New 21st Century Chemistry
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
In-text activities
Checkpoint (page 60)
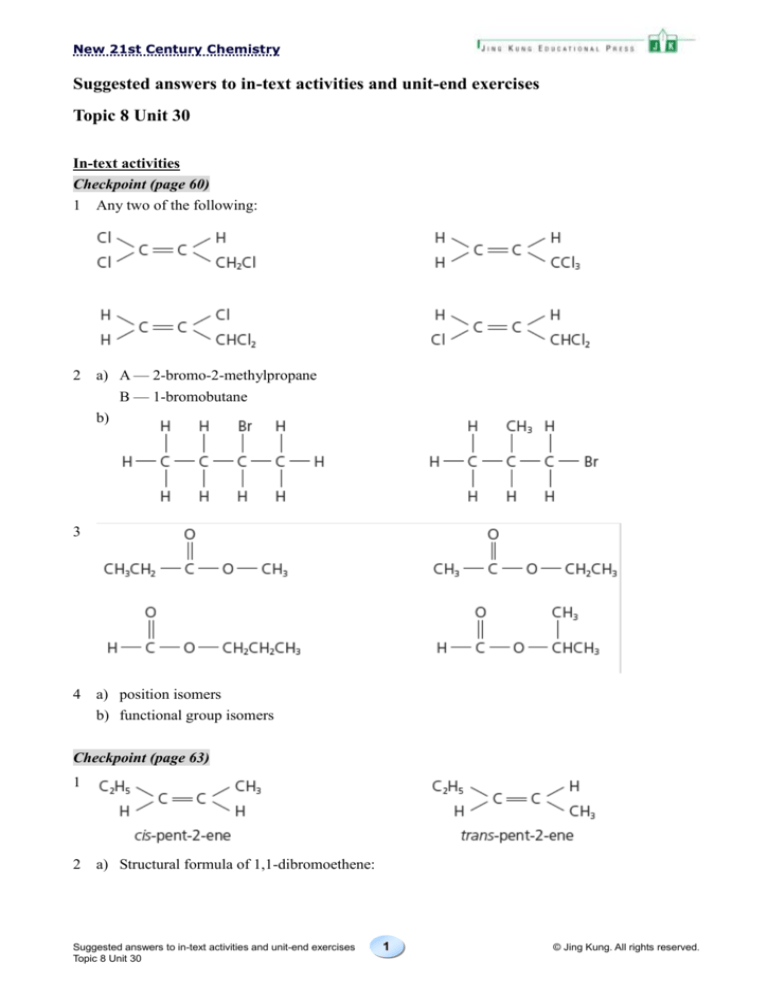
1 Any two of the following:
2
a) A — 2-bromo-2-methylpropane
B — 1-bromobutane
b)
3
4
a) position isomers
b) functional group isomers
Checkpoint (page 63)
1
2
a) Structural formula of 1,1-dibromoethene:
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
1
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
The compound does not exhibit goemetrical isomerism. One of the carbon of the C=C bond
has identical hydrogen / bromine atoms attached to it.
b) Structural formula of ethene-1,2-diol:
The compound can exhibit geometrical isomerism. Two different groups are attached to each
carbon of the C=C bond.
3
a)
b) Geometrical isomerism
Checkpoint (page 66)
1 In addition to intermolecular attractions, the melting point of a compound depends also on the
degree of compactness of molecules in the solid state.
The cis isomer has a lower degree of symmetry. It fits into a crystalline lattice relatively poorly
and thus has a lower melting point.
2 In a molecule of X, due to the close proximity of the –OH group and –CHO group,
intramolecular hydrogen bonds are readily formed. Thus intermolecular hydrogen bonds
between the molecules of X are less extensive.
Molecules of Y forms more intermolecular hydrogen bonds than molecules of X do.
∴ the melting point of Y is much higher than that of X.
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
2
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
Checkpoint (page 68)
a) achiral
b) chiral
c) chiral
Checkpoint (page 76)
1
a) i)
ii) It is chiral.
iii)
b) i)
ii) It is chiral.
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
3
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
iii)
2
a) Identical
Rotation of the second molecule about the C–CH3 bond produces the molecule shown
below:
∴ the second molecule is identical to the first one.
b) The mirror image of the first molecule is shown below:
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
4
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
Rotation of the mirror image about the C–H bond produces the second molecule.
The two given molecules are not superposable.
