Bonding assignment answers
advertisement

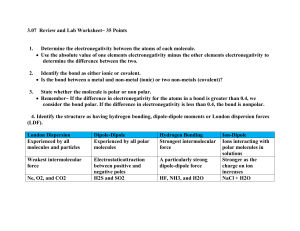
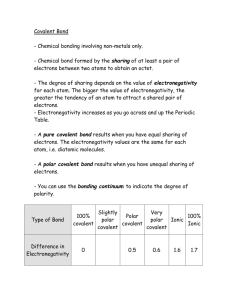
Chemistry 30 Chemical Bonding – Properties of Molecules 1. 2. For the following molecules determine which atoms are bonded (write the symbols with a bond between them), the electronegativity difference between them, and the type of chemical bond it represents. If the bond is ionic, state what ions are produced. If the bond is polar covalent, indicate the direction of the dipole on the symbols from the first part. a) KCl b) LiBr Electronegativity difference = K - Cl = 0.8 - 3.0 = 2.2 Electronegativity difference = Li - Br = 1.0 - 2.8 = 1.8 ionic bond K1+ Cl1ionic bond Li1+ Br1- c) HI Electronegativity difference = H - I = 2.1 - 2.5 = 0.4 polar covalent bond d) CF4 Electronegativity difference = C - F = 2.5 - 4.0 = 1.5 polar covalent bond e) CaS Electronegativity difference = Ca - S = 1.0 - 2.5 = 1.5 polar covalent bond f) H2Se Electronegativity difference = H - Se = 2.1 - 2.4 = 0.3 polar covalent bond g) SiCl4 h) P4 Electronegativity difference = Si - Cl = 1.8 - 3.0 = 1.2 Electronegativity difference = P - P = 2.1 - 2.1 = 0.0 polar covalent bond covalent bond i) j) k) l) Electronegativity Electronegativity Electronegativity Electronegativity polar covalent bond covalent bond covalent bond ionic bond K1+ S2- FeCl3 BrCl7 CS2 K2S difference difference difference difference = = = = Fe - Cl = 1.8 - 3.0 = 1.2 Br - Cl = 2.8 - 3.0 = 0.2 C - S = 2.5 - 2.5 = 0.0 K - S = 0.8 - 2.5 = 1.7 For c, d, f, g, and k from question 1 determine whether the molecules are polar, or nonpolar. Show all work. c) HI Electronegativity difference = H - I = 2.1 - 2.5 = 0.4 shape: only 2 atoms H polar covalent bond I since only 2 atoms the dipole does not cancel; this is a polar molecule. d) CF4 Electronegativity difference = C - F = 2.5 - 4.0 = 1.5 polar covalent bond shape: tetrahedral F F C F F bond dipoles exist but because the molecule is symmetrical the forces cancel. non-polar molecule. This is a f) H2Se Electronegativity difference = H - Se = 2.1 - 2.4 = 0.3 polar covalent bond shape: angular Se H H bond dipoles exist and the shape causes the forces to reinforce each other. This is a polar molecule. g) SiCl4 Electronegativity difference = Si - Cl = 1.8 - 3.0 = 1.2 polar covalent bond shape: tetrahedral Cl Cl Si Cl Cl bond dipoles exist but because the molecule is symmetrical the forces cancel. non-polar molecule. k) CS2 Electronegativity difference = C - S = 2.5 - 2.5 = 0.0 covalent bond shape: linear (bonded to 2 atoms with no lone pairs) S S C There are no bond dipoles; this is non-polar molecule. 3. Consider the following data: Element Helium Neon Argon Krypton Xenon Radon Number of Electrons Boiling Point (K) 2 10 18 36 54 86 4 27 87 121 166 211 Plot a graph of number of electrons (x-axis) vs boiling point (y-axis). Explain the trend. 2 This is a Relationship between number of electrons and boiling temperature Boiling Temperature (K) 250 200 150 100 50 0 2 10 18 36 54 86 Number of electrons These are single, uncharged atoms and so are non-polar. As a result the force drawing them together is London dispersion. London dispersion force increases with increasing number of electrons; thus in the graph as the number of electrons increases, so does the London dispersion force, resulting in an increasing boiling temperature. 4. Explain why argon and fluorine gas have similar boiling points (-186°C for argon, -188°C for fluorine). Both argon and fluorine are non-polar (Ar because it is made of single atoms, F2 because the electronegativity difference is 0.0 and the bond is covalent). Both have London dispersion force drawing them together. These two are isoelectronic so the London force should be the same. This is manifested in similar boiling temperatures. 