Content Standard(s) CS
advertisement

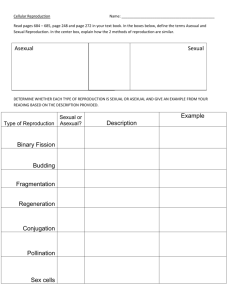
GENETICS and HEREDITY Stage 1 – Desired Results Content Standard(s) CS Science Standard 5: DIVERSITY, GENETICS, AND EVOLUTION: Understand genetics and biological evolution and their impact on the unity and diversity of organisms. Language Arts Standard 1: Reading: CONVENTIONS AND SKILLS – Use knowledge of the conventions of language and texts to construct meaning for a range of literary and informational texts for a variety of purposes Understanding(s) Students will understand that… U (7.5.1) (There are advantages and disadvantages of sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of variation in offspring (e.g., sexual reproduction allows for greater genetic variation; asexual reproduction limits the spread of disadvantageous characteristics in a species)). (7.5.2) (Traits can be determined by one or more genes (e.g., eye color, attached or non-attached earlobes, color of flowers)). (7.5.3) (Small differences due to the exchange and interaction of genetic information from parents are passed down to offspring and over successive generations could result in great differences). (7.1.1) (Use new grade-appropriate vocabulary, including content area vocabulary, learned through word study and reading.) (7.1.2) (Use a variety of grade-appropriate print and online sources to research an inquiry question.) Essential Question(s) (7.5.1) What are the similarities and differences between sexual and asexual reproducers? (7.5.2) How can an inherited trait be determined by one or more genes which are found on chromosomes? (7.5.3) What are the small differences between parents and offspring that could produce descendants that look very different from their ancestors? Students will know… Q K Similarities and differences between sexual and asexual reproducers. An inherited trait be determined by one or more genes which are found on chromosomes. Small differences between parents and offspring could produce descendants that look very different from their ancestors. Students will be able to: S 7.5.1. Show a pedigree using both sexual and asexual reproducers in order to compare and contrast between the two methods of reproduction. 7.5.2. Show how a trait is passed from parent to offspring in a pedigree. 7.5.3. Show how a trait is masked or made more likely to be expressed in any given pedigree. 7.5.1. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of both types of reproduction. 7.5.2. Explain how trait can be determined by one or more genes which are found on chromosomes. 7.5.3. Describe how small differences from parent to offspring could produce descendants that look very different from their ancestors. Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Task: (Link to hook) T PBL Case Study: How do Wii get together? Template Outline Marzano: Level 4.0 7.5.1. Students show a pedigree using both sexual and asexual reproducers in order to compare and contrast between the two methods of reproduction. 7.5.2. Students show how a trait is passed from parent to offspring in a pedigree. 7.5.3. Students show how a trait is masked or made more likely to be expressed in any given pedigree. Level 3.0 7.5.1. Provide students with examples of sexual and asexual reproducers. Ask students to compare the advantages and disadvantages of both types of reproduction. 7.5.2. Provide students with examples of an inherited trait. Ask students to explain how trait can be determined my one or more genes which are found on chromosomes. 7.5.3. Provide students with examples of varying pedigree’s that include mutation, dominant, recessive, and sex linked traits. Ask students to describe how small differences from parent to offspring could produce descendants that look very different from their ancestors. Level 2.0 7.5.1. Ask students to match terms like, “reproduction, sexual and asexual reproduction, meiosis, mitosis” with their definitions. 7.5.2. Ask students to match terms like, “trait, DNA, chromosomes, genes, heredity, homologous, dominant alleles, recessive alleles, punnett square, genotype, phenotype,” with their definitions. 7.5.3. Ask students to match terms like, “chromosomes, meiosis, genes, homologous, fertilization, zygote, cloning, dominant and recessive alleles, genotype, phenotype, mutation, sex linked trait,” with their definitions. Key Criteria/Rubric All in the Family Rubric A Family Portrait Rubric What’s the Chance Science Inquiry/Formal Lab Report Write-up Format PBL Case Study Learning Issues Web Links under Tools to Learning (January & February) Other Evidence Common Formative Assessment “Heredity the Science of Genetics” Common Formative Assessment “Modern Genetics” GLO and Evidence Cover sheet LIINK CFA Cover sheet LINK Relating School-wide Tools to Leaning: Problem Based Learning (PBL) Marzano/Excelsior Grade Book Common Formative Assessment (CFA) Student Led Conference (SLC) Hawaii Content Performance Standards (HCPS III)