B.C.’s are produced called Macrocytes.
• Macrocytes can carry O2 but are extremely fragile.
• B12 deficiency takes 3-4 years to develop.
• Folic acid destroyed by cooking vegetables, meat
& fruits.
Nutrients Required
• Sprue= Small intestinal disease, difficulty in absorbing Folic acid & Vitamin B 12 due to deficiency of Intrinsic factor.
• Iron: Stored in body in form of “Ferritin”.
• Hemoglobin: 65% Iron, Myoglobin 4%, Reticuloendothelial cells in bone marrow and liver 15-
30%.
Erythropoietin
• Concentration of R.B.C.’s is not important but functional ability to transport respiratory gases.
• Protein hormone stimulates R.B.C.’s production.
• Released from Kidneys (90%) & Liver (10%).
• Epinephrine, Nor-epinephrine & Prostaglandins stimulate Erythropoietin release.
• Production starts within minutes, new cells appear after 4-5 days.
• Action: Stimulates Proerythroblast formation from hematopoietic stem cell and accelerates progression
& maturity of cell through different stages of
Erythropoiesis.
http://coolbluez.t15.org