5. Why does liquid propane (C3H8) boil at a much lower temperature than gasoline (C 8H18)? Both are pure hydrocarbons and are non-polar (symmetry causes dipoles to cancel). Both have london dispersion force. Propane has 26 electrons, gasoline has 66. Since gasoline has more electrons, it has a higher london dispersion force and so has a higher boiling temperature than propane. 3 6. Given the following molecules: i) methane ii) propane iii) iv) butane methyl propane a) Draw each structure H H H H C C C C H H H H H H b) Predict the order of increasing melting point. Give reasons for your answer. methane, propane, butane, methyl propane. fewest electrons, lowest melting point. methyl propane is more compact than butane so it packs better in the solid phase and has the highest melting point. c) Predict the order of increasing boiling point. Give reasons for your answer. methane, propane, methyl propane, butane fewest electrons, lowest boiling point. butane has more surface area in the liquid phase so more interactions with surrounding molecules give it a higher boiling point. 7. Both krypton (b.p. -152°C) and hydrogen bromide (b.p. -67°C) are isoelectronic. Explain what factors could cause the difference in boiling points. Kr is non-polar so only has london dispersion forces. HBr is polar (END = 0.7, polar covalent bond, only 2 atoms so dipole cannot cancel) so has dipole-dipole attraction. Dipole-dipole is the stronger of the two forces, so HBr has the higher boiling temperature. 8. The boiling point of Cl2 is -35°C and the boiling point of C2H5Cl is +13°C. Does the explanation given in question 7 apply here? Explain. Yes, it does. Chlorine has an END of 0.0, so no dipole is present and London dispersion forces apply. All the bonds in chloroethane are polar, but they are not symmetrical because Cl has the highest electronegativity and the molecule is polar with Cl being the negative end. Thus the chloroethane has dipole-dipole attraction while chlorine has london dispersion force. 9. Why is ethane (C2H6) a gas at room temperature while ethanol (C2H5OH) is a liquid? Explain your answer in terms of the forces between the molecules. Ethane is a non-polar pure hydrocarbon (the symmetry makes the dipoles cancel). Ethanol has an -OH group which means ethanol molecules are attracted to one another by hydrogen bonding. Since hydrogen bonding is such a strong force, the boiling point of ethanol is much higher than that of ethane. 10. Which of the following covalent molecules exhibit hydrogen bonding: a) CH3OH b) CH3Cl c) HF d) HI 4 11. Which of the following will have the higher boiling point? Explain. a) Cl2 or I2 Both have an electronegativity difference of 0.0 so have no dipoles. London dispersion forces apply and so the element with the greatest number of electrons has the greatest force and the highest boiling point. b) SF2 or SBr2 END = S - F = 2.5 - 4.0 = 1.5 polar covalent bond END = S - Br = 2.5 - 2.8 = 0.3 polar covalent bond both molecules are angular because of S as the central atom and so are polar molecules because the dipoles do not cancel out. The S - F bond is significantly more polar than the S - Br bond, so it is likely that the dipole-dipole attraction in sulfur difluoride will be stronger, giving it a higher boiling point. c) NH3 or PH3 ammonia will have a higher boiling point. The N - H bond gives ammonia molecules hydrogen bonding, while the END for P - H is 0.0, meaning this molecule has no dipoles and so has only London dispersion attraction. 12. Consider the following data Group of Central Atom Formula Number of Electrons Boiling Point (°C) 14 CH4 SiH4 GeH4 SnH4 10 18 36 54 -164 -112 - 88 - 52 15 NH3 PH3 AsH3 SbH3 10 18 36 54 - 16 H2O H2S H2Se H2Te 10 18 36 54 +100 - 61 - 42 - 49 17 HF HCl HBr HI 10 18 36 54 + - 33 88 55 17 20 85 67 51 Graph the data. Connect the points representing the boiling points of the molecules from each group (you will have four lines) 5 Relationship of Boiling Point With Number of Electrons For Molecules With Central Atoms From Groups 14, 15, 16 and 17 Boiling Point (degrees Celsius) 150 100 50 CH4, SiH4, GeH4, SnH4 