Medieval Church Student Handout
advertisement
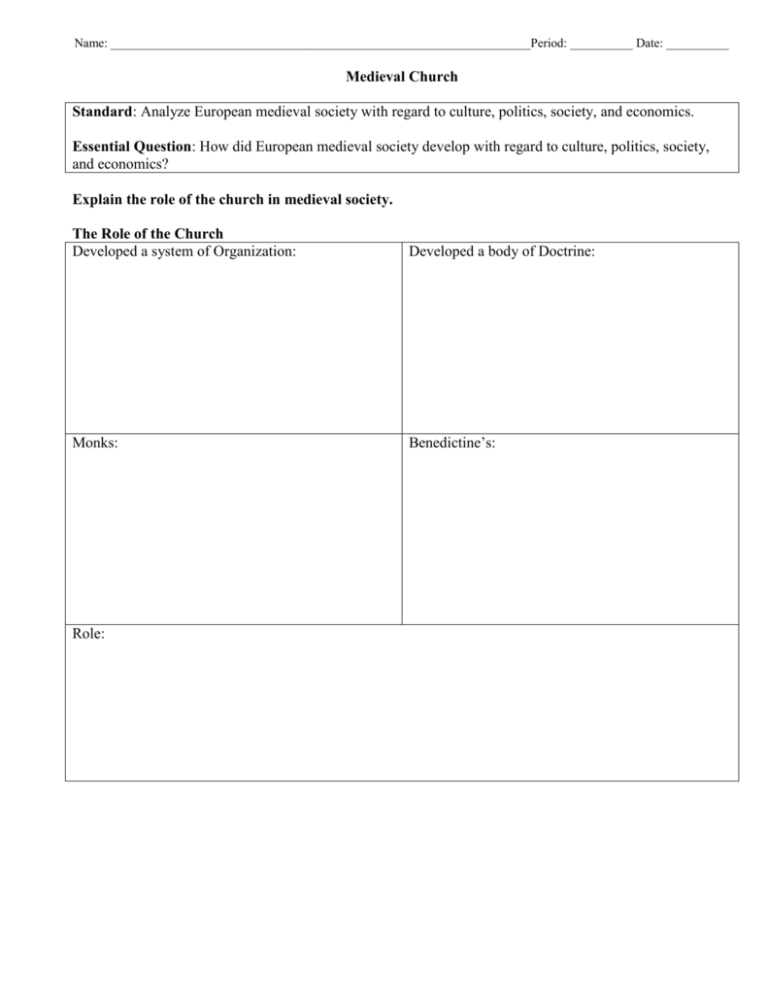
Name: ___________________________________________________________________Period: __________ Date: __________ Medieval Church Standard: Analyze European medieval society with regard to culture, politics, society, and economics. Essential Question: How did European medieval society develop with regard to culture, politics, society, and economics? Explain the role of the church in medieval society. The Role of the Church Developed a system of Organization: Developed a body of Doctrine: Monks: Benedictine’s: Role: Describe the political impact of Christianity; include Pope Gregory VII and King Henry IV of Germany (Holy Roman Emperor). The Papal Monarchy Papal State: Feudalism Impact on the Church: Pope Gregory VII: Church v. State: Pope Innocent III: Medieval Church Standard: Analyze European medieval society with regard to culture, politics, society, and economics. Essential Question: How did European medieval society develop with regard to culture, politics, society, and economics? Explain the role of the church in medieval society. The Role of the Church Developed a system of Organization: Priests headed local communities called parishes group of parishes(bishopric/diocese) headed by a bishop bishop of Rome claimed he was the leader of the Roman Catholic Church later called popes from the Latin word papa, “father” Monks: played an important role in the Church a man who separates himself from worldly life dedicated himself to God (monasticism) Developed a body of Doctrine: Church councils met to define Church teachings Benedictine’s: sixth century order of monks founded by Saint Benedict wrote rules for their practice, The Benedictine rule used by other monastic groups social work in their communities made them the new heroes of Christian civilization Role: provided a basis for unity and order most powerful entity of the period largest land holder of the period Describe the political impact of Christianity; include Pope Gregory VII and King Henry IV of Germany (Holy Roman Emperor). The Papal Monarchy Papal State: control over the territory in central Italy involved the popes in politics often at the expense of their spiritual duties Pope Gregory VII: eleventh century pope claimed that the pope’s authority extended over all the Christian world (including rulers) asserted the Church’s right to appoint clergy and run its affairs (College of Cardinals) in 1075 issued a decree forbidding high-ranking clerics from receiving their offices from lay (secular) leaders (lay investiture) Feudalism Impact on the Church: Bishops and abbots held offices as grants from nobles were vassals with allegiance to a secular authority obligated to carry out military duties (Crusades) Church v. State: Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV opposed the reform of Gregory VII in 1076, Gregory excommunicated Henry and all the bishops he had appointed the princes subsequently meet to elect a new king Henry held a private penance with Gregory VII ceded the superiority and equality of imperial rulers to the church lessened the power of kings (King Henry IV of Germany) Pope Innocent III: thirteenth century reached the height of political power believed he was the supreme judge of European affairs ordered Philip Augustus to take back his wife after Philip had sought an annulment