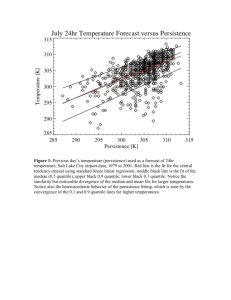
Glossary terms

Glossary terms:
Attributes diagram: See reliability table .
Bin (binning)
: The act of partitioning a continuous variable into N categories (or “bins”) using N-1 thresholds. In verification applications, probability forecasts are binned in order to construct reliability tables and the ROC curve. Bins often encompass ranges of
0.10 width (deciles).
Confidence limits : A means of objectively stating the degree of confidence in the value of a score value, or other value estimated from data. Confidence limits comprise an upper and lower bound and a statement of the probability that the true value of the variable lies between the limits. For example, it might be stated that the MAE is 2+/-1.5 degrees with
95% confidence. This means there is a 95% probability the true MAE lies within the range of 0.5 to 3.5.
Continuous distribution : See Probability distribution
Control (run) : In ensemble forecasting it is customary to run the ensemble model without any form of perturbation, using the “best” possible estimate of the initial conditions at the model resolution. This is called the “control run” or the “unperturbed control” or just simply the “control”.
Cumulative distribution function (cdf) : This is the probability that a variable x is less than or equal to a specific value X, plotted as a function of x. It is the integral of the probability density function , and is non-decreasing over the range of x.
Discrete variable : A variable which may take on only a limited set of values.
Meteorological variables may be inherently discrete such as precipitation type (“solid”,
“liquid”, “freezing precipitation”) or it may be a continuous variable which is rendered discrete by binning (e.g. wind speed).
Dressing (Gaussian dressing) : One method of converting a deterministic forecast into a probabilistic forecast. The deterministic forecast value is taken to be the mean or median of the forecast probability distribution, and errors from previous forecasts are used to estimate the full forecast distribution. Gaussian dressing is the most common form, where the forecast probability density function is defined by a Gaussian distribution with mean equal to the deterministic forecast value and variance estimated from the errors of recent forecasts.
Empirical distribution : A probability distribution , usually discrete , estimated by tallying up and plotting the number of times each value of the variable occurs over a dataset.
Ensemble forecast : The set of deterministic forecasts produced by an ensemble system.
These are usually interpreted in various ways to estimate the probability of occurrence of events of interest. Ensemble forecasts are not probability forecasts in themselves; interpretation is necessary.
Ensemble member(s) : Refers to one or more single forecasts from an ensemble system , using initial conditions which have been subjected to specific perturbations, and possibly also specific versions of the model.
Event : A generic term for what is predicted by categorical or probabilistic forecast methods. Events are categorical; they either occur or not, and are represented by “1” for occurrence and “0” for non-occurrence in verification datasets. Examples are
“Precipitation > 1 mm in 6 h” and “wind speed > 10 m per second”.
Heaviside function : A step function which takes the value 0 for values of a variable below a specific threshold, and 1 for values above the threshold. In verification methodology, the Heaviside function is used to represent a deterministic forecast as a cumulative distribution function .
Mean : The average value of a variable.
Median : The value of a variable which splits the probability distribution in two equal parts. The median is the 50 th
percentile of the distribution: half the time lower values occur and half the time higher values occur.
Mode : The value of a variable which occurs most frequently in a dataset or a probability distribution .
No skill line : On a reliability table, the line which bisects the angle between the perfect reliability line (diagonal) and the horizontal line representing the sample average frequency of the event. This line is the locus of points for which the reliability exactly balances the resolution in a set of probability forecasts.
Poor man’s ensemble : An ensemble made up of existing forecasts, which therefore requires no additional computation to generate, and is much cheaper to produce. The most common example is an ensemble made up of the operational deterministic forecasts from several different national meteorological services.
Probability density function (pdf) : A function which describes the frequency or probability of occurrence of all the possible values of a variable. Pdfs may be discrete if the variable can take on a restricted set of values, or continuous if the variable may take on any value within its range. Pdfs may also be “empirical” if they are based on data or
“theoretical” if they are described by a mathematical function. This term is often used interchangeably with probability distribution .
Probability distribution : A plot or a description of the frequency of occurrence of all the possible values of a variable. Distributions may be discrete if the variable can take on a restricted set of values, or continuous if the variable may take on any value within its range. They may also be empirical if based on data, or theoretical if described by a mathematical function. A slightly more general term for probability density function .
Rank histogram : A histogram which evaluates the average spread of ensemble forecasts compared to the spread of the distribution of observations, under certain assumptions.
Reliability table : A plot of the observed frequency of occurrence of an event vs. the forecast probability of that event. In addition to the reliability plot, a fully informative reliability table contains also a horizontal line representing the sample climatology of the event, the no skill line , and the sharpness histogram as an inset. The complete version of the reliability table is also called an attributes diagram .
ROCA : The area under the relative operating characteristic curve.
Ensemble spread : The dispersion of the members of an ensemble forecast, usually measured by the variance or the standard deviation.
Spread : See ensemble spread .
Uncertainty : The lack of knowledge about the exact value of a variable. Uncertainty is quantified by means of a probability distribution , or a probability estimate.
In the glossary, italicize “ probability distribution
” in the definition of ensemble system and anywhere else it occurs.