0 10 18 36 -50 54 NH3, PH3, AsH3, SbH3 H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te HF, HCl, HBr, HI -100 -150 -200 Number of Electrons a) Explain why the boiling point of the first hydrogen compounds of groups 15, 16 and 17 display a reversal in the trend of higher boiling points with increasing number of electrons. NH3, H2O, and HF all display hydrogen bonding and so have significantly higher boiling points compared to other members of the groups. b) Explain why CH4, the first member of the group 14 hydrogen compounds, does not show the reversal in trend displayed by the first hydrogen compound of the other elements. All molecules in this group are symmetrical and bond dipoles, if present, cancel out, making them non-polar. Since all members of this group are non-polar they exhibit London dispersion forces and so boiling point increases steadily with number of electrons. c) The boiling points of the hydrogen compounds of the group 14 elements are consistently lower than the boiling points of the other hydrogen compounds. Give a reason for this effect. The molecules with central atoms from groups 15, 16 and 17 are all non-symmetrical so, if bond dipoles exist, they will be polar. This contrasts with the molecules with group 14 central atoms which are all non-polar. Since the group 14 molecules have London dispersion forces while the others have dipole-dipole attraction, the group 14 molecules all have lower boiling points. 6 13. Explain in a few sentences the difference in the structure of diamond and graphite. Both diamond and graphite are made of pure carbon bonded by network covalent bonds. The major difference between them is that graphite is made of carbon bonded in 2 dimensional sheets while diamond is bonded in 3 dimensions. This results in property differences; graphite sheets are attracted to each other only with weak London dispersion forces so they slide over each other easily. This makes graphite good for pencil leads and as oil less lubricants. Diamond forms small, individual crystals valued for their beauty and hardness. 14. Predict which of the following pairs of metals is more metallic: Generally elements are more metallic if they are lower on the Periodic Table, or further to the right. a) Al or Mg b) Na or Mg c) K or Sn d) Li or Be e) Na or Ca f) Mg or Ca 15. Why does solid metallic silver have a much higher electrical conductivity than solid silver chloride? Solid silver is made up only of silver atoms connected by metallic bonds. This gives the silver electrons freedom to move (delocalized electrons) and allows silver to conduct electricity. Silver chloride is an ionic substance in which the electrons are held tightly by the respective ions. As such it cannot conduct electricity in the solid phase; only if the ions are free to move as in the liquid or dissolved state can these substances conduct electricity. 16. Why is it that when we hit a metal such as silver with a hammer it will only deform it, whereas it would shatter NaCl? Again, the delocalized electrons of a metal cause it to be malleable and ductile. An ionic compound is brittle because of the nature of the ionic bond. 17. Would you expect SiO2 to be ductile? This substance is held together by network covalent bonds. As a result this substance will be brittle, rather than ductile. 18. Why is aluminum able to conduct heat better than quartz glass? The delocalized electrons of a metal allow it to conduct heat as the electrons transfer their kinetic energy throughout the material. Quartz has network covalent bonds in which the electrons are tightly held in the bonds so they do not transfer heat well. 19. What kind of chemical bonds or attractive forces must be broken or overcome in order to: a) melt diamond b) sublime solid iodine c) melt table salt d) boil liquid ammonia e) melt solid neon f) melt iron network covalent London dispersion forces ionic hydrogen bonds London dispersion forces metallic 7