∴ the two given molecules are non-superposable mirror images of each other; i.e. they are
enantiomers.
c) The mirror image of the first molecule is shown below:
The first molecule and its mirror image are not superposable.
Rotation of the mirror image about the C–F bond produces the second molecule.
∴ the two given molecules are non-superposable mirror images of each other; i.e. they are
enantiomers.
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
5
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
3
a) The compound exhibits stereoisomerism. Its molecule contains a chiral carbon.
Enantiomers:
b) No
There is no carbon atom with four different atoms or groups of atoms attached to it.
c) Geometrical isomerism
Checkpoint (page 79)
1 a) Identical
b) The mirror image of the first molecule is shown below:
The first molecule and its mirror image are not superposable.
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
6
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
Rotation of the mirror image produces the second molecule.
∴ the two molecules are non-superposable mirror images of each other;
i.e. their relationship is enantiomeric.
2
c)
d)
a)
b)
Geometrically isomeric
Structurally isomeric
It contains a carbon atom with four different groups attached.
Higher doses are required.
The other stereoisomers may have harmful side effects.
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
7
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
Unit-end exercises (pages 83 – 91)
Answers for the HKCEE (Paper 1) and HKALE questions are not provided.
1
2
3
a)
b)
c)
d)
a)
C4H10
C2H5O
B and E
A and F
carbon-carbon double bond
carboxyl group
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
8
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
b)
4
a)
b)
c)
5
a) The molecule contains one carbon atom bonded to four different groups of atoms.
b)
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
9
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
6
B
7
C Option A —
Both CH3COOCH2CH3 and CH3CH2COOCH3 contain an ester functional
group (
).
Option B —
Both (CH3)2CHCH(CH3)2 and (CH3)3CCH2CH3 are alkanes.
Option C —
H2NCH2CH2CH2COOH contains a carboxyl group (
) while
H2NCH2COOCH2CH3 contains an ester functional group (
Option D —
8
).
Both ClCH2CH2CH=CH2 and CH3CH=CHCH2Cl contain carbon-carbon
double bond.
A
9 B
10 C Option C —
The two isomers are enantiomers. They have identical boiling point.
11 A
12 A (1)
The molecule is chiral. It has enantiomers.
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
10
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
(2)
Identical methyl groups are attached to one of the carbon atoms of the C=C bond. Hence
the compound does NOT have stereoisomers.
(3)
Identical chloro groups are attached to one of the carbon atoms of the C=C bond. Hence
the compound does NOT have stereoisomers.
13 D (1) The pair of molecules are identical.
(2) The molecules are geometrical isomers.
(3) The molecules are position isomers.
14 a) Compound A contains a carbon-carbon double bond.
Any one of the following:
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
11
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
Compound B does not contain a carbon-carbon double bond. It should be a cyclic compound.
Any one of the following:
b) The following structures have the molecular formula C3H6Cl2.
Structure W has a chiral carbon. It shows optical activity. Thus compound C should have
this structure.
The other three structures have NO chiral carbon. They do not show optical activity. Thus
these are possible structures of compound D.
15 a) 3-bromohexane
b) There is restricted rotation about a carbon-carbon double bond. Two different groups are
attached to each carbon of the double bond.
c) The product contains only single bonds. There is free rotation and NO cis-trans isomers
exist.
16 a)
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
12
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
b) Isomer A is methylpropan-2-ol.
c) Isomer B is butan-2-ol.
17
18
19
20
—
—
—
a) carbon-carbon double bond
hydroxyl group
b) i) Stereoisomers have their atoms linked in the same way, but they differ in the spatial
arrangement of their atoms.
ii) Geometrical isomerism
iii) Due to the restricted rotation about a carbon-carbon double bond.
iv) Identical methyl groups are attached to one of the carbon atoms of one of the C=C
bonds.
21 a)
b) i) Geometrical isomerism
ii)
22 —
23 —
24 The compounds shown below exhibit structural isomerism. Structural isomers have the same
molecular formula but differ in the order in which atoms are linked.
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
13
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.
New 21st Century Chemistry
Examples:
The compounds shown below exhibit stereoisomerism. Stereoisomers have their atoms linked in
the same way, but they differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
The following two compounds are geometrical isomers. They have a different arrangement of
their atoms in space due to the restricted rotation about a carbon-carbon double bond.
Compounds with two different groups attached to each carbon of the double bond have two
alternative structures, which are geometrical isomers.
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 8 Unit 30
14
© Jing Kung. All rights reserved.